Squashed commit of the following:
commit 1c649e4663f37b51b42a561548c7e03d7efb209e
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Mon Sep 12 13:29:16 2022 -0400
fix torchvision dependency version #511
commit 4d197f699e1e8c3b0e7c1b71c30261a49370ee8d
Merge: a3e07fb 190ba78
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Mon Sep 12 07:29:19 2022 -0400
Merge branch 'development' of github.com:lstein/stable-diffusion into development
commit a3e07fb84ad51eab2aa586edaa011bbd4e01b395
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Mon Sep 12 07:28:58 2022 -0400
fix grid crash
commit 9fa1f31bf2f80785492927959c58e4b0825fb2e4
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Mon Sep 12 07:07:05 2022 -0400
fix opencv and realesrgan dependencies in mac install
commit 190ba78960c0c45bd1c51626e303b8c78a17b0c1
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Mon Sep 12 01:50:58 2022 -0400
Update requirements-mac.txt
Fixed dangling dash on last line.
commit 25d9ccc5091cc6452d8597453dcfe6c79327aa3a
Author: Any-Winter-4079 <50542132+Any-Winter-4079@users.noreply.github.com>
Date: Mon Sep 12 03:17:29 2022 +0200
Update model.py
commit 9cdf3aca7d2a7a6e85ec0a2732eb8e5a2dd60329
Author: Any-Winter-4079 <50542132+Any-Winter-4079@users.noreply.github.com>
Date: Mon Sep 12 02:52:36 2022 +0200
Update attention.py
Performance improvements to generate larger images in M1 #431
Update attention.py
Added dtype=r1.dtype to softmax
commit 49a96b90d846bcff17582273cacad596eff30658
Author: Mihai <299015+mh-dm@users.noreply.github.com>
Date: Sat Sep 10 16:58:07 2022 +0300
~7% speedup (1.57 to 1.69it/s) from switch to += in ldm.modules.attention. (#482)
Tested on 8GB eGPU nvidia setup so YMMV.
512x512 output, max VRAM stays same.
commit aba94b85e88cde654dd03bdec493a6d3b232f931
Author: Niek van der Maas <mail@niekvandermaas.nl>
Date: Fri Sep 9 15:01:37 2022 +0200
Fix macOS `pyenv` instructions, add code block highlight (#441)
Fix: `anaconda3-latest` does not work, specify the correct virtualenv, add missing init.
commit aac5102cf3850781a635cacc3150dd6bb4f486a8
Author: Henry van Megen <h.vanmegen@gmail.com>
Date: Thu Sep 8 05:16:35 2022 +0200
Disabled debug output (#436)
Co-authored-by: Henry van Megen <hvanmegen@gmail.com>
commit 0ab5a3646424467b459ea878d49cfc23f4a5ea35
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Sun Sep 11 17:19:46 2022 -0400
fix missing lines in outputs
commit 5e433728b550de9f56a2f124c8b325b3a5f2bd2f
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Sun Sep 11 16:20:14 2022 -0400
upped max_steps in v1-finetune.yaml and fixed TI docs to address #493
commit 7708f4fb98510dff504041231261c039a2c718de
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Sun Sep 11 16:03:37 2022 -0400
slight efficiency gain by using += in attention.py
commit b86a1deb00892f2b5f260659377d27790ef14016
Author: blessedcoolant <54517381+blessedcoolant@users.noreply.github.com>
Date: Mon Sep 12 07:47:12 2022 +1200
Remove print statement styling (#504)
Co-authored-by: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
commit 4951e66103878e5d5c8943a710ebce9320888252
Author: chromaticist <mhostick@gmail.com>
Date: Sun Sep 11 12:44:26 2022 -0700
Adding support for .bin files from huggingface concepts (#498)
* Adding support for .bin files from huggingface concepts
* Updating documentation to include huggingface .bin info
commit 79b445b0ca43b3592a829909dc4507cb1ecbe9e0
Merge: a323070 f7662c1
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Sun Sep 11 15:39:38 2022 -0400
Merge branch 'development' of github.com:lstein/stable-diffusion into development
commit a323070a4dbb1ce62db94342a2ab8e4adef833d6
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Sun Sep 11 15:28:57 2022 -0400
update requirements for new location of gfpgan
commit f7662c1808acc1704316d3b84d4baeacf1b24018
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Sun Sep 11 15:00:24 2022 -0400
update requirements for changed location of gfpgan
commit 93c242c9fbef91d87a6bbf42db2267dbd51e5739
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Sun Sep 11 14:47:58 2022 -0400
make gfpgan_model_exists flag available to web interface
commit c7c6cd7735b5c32e58349ca998a925cbaed7b376
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Sun Sep 11 14:43:07 2022 -0400
Update UPSCALE.md
New instructions needed to accommodate fact that the ESRGAN and GFPGAN packages are now installed by environment.yaml.
