mirror of
https://github.com/invoke-ai/InvokeAI
synced 2024-08-30 20:32:17 +00:00
Merge branch 'development' into patch-1
This commit is contained in:
141
docs/help/SAMPLER_CONVERGENCE.md
Normal file
141
docs/help/SAMPLER_CONVERGENCE.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,141 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: SAMPLER CONVERGENCE
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## *Sampler Convergence*
|
||||
|
||||
As features keep increasing, making the right choices for your needs can become increasingly difficult. What sampler to use? And for how many steps? Do you change the CFG value? Do you use prompt weighting? Do you allow variations?
|
||||
|
||||
Even once you have a result, do you blend it with other images? Pass it through `img2img`? With what strength? Do you use inpainting to correct small details? Outpainting to extend cropped sections?
|
||||
|
||||
The purpose of this series of documents is to help you better understand these tools, so you can make the best out of them. Feel free to contribute with your own findings!
|
||||
|
||||
In this document, we will talk about sampler convergence.
|
||||
|
||||
Looking for a short version? Here's a TL;DR in 3 tables.
|
||||
|
||||
| Remember |
|
||||
|:---|
|
||||
| Results converge as steps (`-s`) are increased (except for `K_DPM_2_A` and `K_EULER_A`). Often at ≥ `-s100`, but may require ≥ `-s700`). |
|
||||
| Producing a batch of candidate images at low (`-s8` to `-s30`) step counts can save you hours of computation. |
|
||||
| `K_HEUN` and `K_DPM_2` converge in less steps (but are slower). |
|
||||
| `K_DPM_2_A` and `K_EULER_A` incorporate a lot of creativity/variability. |
|
||||
|
||||
| Sampler | (3 sample avg) it/s (M1 Max 64GB, 512x512) |
|
||||
|---|---|
|
||||
| `DDIM` | 1.89 |
|
||||
| `PLMS` | 1.86 |
|
||||
| `K_EULER` | 1.86 |
|
||||
| `K_LMS` | 1.91 |
|
||||
| `K_HEUN` | 0.95 (slower) |
|
||||
| `K_DPM_2` | 0.95 (slower) |
|
||||
| `K_DPM_2_A` | 0.95 (slower) |
|
||||
| `K_EULER_A` | 1.86 |
|
||||
|
||||
| Suggestions |
|
||||
|:---|
|
||||
| For most use cases, `K_LMS`, `K_HEUN` and `K_DPM_2` are the best choices (the latter 2 run 0.5x as quick, but tend to converge 2x as quick as `K_LMS`). At very low steps (≤ `-s8`), `K_HEUN` and `K_DPM_2` are not recommended. Use `K_LMS` instead.|
|
||||
| For variability, use `K_EULER_A` (runs 2x as quick as `K_DPM_2_A`). |
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
### *Sampler results*
|
||||
|
||||
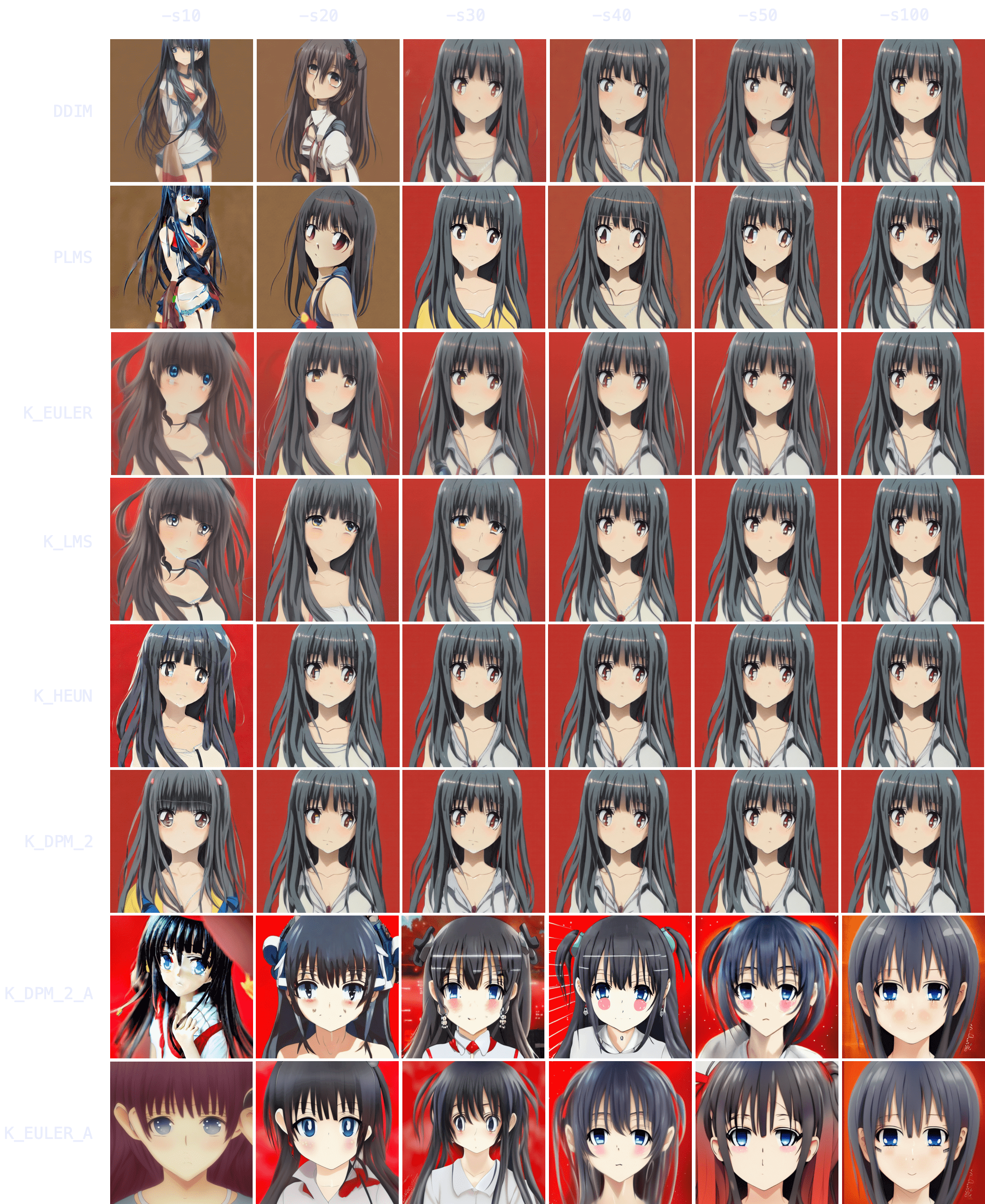
Let's start by choosing a prompt and using it with each of our 8 samplers, running it for 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 and 100 steps.
|
||||
|
||||
Anime. `"an anime girl" -W512 -H512 -C7.5 -S3031912972`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### *Sampler convergence*
|
||||
|
||||
Immediately, you can notice results tend to converge -that is, as `-s` (step) values increase, images look more and more similar until there comes a point where the image no longer changes.
|
||||
|
||||
You can also notice how `DDIM` and `PLMS` eventually tend to converge to K-sampler results as steps are increased.
|
||||
Among K-samplers, `K_HEUN` and `K_DPM_2` seem to require the fewest steps to converge, and even at low step counts they are good indicators of the final result. And finally, `K_DPM_2_A` and `K_EULER_A` seem to do a bit of their own thing and don't keep much similarity with the rest of the samplers.
|
||||
|
||||
### *Batch generation speedup*
|
||||
|
||||
This realization is very useful because it means you don't need to create a batch of 100 images (`-n100`) at `-s100` to choose your favorite 2 or 3 images.
|
||||
You can produce the same 100 images at `-s10` to `-s30` using a K-sampler (since they converge faster), get a rough idea of the final result, choose your 2 or 3 favorite ones, and then run `-s100` on those images to polish some details.
|
||||
The latter technique is 3-8x as quick.
|
||||
|
||||
Example:
|
||||
|
||||
At 60s per 100 steps.
|
||||
|
||||
(Option A) 60s * 100 images = 6000s (100 images at `-s100`, manually picking 3 favorites)
|
||||
|
||||
(Option B) 6s * 100 images + 60s * 3 images = 780s (100 images at `-s10`, manually picking 3 favorites, and running those 3 at `-s100` to polish details)
|
||||
|
||||
The result is 1 hour and 40 minutes (Option A) vs 13 minutes (Option B).
|
||||
|
||||
### *Topic convergance*
|
||||
|
||||
Now, these results seem interesting, but do they hold for other topics? How about nature? Food? People? Animals? Let's try!