commit 77ca83e1031639f1e15cb7451e53dd8e37d1e971
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Sun Sep 11 14:31:56 2022 -0400
Update CLI.md
Final documentation tweak.
commit 0ea145d1884ce2316452124fd51a879506e2988d
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Sun Sep 11 14:29:26 2022 -0400
Update CLI.md
More doc fixes.
commit 162285ae86a2ab0bb26749387186c82b6bbf851d
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Sun Sep 11 14:28:45 2022 -0400
Update CLI.md
Minor documentation fix
commit 37c921dfe2aa25342934a101bf83eea4c0f5cfb7
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Sun Sep 11 14:26:41 2022 -0400
documentation enhancements
commit 4f72cb44ad0429874c9ba507d325267e295a040c
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Sun Sep 11 13:05:38 2022 -0400
moved the notebook files into their own directory
commit 878ef2e9e095ab08d00532f8a19556b8949b2dbb
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Sun Sep 11 12:58:06 2022 -0400
documentation tweaks
commit 4923118610ecaced2a670d108aef81c220d3507a
Merge: 16f6a67 defafc0
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Sun Sep 11 12:51:25 2022 -0400
Merge branch 'development' of github.com:lstein/stable-diffusion into development
commit defafc0e8e0e69b39fd13db12036e1d01e7a19f1
Author: Dominic Letz <dominic@diode.io>
Date: Sun Sep 11 18:51:01 2022 +0200
Enable upscaling on m1 (#474)
commit 16f6a6731d80fcc04dcdb693d74fc5c21e753c10
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Sun Sep 11 12:47:26 2022 -0400
install GFPGAN inside SD repository in order to fix 'dark cast' issue #169
commit 0881d429f2ddcd288aa673b2b5e9435a8a44371a
Author: blessedcoolant <54517381+blessedcoolant@users.noreply.github.com>
Date: Mon Sep 12 03:52:43 2022 +1200
Docs Update (#466)
Authored-by: @blessedcoolant
Co-authored-by: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
commit 9a29d442b437d650bd42516bbb24ebbcd0d6cd74
Author: Gérald LONLAS <gerald@lonlas.com>
Date: Sun Sep 11 23:23:18 2022 +0800
Revert "Add 3x Upscale option on the Web UI (#442)" (#488)
This reverts commit f8a540881c79ae657dc05b47bc71f8648e9f9782.
commit d301836fbdfce0a3f12b19ae6415e7ae14f53ed2
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Sun Sep 11 10:52:19 2022 -0400
can select prior output for init_img using -1, -2, etc
commit 70aa674e9e10d03eb462249764695ef1d4e1e28c
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Sun Sep 11 10:34:06 2022 -0400
merge PR #495 - keep using float16 in ldm.modules.attention
commit 8748370f44e28b104fbaa23b4e2e54e64102d799
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Sun Sep 11 10:22:32 2022 -0400
negative -S indexing recovers correct previous seed; closes issue #476
commit 839e30e4b8ca6554017fbab671bdf85fadf9a6ea
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Sun Sep 11 10:02:44 2022 -0400
improve CUDA VRAM monitoring
extra check that device==cuda before getting VRAM stats
commit bfb278127923fbd461c4549a4b7f2f2c1dd34b8c
Author: tildebyte <337875+tildebyte@users.noreply.github.com>
Date: Sat Sep 10 10:15:56 2022 -0400
fix(readme): add note about updating env via conda (#475)
commit 5c439888626145f94db1fdb00f5787ad27b64602
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Sat Sep 10 10:02:43 2022 -0400
reduce VRAM memory usage by half during model loading
* This moves the call to half() before model.to(device) to avoid GPU
copy of full model. Improves speed and reduces memory usage dramatically
* This fix contributed by @mh-dm (Mihai)
commit 99122708ca3342e00063c687f149c950cfd87200
Merge: 817c4a2 ecc6b75
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Sat Sep 10 09:54:34 2022 -0400
Merge branch 'development' of github.com:lstein/stable-diffusion into development
commit 817c4a26de0d01b109550e6db9d4c3ece9f37c1b
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Sat Sep 10 09:53:27 2022 -0400
remove -F option from normalized prompt; closes #483
commit ecc6b75a3ede6d1d2850d69e998c92c342efdf2d
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Sat Sep 10 09:53:27 2022 -0400
remove -F option from normalized prompt
commit 723d07444205a9c3da96926630c1dc705db3f130
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Fri Sep 9 18:49:51 2022 -0400
Allow ctrl c when using --from_file (#472)
* added ansi escapes to highlight key parts of CLI session
* adjust exception handling so that ^C will abort when reading prompts from a file
commit 75f633cda887d7bfcca3ef529d25c52461e11d99
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Fri Sep 9 12:03:45 2022 -0400
re-add new logo
commit 10db192cc4be66b3cebbdaa48a1806807578b56f
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Fri Sep 9 09:26:10 2022 -0400
changes to dogettx optimizations to run on m1
* Author @any-winter-4079
* Author @dogettx
Thanks to many individuals who contributed time and hardware to
benchmarking and debugging these changes.