|
||||
|
||||
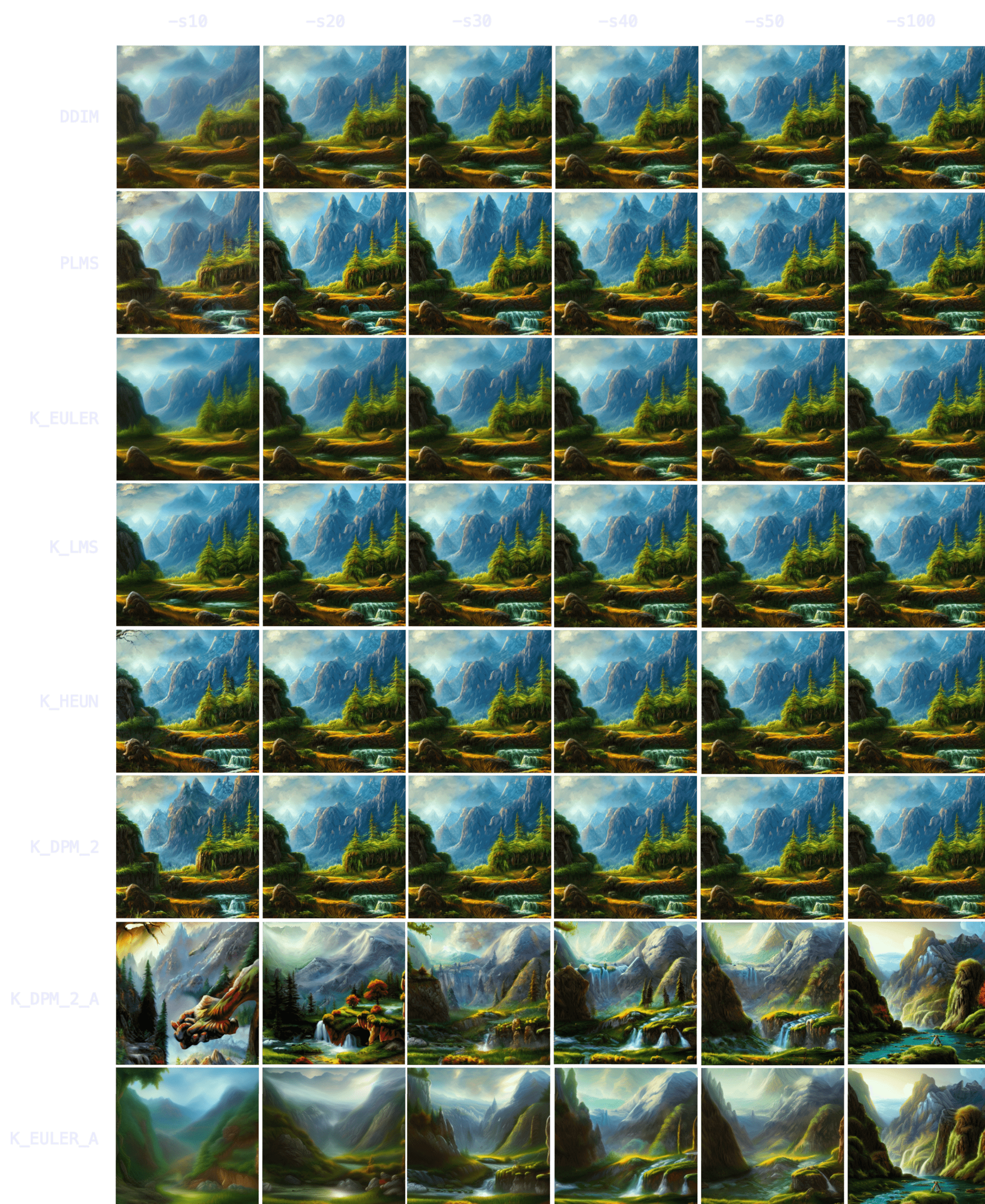
Nature. `"valley landscape wallpaper, d&d art, fantasy, painted, 4k, high detail, sharp focus, washed colors, elaborate excellent painted illustration" -W512 -H512 -C7.5 -S1458228930`
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
With nature, you can see how initial results are even more indicative of final result -more so than with characters/people. `K_HEUN` and `K_DPM_2` are again the quickest indicators, almost right from the start. Results also converge faster (e.g. `K_HEUN` converged at `-s21`).