commit c85ae00b33d619ab5448246ecda6c8e40d66fa3e
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Thu Sep 8 23:57:45 2022 -0400
fix bug which caused seed to get "stuck" on previous image even when UI specified -1
commit 1b5aae3ef3218b3f07b9ec48ce72589c0ad33746
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Thu Sep 8 22:36:47 2022 -0400
add icon to dream web server
commit 6abf739315ef83202ff5ad2144888f79f480d88d
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Thu Sep 8 22:25:09 2022 -0400
add favicon to web server
commit db825b813805b7428465e42377d756009e09e836
Merge: 33874ba afee7f9
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Thu Sep 8 22:17:37 2022 -0400
Merge branch 'deNULL-development' into development
commit 33874bae8db71dcdb5525826a1ec93b105e841ad
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Thu Sep 8 22:16:29 2022 -0400
Squashed commit of the following:
commit afee7f9cea2a73a3d62ced667e88aa0fe15020e4
Merge: 6531446 171f8db
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Thu Sep 8 22:14:32 2022 -0400
Merge branch 'development' of github.com:deNULL/stable-diffusion into deNULL-development
commit 171f8db742f18532b6fa03cdfbf4be2bbf6cf3ad
Author: Denis Olshin <me@denull.ru>
Date: Thu Sep 8 03:15:20 2022 +0300
saving full prompt to metadata when using web ui
commit d7e67b62f0ea9b7c8394b7c48786f5cf9c6f9e94
Author: Denis Olshin <me@denull.ru>
Date: Thu Sep 8 01:51:47 2022 +0300
better logic for clicking to make variations
commit afee7f9cea2a73a3d62ced667e88aa0fe15020e4
Merge: 6531446 171f8db
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Thu Sep 8 22:14:32 2022 -0400
Merge branch 'development' of github.com:deNULL/stable-diffusion into deNULL-development
commit 653144694fbb928d387c615c013ab0f2f1d5ca7f
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Thu Sep 8 20:41:37 2022 -0400
work around unexplained crash when timesteps=1000 (#440)
* work around unexplained crash when timesteps=1000
* this fix seems to work
commit c33a84cdfdb861a77916cd499e561d4c68ee192a
Author: blessedcoolant <54517381+blessedcoolant@users.noreply.github.com>
Date: Fri Sep 9 12:39:51 2022 +1200
Add New Logo (#454)
* Add instructions on how to install alongside pyenv (#393)
Like probably many others, I have a lot of different virtualenvs, one for each project. Most of them are handled by `pyenv`.
After installing according to these instructions I had issues with ´pyenv`and `miniconda` fighting over the $PATH of my system.
But then I stumbled upon this nice solution on SO: https://stackoverflow.com/a/73139031 , upon which I have based my suggested changes.
It runs perfectly on my M1 setup, with the anaconda setup as a virtual environment handled by pyenv.
Feel free to incorporate these instructions as you see fit.
Thanks a million for all your hard work.
* Disabled debug output (#436)
Co-authored-by: Henry van Megen <hvanmegen@gmail.com>
* Add New Logo
Co-authored-by: Håvard Gulldahl <havard@lurtgjort.no>
Co-authored-by: Henry van Megen <h.vanmegen@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Henry van Megen <hvanmegen@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
commit f8a540881c79ae657dc05b47bc71f8648e9f9782
Author: Gérald LONLAS <gerald@lonlas.com>
Date: Fri Sep 9 01:45:54 2022 +0800
Add 3x Upscale option on the Web UI (#442)
commit 244239e5f656e1f34830b8e8ce99a40decbea324
Author: James Reynolds <magnusviri@users.noreply.github.com>
Date: Thu Sep 8 05:36:33 2022 -0600
macOS CI workflow, dream.py exits with an error, but the workflow com… (#396)
* macOS CI workflow, dream.py exits with an error, but the workflow completes.