|
||||
|
||||
Food. `"a hamburger with a bowl of french fries" -W512 -H512 -C7.5 -S4053222918`
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Again, `K_HEUN` and `K_DPM_2` take the fewest number of steps to be good indicators of the final result. `K_DPM_2_A` and `K_EULER_A` seem to incorporate a lot of creativity/variability, capable of producing rotten hamburgers, but also of adding lettuce to the mix. And they're the only samplers that produced an actual 'bowl of fries'!
|
||||
|
||||
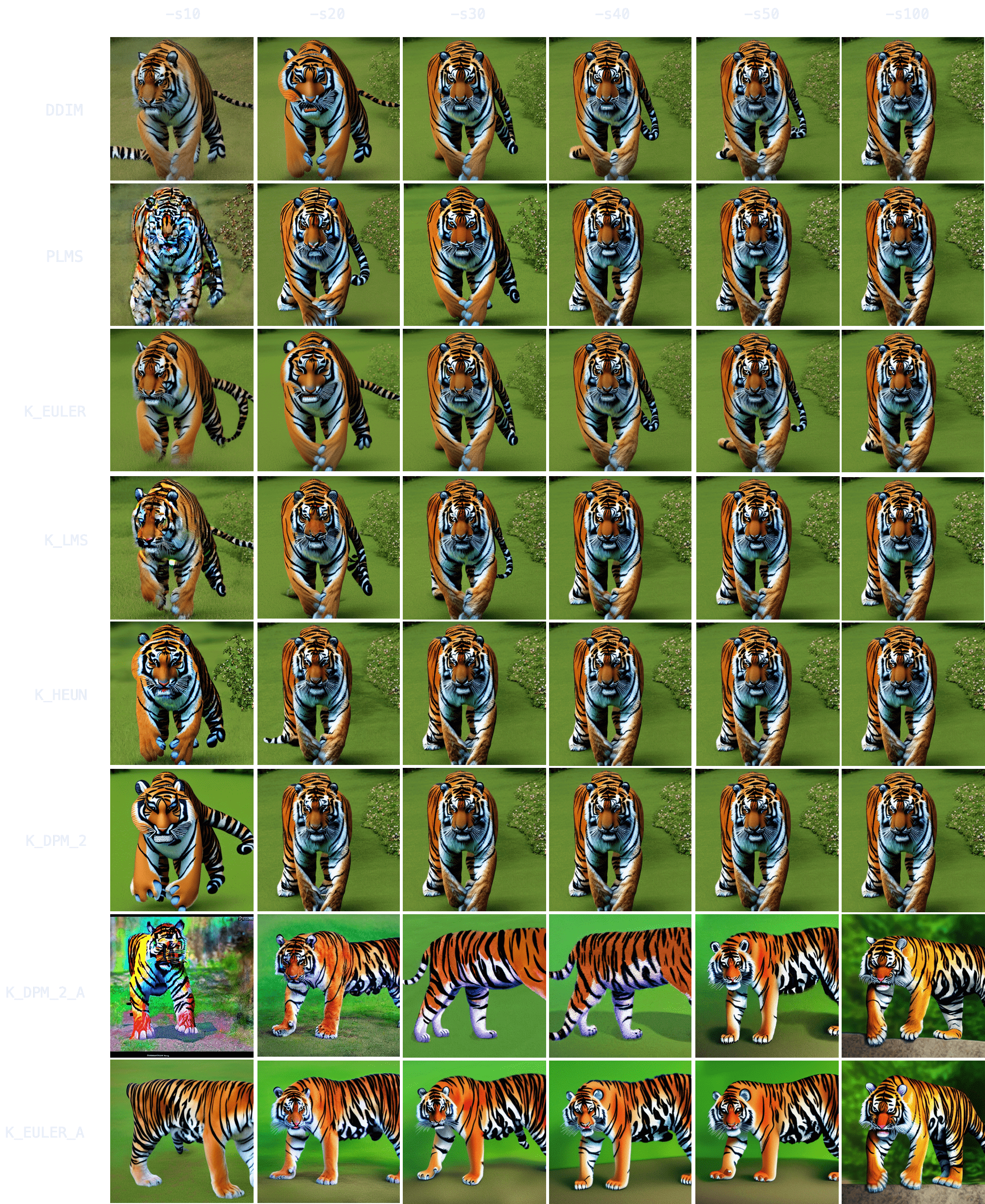
Animals. `"grown tiger, full body" -W512 -H512 -C7.5 -S3721629802`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
`K_HEUN` and `K_DPM_2` once again require the least number of steps to be indicative of the final result (around `-s30`), while other samplers are still struggling with several tails or malformed back legs.
|
||||
|
||||
It also takes longer to converge (for comparison, `K_HEUN` required around 150 steps to converge). This is normal, as producing human/animal faces/bodies is one of the things the model struggles the most with. For these topics, running for more steps will often increase coherence within the composition.
|
||||
|
||||
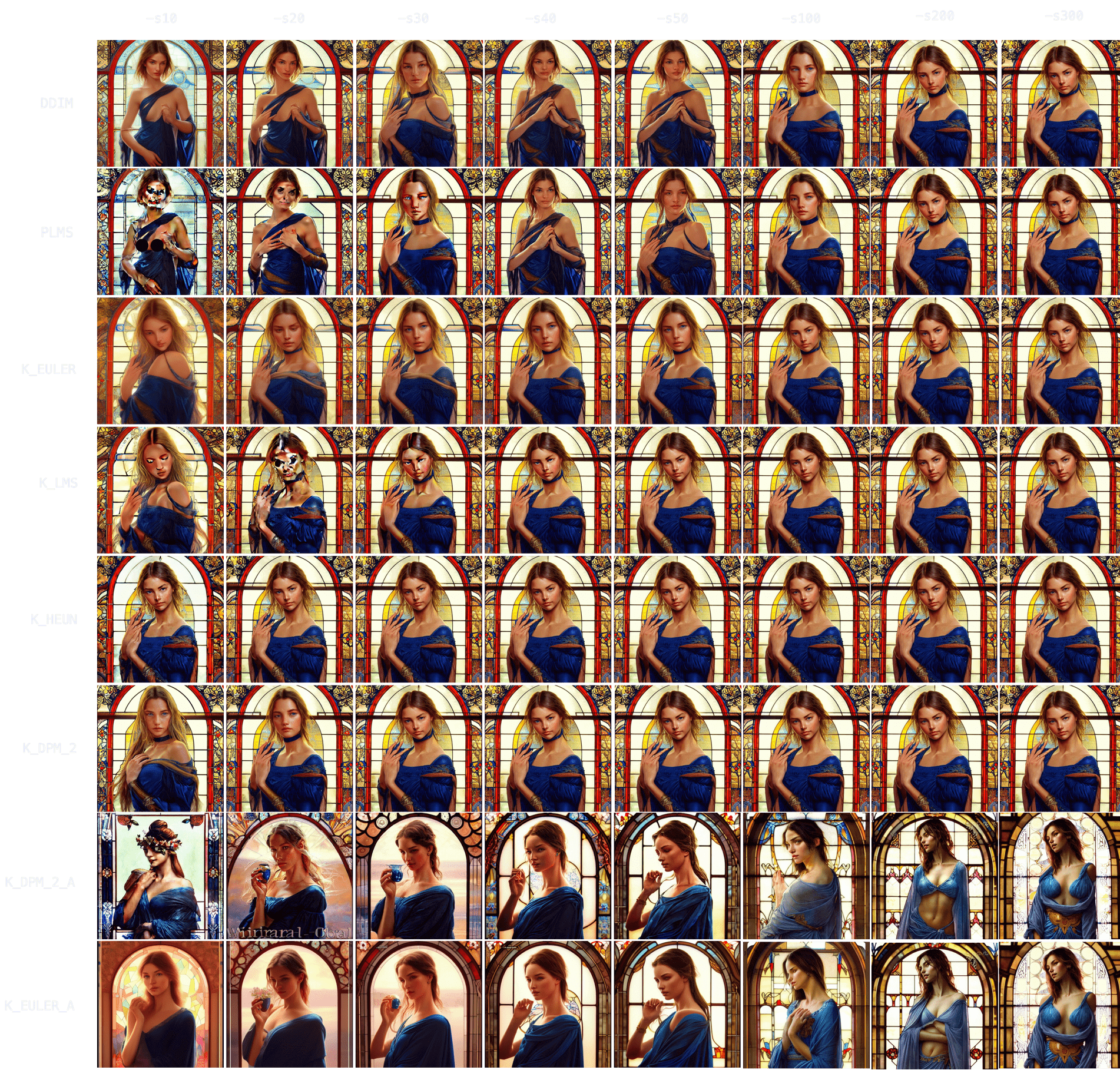
People. `"Ultra realistic photo, (Miranda Bloom-Kerr), young, stunning model, blue eyes, blond hair, beautiful face, intricate, highly detailed, smooth, art by artgerm and greg rutkowski and alphonse mucha, stained glass" -W512 -H512 -C7.5 -S2131956332`. This time, we will go up to 300 steps.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Observing the results, it again takes longer for all samplers to converge (`K_HEUN` took around 150 steps), but we can observe good indicative results much earlier (see: `K_HEUN`). Conversely, `DDIM` and `PLMS` are still undergoing moderate changes (see: lace around her neck), even at `-s300`.