* Files for testing
Co-authored-by: James Reynolds <magnsuviri@me.com>
Co-authored-by: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
commit 711d49ed30a0741558ed06d6be38680e00272774
Author: James Reynolds <magnusviri@users.noreply.github.com>
Date: Thu Sep 8 05:35:08 2022 -0600
Cache model workflow (#394)
* Add workflow that caches the model, step 1 for CI
* Change name of workflow job
Co-authored-by: James Reynolds <magnsuviri@me.com>
Co-authored-by: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
commit 7996a30e3aea1ae9611bbce6e6efaac60aeb95d4
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Thu Sep 8 07:34:03 2022 -0400
add auto-creation of mask for inpainting (#438)
* now use a single init image for both image and mask
* turn on debugging for now to write out mask and image
* add back -M option as a fallback
commit a69ca31f349ddcf4c94fd009dc896f4e653f7fa4
Author: elliotsayes <elliotsayes@gmail.com>
Date: Thu Sep 8 15:30:06 2022 +1200
.gitignore WebUI temp files (#430)
* Add instructions on how to install alongside pyenv (#393)
Like probably many others, I have a lot of different virtualenvs, one for each project. Most of them are handled by `pyenv`.
After installing according to these instructions I had issues with ´pyenv`and `miniconda` fighting over the $PATH of my system.
But then I stumbled upon this nice solution on SO: https://stackoverflow.com/a/73139031 , upon which I have based my suggested changes.
It runs perfectly on my M1 setup, with the anaconda setup as a virtual environment handled by pyenv.
Feel free to incorporate these instructions as you see fit.
Thanks a million for all your hard work.
* .gitignore WebUI temp files
Co-authored-by: Håvard Gulldahl <havard@lurtgjort.no>
commit 5c6b612a722ff9cde1a5ddf9b29874842f1d5a26
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Wed Sep 7 22:50:55 2022 -0400
fix bug that caused same seed to be redisplayed repeatedly
commit 56f155c5907224b4276adb6ba01bd5c1a3401ee3
Author: Johan Roxendal <johan@roxendal.com>
Date: Thu Sep 8 04:50:06 2022 +0200
added support for parsing run log and displaying images in the frontend init state (#410)
Co-authored-by: Johan Roxendal <johan.roxendal@litteraturbanken.se>
Co-authored-by: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
commit 41687746be5290a4c3d3437957307666d956ae9d
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Wed Sep 7 20:24:35 2022 -0400
added missing initialization of latent_noise to None
commit 171f8db742f18532b6fa03cdfbf4be2bbf6cf3ad
Author: Denis Olshin <me@denull.ru>
Date: Thu Sep 8 03:15:20 2022 +0300
saving full prompt to metadata when using web ui
commit d7e67b62f0ea9b7c8394b7c48786f5cf9c6f9e94
Author: Denis Olshin <me@denull.ru>
Date: Thu Sep 8 01:51:47 2022 +0300
better logic for clicking to make variations
commit d1d044aa87cf8ba95a7e2e553c7fd993ec81a6d7
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Wed Sep 7 17:56:59 2022 -0400
actual image seed now written into web log rather than -1 (#428)
commit edada042b318028c77ab50dfbaa0b2671cc69e61
Author: Arturo Mendivil <60411196+artmen1516@users.noreply.github.com>
Date: Wed Sep 7 10:42:26 2022 -0700
Improve notebook and add requirements file (#422)
commit 29ab3c20280bfa73b9a89c8bd9dc99dc0ad7b651
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Wed Sep 7 13:28:11 2022 -0400
disable neonpixel optimizations on M1 hardware (#414)
* disable neonpixel optimizations on M1 hardware
* fix typo that was causing random noise images on m1
commit 7670ecc63f3e30e320e2c4197eb7140c6196c168
Author: cody <cnmizell@gmail.com>
Date: Wed Sep 7 12:24:41 2022 -0500
add more keyboard support on the web server (#391)
add ability to submit prompts with the "enter" key
add ability to cancel generations with the "escape" key
commit dd2aedacaf27d8fe750a342c310bc88de5311931
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Wed Sep 7 13:23:53 2022 -0400
report VRAM usage stats during initial model loading (#419)
commit f6284777e6d79bd3d1e85b83aa72d774299a7403
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Tue Sep 6 17:12:39 2022 -0400
Squashed commit of the following:
commit 7d1344282d942a33dcecda4d5144fc154ec82915
Merge: caf4ea3 ebeb556
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Mon Sep 5 10:07:27 2022 -0400
Merge branch 'development' of github.com:WebDev9000/stable-diffusion into WebDev9000-development
commit ebeb556af9c99b491a83c72f83512683a02a82ad
Author: Web Dev 9000 <rirath@gmail.com>
Date: Sun Sep 4 18:05:15 2022 -0700
Fixed unintentionally removed lines
commit ff2c4b9a1b773b95686d5f3e546e1194de054694
Author: Web Dev 9000 <rirath@gmail.com>
Date: Sun Sep 4 17:50:13 2022 -0700
Add ability to recreate variations via image click
commit c012929cdae7c37aa3b3b4fa2e7de465458f732a
Author: Web Dev 9000 <rirath@gmail.com>
Date: Sun Sep 4 14:35:33 2022 -0700
Add files via upload
commit 02a601899214adfe4536ce0ba67694a46319fd51
Author: Web Dev 9000 <rirath@gmail.com>
Date: Sun Sep 4 14:35:07 2022 -0700
Add files via upload
commit eef788981cbed7c68ffd58b4eb22a2df2e59ae0b
Author: Olivier Louvignes <olivier@mg-crea.com>
Date: Tue Sep 6 12:41:08 2022 +0200
feat(txt2img): allow from_file to work with len(lines) < batch_size (#349)
commit 720e5cd6513cd27e6d53feb6475dde20bd39841a
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Mon Sep 5 20:40:10 2022 -0400
Refactoring simplet2i (#387)
* start refactoring -not yet functional
* first phase of refactor done - not sure weighted prompts working
* Second phase of refactoring. Everything mostly working.
* The refactoring has moved all the hard-core inference work into
ldm.dream.generator.*, where there are submodules for txt2img and
img2img. inpaint will go in there as well.
* Some additional refactoring will be done soon, but relatively
minor work.
* fix -save_orig flag to actually work
* add @neonsecret attention.py memory optimization
* remove unneeded imports
* move token logging into conditioning.py
* add placeholder version of inpaint; porting in progress
* fix crash in img2img
* inpainting working; not tested on variations
* fix crashes in img2img
* ported attention.py memory optimization #117 from basujindal branch
* added @torch_no_grad() decorators to img2img, txt2img, inpaint closures
* Final commit prior to PR against development
* fixup crash when generating intermediate images in web UI
* rename ldm.simplet2i to ldm.generate
* add backward-compatibility simplet2i shell with deprecation warning
* add back in mps exception, addresses @vargol comment in #354
* replaced Conditioning class with exported functions
* fix wrong type of with_variations attribute during intialization
* changed "image_iterator()" to "get_make_image()"
* raise NotImplementedError for calling get_make_image() in parent class
* Update ldm/generate.py
better error message
Co-authored-by: Kevin Gibbons <bakkot@gmail.com>
* minor stylistic fixes and assertion checks from code review
* moved get_noise() method into img2img class
* break get_noise() into two methods, one for txt2img and the other for img2img
* inpainting works on non-square images now
* make get_noise() an abstract method in base class
* much improved inpainting
Co-authored-by: Kevin Gibbons <bakkot@gmail.com>
commit 1ad2a8e567b054cfe9df1715aa805218ee185754
Author: thealanle <35761977+thealanle@users.noreply.github.com>
Date: Mon Sep 5 17:35:04 2022 -0700
Fix --outdir function for web (#373)
* Fix --outdir function for web
* Removed unnecessary hardcoded path
commit 52d8bb2836cf05994ee5e2c5cf9c8d190dac0524
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Mon Sep 5 10:31:59 2022 -0400
Squashed commit of the following:
commit 0cd48e932f1326e000c46f4140f98697eb9bdc79
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Mon Sep 5 10:27:43 2022 -0400
resolve conflicts with development
commit d7bc8c12e05535a363ac7c745a3f3abc2773bfcf
Author: Scott McMillin <scott@scottmcmillin.com>
Date: Sun Sep 4 18:52:09 2022 -0500
Add title attribute back to img tag
commit 5397c89184ebfb8260bc2d8c3f23e73e103d24e6
Author: Scott McMillin <scott@scottmcmillin.com>
Date: Sun Sep 4 13:49:46 2022 -0500
Remove temp code
commit 1da080b50972696db2930681a09cb1c14e524758
Author: Scott McMillin <scott@scottmcmillin.com>
Date: Sun Sep 4 13:33:56 2022 -0500
Cleaned up HTML; small style changes; image click opens image; add seed to figcaption beneath image
commit caf4ea3d8982416dcf5a80fe4601ac4fbc126cc0
Author: Adam Rice <adam@askadam.io>
Date: Mon Sep 5 10:05:39 2022 -0400
Add a 'Remove Image' button to clear the file upload field (#382)
* added "remove image" button
* styled a new "remove image" button
* Update index.js
commit 95c088b30342c75ec2ab8c7d7a423ffd11c50099
Author: Kevin Gibbons <bakkot@gmail.com>
Date: Sun Sep 4 19:04:14 2022 -0700
Revert "Add CORS headers to dream server to ease integration with third-party web interfaces" (#371)
This reverts commit 91e826e5f425333674d1e3bec1fa1ac63cfb382d.