|
||||
|
||||
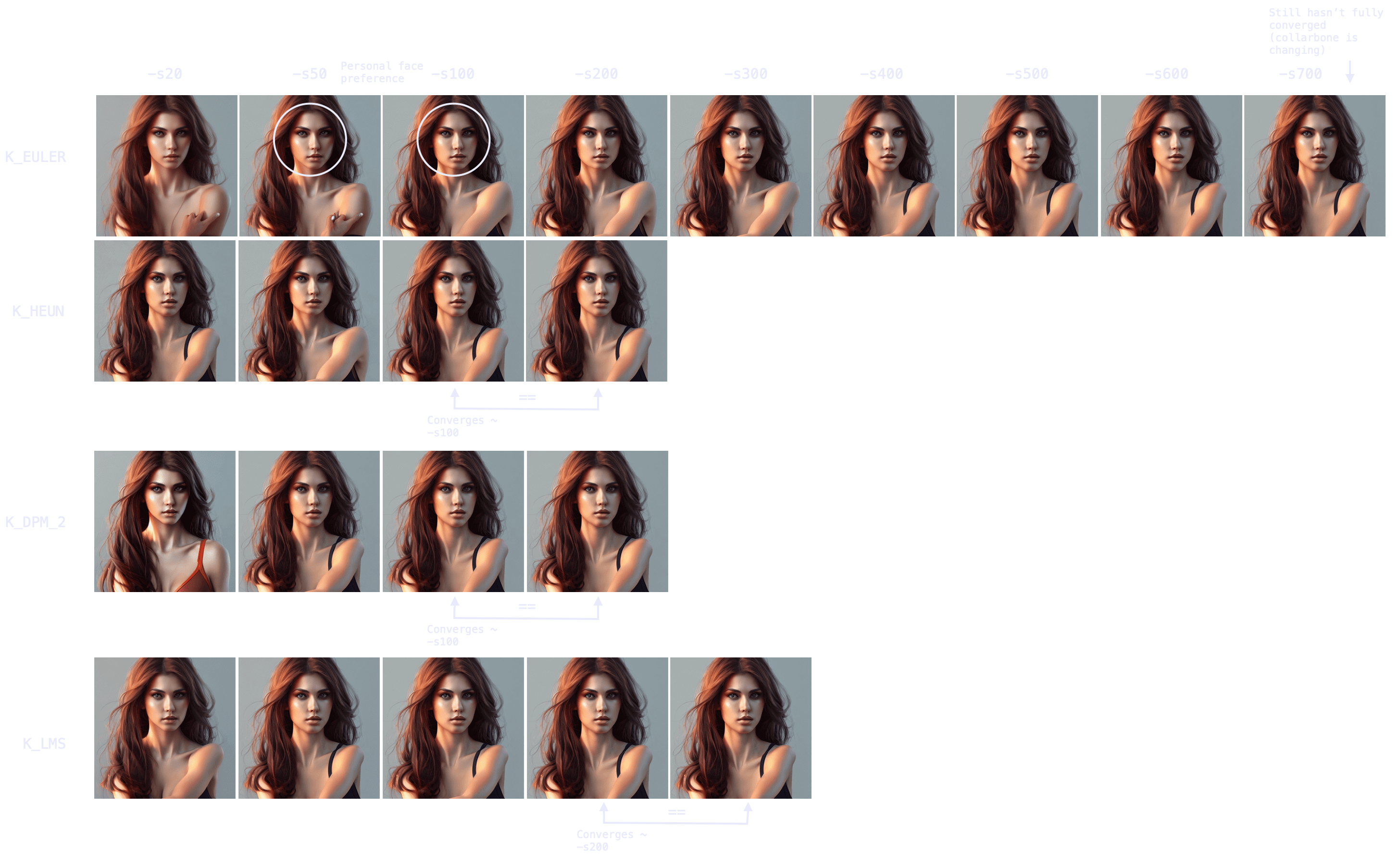
In fact, as we can see in this other experiment, some samplers can take 700+ steps to converge when generating people.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Note also the point of convergence may not be the most desirable state (e.g. I prefer an earlier version of the face, more rounded), but it will probably be the most coherent arms/hands/face attributes-wise. You can always merge different images with a photo editing tool and pass it through `img2img` to smoothen the composition.
|
||||
|
||||
### *Sampler generation times*
|
||||
|
||||
Once we understand the concept of sampler convergence, we must look into the performance of each sampler in terms of steps (iterations) per second, as not all samplers run at the same speed.
|
||||
|
||||
On my M1 Max with 64GB of RAM, for a 512x512 image:
|
||||
| Sampler | (3 sample average) it/s |
|
||||
|---|---|
|
||||
| `DDIM` | 1.89 |
|
||||
| `PLMS` | 1.86 |
|
||||
| `K_EULER` | 1.86 |
|
||||
| `K_LMS` | 1.91 |
|
||||
| `K_HEUN` | 0.95 (slower) |
|
||||
| `K_DPM_2` | 0.95 (slower) |
|
||||
| `K_DPM_2_A` | 0.95 (slower) |
|
||||
| `K_EULER_A` | 1.86 |
|
||||
|
||||
Combining our results with the steps per second of each sampler, three choices come out on top: `K_LMS`, `K_HEUN` and `K_DPM_2` (where the latter two run 0.5x as quick but tend to converge 2x as quick as `K_LMS`). For creativity and a lot of variation between iterations, `K_EULER_A` can be a good choice (which runs 2x as quick as `K_DPM_2_A`).
|
||||
|
||||
Additionally, image generation at very low steps (≤ `-s8`) is not recommended for `K_HEUN` and `K_DPM_2`. Use `K_LMS` instead.
|
||||
|
||||
<img width="397" alt="192044949-67d5d441-a0d5-4d5a-be30-5dda4fc28a00-min" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/50542132/192046823-2714cb29-bbf3-4eb1-9213-e27a0963905c.png">
|
||||
|
||||
### *Three key points*
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, it is relevant to mention that, in general, there are 3 important moments in the process of image formation as steps increase:
|
||||
|
||||
* The (earliest) point at which an image becomes a good indicator of the final result (useful for batch generation at low step values, to then improve the quality/coherence of the chosen images via running the same prompt and seed for more steps).
|
||||
|
||||
* The (earliest) point at which an image becomes coherent, even if different from the result if steps are increased (useful for batch generation at low step values, where quality/coherence is improved via techniques other than increasing the steps -e.g. via inpainting).
|
||||
|
||||
* The point at which an image fully converges.
|
||||
|
||||
Hence, remember that your workflow/strategy should define your optimal number of steps, even for the same prompt and seed (for example, if you seek full convergence, you may run `K_LMS` for `-s200` in the case of the red-haired girl, but `K_LMS` and `-s20`-taking one tenth the time- may do as well if your workflow includes adding small details, such as the missing shoulder strap, via `img2img`).
|
||||
@ -1,11 +1,17 @@
|
||||
# **Frequently Asked Questions**
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: F.A.Q.
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Here are a few common installation problems and their solutions. Often these are caused by incomplete installations or crashes during the
|
||||
install process.
|
||||
# :material-frequently-asked-questions: F.A.Q.
|
||||
|
||||
## **Frequently-Asked-Questions**
|
||||
|
||||
Here are a few common installation problems and their solutions. Often these are caused by
|
||||
incomplete installations or crashes during the install process.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
**QUESTION**
|
||||
### **QUESTION**
|
||||
|
||||
During `conda env create -f environment.yaml`, conda hangs indefinitely.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -21,58 +27,75 @@ rm ${PIP_LOG}
|
||||
|
||||
**SOLUTION**
|
||||
|
||||
Enter the stable-diffusion directory and completely remove the `src` directory and all its contents. The safest way to do this is to enter the stable-diffusion directory and give the command `git clean -f`. If this still doesn't fix the problem, try "conda clean -all" and then restart at the `conda env create` step.
|
||||
Enter the stable-diffusion directory and completely remove the `src` directory and all its contents.
|
||||
The safest way to do this is to enter the stable-diffusion directory and give the command
|
||||
`git clean -f`. If this still doesn't fix the problem, try "conda clean -all" and then restart at
|
||||
the `conda env create` step.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
**QUESTION**
|
||||
### **QUESTION**
|
||||
|
||||
`dream.py` crashes with the complaint that it can't find `ldm.simplet2i.py`. Or it complains that function is being passed incorrect parameters.