commit a20113d5a3985a23b7e19301acb57688e31e975c
Author: Kevin Gibbons <bakkot@gmail.com>
Date: Sun Sep 4 18:59:12 2022 -0700
put no_grad decorator on make_image closures (#375)
commit 0f93dadd6ac5aa0fbeee5d72150def775752a153
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Sun Sep 4 21:39:15 2022 -0400
fix several dangling references to --gfpgan option, which no longer exists
commit f4004f660e5daba721426cfcd3fe95318fd10bc3
Author: tildebyte <337875+tildebyte@users.noreply.github.com>
Date: Sun Sep 4 19:43:04 2022 -0400
TOIL(requirements): Split requirements to per-platform (#355)
* toil(reqs): split requirements to per-platform
Signed-off-by: Ben Alkov <ben.alkov@gmail.com>
* toil(reqs): fix for Win and Lin...
...allow pip to resolve latest torch, numpy
Signed-off-by: Ben Alkov <ben.alkov@gmail.com>
* toil(install): update reqs in Win install notebook
Signed-off-by: Ben Alkov <ben.alkov@gmail.com>
Signed-off-by: Ben Alkov <ben.alkov@gmail.com>
commit 4406fd138dec0e25409aeaa2b716f88dd95b76d1
Merge: 5116c81 fd7a72e
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Sun Sep 4 08:23:53 2022 -0400
Merge branch 'SebastianAigner-main' into development
Add support for full CORS headers for dream server.
commit fd7a72e147393f32fc40d8f5918ea9bf1401e723
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Sun Sep 4 08:23:11 2022 -0400
remove debugging message
commit 3a2be621f36e66b16e60b7f4f9210babfe84c582
Merge: 91e826e 5116c81
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Sun Sep 4 08:15:51 2022 -0400
Merge branch 'development' into main
commit 5116c8178c67f550e57f5d16fe931ee1a7cdb0ba
Author: Justin Wong <1584142+wongjustin99@users.noreply.github.com>
Date: Sun Sep 4 07:17:58 2022 -0400
fix save_original flag saving to the same filename (#360)
* Update README.md with new Anaconda install steps (#347)
pip3 version did not work for me and this is the recommended way to install Anaconda now it seems
* fix save_original flag saving to the same filename
Before this, the `--save_orig` flag was not working. The upscaled/GFPGAN would overwrite the original output image.
Co-authored-by: greentext2 <112735219+greentext2@users.noreply.github.com>
commit 91e826e5f425333674d1e3bec1fa1ac63cfb382d
Author: Sebastian Aigner <SebastianAigner@users.noreply.github.com>
Date: Sun Sep 4 10:22:54 2022 +0200
Add CORS headers to dream server to ease integration with third-party web interfaces
commit 6266d9e8d6421ee732338560f825771e461cefb0
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Sat Sep 3 15:45:20 2022 -0400
remove stray debugging message
commit 138956e5162679f6894ce75462907c9eeed83cbb
Author: greentext2 <112735219+greentext2@users.noreply.github.com>
Date: Sat Sep 3 13:38:57 2022 -0500
Update README.md with new Anaconda install steps (#347)
pip3 version did not work for me and this is the recommended way to install Anaconda now it seems
commit 60be735e802a1c3cd2812c5d8e63f9ed467ea9d9
Author: Cora Johnson-Roberson <cora.johnson.roberson@gmail.com>
Date: Sat Sep 3 14:28:34 2022 -0400
Switch to regular pytorch channel and restore Python 3.10 for Macs. (#301)
* Switch to regular pytorch channel and restore Python 3.10 for Macs.
Although pytorch-nightly should in theory be faster, it is currently
causing increased memory usage and slower iterations:
https://github.com/lstein/stable-diffusion/pull/283#issuecomment-1234784885
This changes the environment-mac.yaml file back to the regular pytorch
channel and moves the `transformers` dep into pip for now (since it
cannot be satisfied until tokenizers>=0.11 is built for Python 3.10).
* Specify versions for Pip packages as well.
commit d0d95d3a2a4b7a91c5c4f570d88af43a2c3afe75
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Sat Sep 3 14:10:31 2022 -0400
make initimg appear in web log
commit b90a21500037f07bb1b5d143045253ee6bc67391
Merge: 1eee811 6270e31
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Sat Sep 3 13:47:15 2022 -0400
Merge branch 'prixt-seamless' into development
commit 6270e313b8d87b33cb914f12558e34bc2f0ae357
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Sat Sep 3 13:46:29 2022 -0400
add credit to prixt for seamless circular tiling
commit a01b7bdc40af5376177de30b76dc075b523b3450
Merge: 1eee811 9d88abe
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Sat Sep 3 13:43:04 2022 -0400
add web interface for seamless option
commit 1eee8111b95241f54b49f58605ab343a52325b89
Merge: 64eca42 fb857f0
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Sat Sep 3 12:33:39 2022 -0400
Merge branch 'development' of github.com:lstein/stable-diffusion into development
commit 64eca42610b92cb73a30c405ab9dad28990c15e1
Merge: 9130ad7 21a1f68
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Sat Sep 3 12:33:05 2022 -0400
Merge branch 'main' into development
* brings in small documentation fixes that were
added directly to main during release tweaking.
commit fb857f05ba0eda5cf9bbe0f60b73a73d75562d85
Author: Lincoln Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
Date: Sat Sep 3 12:07:07 2022 -0400
fix typo in docs
commit 9d88abe2ea1fed6231ffd822956614589a1075b7
Author: prixt <paraxite@naver.com>
Date: Sat Sep 3 22:42:16 2022 +0900
fixed typo
commit a61e49bc974af0fc01c8424d7df9262f63ecf289
Author: prixt <paraxite@naver.com>
Date: Sat Sep 3 22:39:35 2022 +0900
* Removed unnecessary code
* Added description about --seamless
commit 02bee4fdb1534b71c5e609204506efb66699b2bc
Author: prixt <paraxite@naver.com>
Date: Sat Sep 3 16:08:03 2022 +0900
added --seamless tag logging to normalize_prompt
commit d922b53c26f3e9a11ecb920536b9632ec69df5f6
Author: prixt <paraxite@naver.com>
Date: Sat Sep 3 15:13:31 2022 +0900
added seamless tiling mode and commands
64
.github/workflows/cache-model.yml
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
|
||||
name: Cache Model
|
||||
on:
|
||||
workflow_dispatch
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
build:
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
os: [ macos-12 ]
|
||||
name: Create Caches using ${{ matrix.os }}
|
||||
runs-on: ${{ matrix.os }}
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout sources
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
- name: Cache model
|
||||
id: cache-sd-v1-4
|
||||
uses: actions/cache@v3
|
||||
env:
|
||||
cache-name: cache-sd-v1-4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
path: models/ldm/stable-diffusion-v1/model.ckpt
|
||||
key: ${{ env.cache-name }}
|
||||
restore-keys: |
|
||||
${{ env.cache-name }}
|
||||
- name: Download Stable Diffusion v1.4 model
|
||||
if: ${{ steps.cache-sd-v1-4.outputs.cache-hit != 'true' }}
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
if [ ! -e models/ldm/stable-diffusion-v1 ]; then
|
||||
mkdir -p models/ldm/stable-diffusion-v1
|
||||
fi
|
||||
if [ ! -e models/ldm/stable-diffusion-v1/model.ckpt ]; then
|
||||
curl -o models/ldm/stable-diffusion-v1/model.ckpt ${{ secrets.SD_V1_4_URL }}
|
||||
fi
|
||||
# Uncomment this when we no longer make changes to environment-mac.yaml
|
||||
# - name: Cache environment
|
||||
# id: cache-conda-env-ldm
|
||||
# uses: actions/cache@v3
|
||||
# env:
|
||||
# cache-name: cache-conda-env-ldm
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# path: ~/.conda/envs/ldm
|
||||
# key: ${{ env.cache-name }}
|
||||
# restore-keys: |
|
||||
# ${{ env.cache-name }}
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
# if: ${{ steps.cache-conda-env-ldm.outputs.cache-hit != 'true' }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
conda env create -f environment-mac.yaml
|
||||
- name: Cache hugginface and torch models
|
||||
id: cache-hugginface-torch
|
||||
uses: actions/cache@v3
|
||||
env:
|
||||
cache-name: cache-hugginface-torch
|
||||
with:
|
||||
path: ~/.cache
|
||||
key: ${{ env.cache-name }}
|
||||
restore-keys: |
|
||||
${{ env.cache-name }}
|
||||
- name: Download Huggingface and Torch models
|
||||
if: ${{ steps.cache-hugginface-torch.outputs.cache-hit != 'true' }}
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
export PYTHON_BIN=/usr/local/miniconda/envs/ldm/bin/python
|
||||
$PYTHON_BIN scripts/preload_models.py
|
||||
80
.github/workflows/macos12-miniconda.yml
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
|
||||
name: Build
|
||||
on:
|
||||
push:
|
||||
branches: [ main ]
|
||||
pull_request:
|
||||
branches: [ main ]
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
build:
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
os: [ macos-12 ]
|
||||
name: Build on ${{ matrix.os }} miniconda
|
||||
runs-on: ${{ matrix.os }}
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout sources
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
- name: Cache model
|
||||
id: cache-sd-v1-4
|
||||
uses: actions/cache@v3
|
||||
env:
|
||||
cache-name: cache-sd-v1-4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
path: models/ldm/stable-diffusion-v1/model.ckpt
|
||||
key: ${{ env.cache-name }}
|
||||
restore-keys: |
|
||||
${{ env.cache-name }}
|
||||