|
||||
`dream.py` crashes with the complaint that it can't find `ldm.simplet2i.py`. Or it complains that
|
||||
function is being passed incorrect parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
**SOLUTION**
|
||||
### **SOLUTION**
|
||||
|
||||
Reinstall the stable diffusion modules. Enter the `stable-diffusion` directory and give the command `pip install -e .`
|
||||
Reinstall the stable diffusion modules. Enter the `stable-diffusion` directory and give the command
|
||||
`pip install -e .`
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
**QUESTION**
|
||||
### **QUESTION**
|
||||
|
||||
`dream.py` dies, complaining of various missing modules, none of which starts with `ldm``.
|
||||
|
||||
**SOLUTION**
|
||||
### **SOLUTION**
|
||||
|
||||
From within the `stable-diffusion` directory, run `conda env update -f environment.yaml` This is also frequently the solution to
|
||||
complaints about an unknown function in a module.
|
||||
From within the `stable-diffusion` directory, run `conda env update -f environment.yaml` This is
|
||||
also frequently the solution to complaints about an unknown function in a module.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
**QUESTION**
|
||||
### **QUESTION**
|
||||
|
||||
There's a feature or bugfix in the Stable Diffusion GitHub that you want to try out.
|
||||
|
||||
**SOLUTION**
|
||||
### **SOLUTION**
|
||||
|
||||
**Main Branch**
|
||||
#### **Main Branch**
|
||||
|
||||
If the fix/feature is on the `main` branch, enter the stable-diffusion directory and do a `git pull`.
|
||||
If the fix/feature is on the `main` branch, enter the stable-diffusion directory and do a
|
||||
`git pull`.
|
||||
|
||||
Usually this will be sufficient, but if you start to see errors about missing or incorrect modules, use the command `pip install -e .` and/or `conda env update -f environment.yaml` (These commands won't break anything.)
|
||||
Usually this will be sufficient, but if you start to see errors about missing or incorrect modules,
|
||||
use the command
|
||||
|
||||
**Sub Branch**
|
||||
`pip install -e .` and/or
|
||||
|
||||
If the feature/fix is on a branch (e.g. "_foo-bugfix_"), the recipe is similar, but do a `git pull <name of branch>`.
|
||||
`conda env update -f environment.yaml`
|
||||
|
||||
**Not Committed**
|
||||
(These commands won't break anything.)
|
||||
|
||||
If the feature/fix is in a pull request that has not yet been made part of the main branch or a feature/bugfix branch, then from the page for the desired pull request, look for the line at the top that reads "_xxxx wants to merge xx commits into lstein:main from YYYYYY_". Copy the URL in YYYY. It should have the format `https://github.com/<name of contributor>/stable-diffusion/tree/<name of branch>`
|
||||
#### **Sub Branch**
|
||||
|
||||
Then **go to the directory above stable-diffusion** and rename the directory to "_stable-diffusion.lstein_", "_stable-diffusion.old_", or anything else. You can then git clone the branch that contains the pull request:
|
||||
If the feature/fix is on a branch (e.g. "_foo-bugfix_"), the recipe is similar, but do a
|
||||
`git pull <name of branch>`.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/<name of contributor>/stable-diffusion/tree/<name
|
||||
of branch>
|
||||
```
|
||||
#### **Not Committed**
|
||||
|
||||
You will need to go through the install procedure again, but it should be fast because all the dependencies are already loaded.
|
||||
If the feature/fix is in a pull request that has not yet been made part of the main branch or a
|
||||
feature/bugfix branch, then from the page for the desired pull request, look for the line at the top
|
||||
that reads "_xxxx wants to merge xx commits into lstein:main from YYYYYY_". Copy the URL in YYYY. It
|
||||
should have the format
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
`https://github.com/<name of contributor>/stable-diffusion/tree/<name of branch>`
|
||||
|
||||
Then **go to the directory above stable-diffusion** and rename the directory to
|
||||
"_stable-diffusion.lstein_", "_stable-diffusion.old_", or anything else. You can then git clone the
|
||||
branch that contains the pull request:
|
||||
|
||||
`git clone https://github.com/<name of contributor>/stable-diffusion/tree/<name of branch>`
|
||||
|
||||
You will need to go through the install procedure again, but it should be fast because all the
|
||||
dependencies are already loaded.
|
||||
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user