- name: Download Stable Diffusion v1.4 model
|
||||
if: ${{ steps.cache-sd-v1-4.outputs.cache-hit != 'true' }}
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
if [ ! -e models/ldm/stable-diffusion-v1 ]; then
|
||||
mkdir -p models/ldm/stable-diffusion-v1
|
||||
fi
|
||||
if [ ! -e models/ldm/stable-diffusion-v1/model.ckpt ]; then
|
||||
curl -o models/ldm/stable-diffusion-v1/model.ckpt ${{ secrets.SD_V1_4_URL }}
|
||||
fi
|
||||
# Uncomment this when we no longer make changes to environment-mac.yaml
|
||||
# - name: Cache environment
|
||||
# id: cache-conda-env-ldm
|
||||
# uses: actions/cache@v3
|
||||
# env:
|
||||
# cache-name: cache-conda-env-ldm
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# path: ~/.conda/envs/ldm
|
||||
# key: ${{ env.cache-name }}
|
||||
# restore-keys: |
|
||||
# ${{ env.cache-name }}
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
# if: ${{ steps.cache-conda-env-ldm.outputs.cache-hit != 'true' }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
conda env create -f environment-mac.yaml
|
||||
- name: Cache hugginface and torch models
|
||||
id: cache-hugginface-torch
|
||||
uses: actions/cache@v3
|
||||
env:
|
||||
cache-name: cache-hugginface-torch
|
||||
with:
|
||||
path: ~/.cache
|
||||
key: ${{ env.cache-name }}
|
||||
restore-keys: |
|
||||
${{ env.cache-name }}
|
||||
- name: Download Huggingface and Torch models
|
||||
if: ${{ steps.cache-hugginface-torch.outputs.cache-hit != 'true' }}
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
export PYTHON_BIN=/usr/local/miniconda/envs/ldm/bin/python
|
||||
$PYTHON_BIN scripts/preload_models.py
|
||||
- name: Run the tests
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
# Note, can't "activate" via automation, and activation is just env vars and path
|
||||
export PYTHON_BIN=/usr/local/miniconda/envs/ldm/bin/python
|
||||
export PYTORCH_ENABLE_MPS_FALLBACK=1
|
||||
$PYTHON_BIN scripts/preload_models.py
|
||||
mkdir -p outputs/img-samples
|
||||
time $PYTHON_BIN scripts/dream.py --from_file tests/prompts.txt </dev/null 2> outputs/img-samples/err.log > outputs/img-samples/out.log
|
||||
- name: Archive results
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: results
|
||||
path: outputs/img-samples
|
||||
3
.gitignore
vendored
@ -77,6 +77,9 @@ db.sqlite3-journal
|
||||
instance/
|
||||
.webassets-cache
|
||||
|
||||
# WebUI temp files:
|
||||
img2img-tmp.png
|
||||
|
||||
# Scrapy stuff:
|
||||
.scrapy
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
789
README.md
@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
<h1 align='center'><b>Stable Diffusion Dream Script</b></h1>
|
||||
|
||||
<p align='center'>
|
||||
<img src="static/logo_temp.png"/>
|
||||
<img src="docs/assets/logo.png"/>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
@ -12,397 +12,118 @@
|
||||
<img src="https://img.shields.io/github/issues-pr/lstein/stable-diffusion?logo=GitHub&style=for-the-badge" alt="pull-requests"/>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
This is a fork of CompVis/stable-diffusion, the wonderful open source
|
||||
text-to-image generator. This fork supports:
|
||||
# **Stable Diffusion Dream Script**
|
||||
|
||||
1. An interactive command-line interface that accepts the same prompt
|
||||
and switches as the Discord bot.
|
||||
This is a fork of
|
||||
[CompVis/stable-diffusion](https://github.com/CompVis/stable-diffusion),
|
||||
the open source text-to-image generator. It provides a streamlined
|
||||
process with various new features and options to aid the image
|
||||
generation process. It runs on Windows, Mac and Linux machines,
|
||||
and runs on GPU cards with as little as 4 GB or RAM.
|
||||
|
||||
2. A basic Web interface that allows you to run a local web server for
|
||||
generating images in your browser.
|
||||
_Note: This fork is rapidly evolving. Please use the
|
||||
[Issues](https://github.com/lstein/stable-diffusion/issues) tab to
|
||||
report bugs and make feature requests. Be sure to use the provided
|
||||
templates. They will help aid diagnose issues faster._
|
||||
|
||||
3. Support for img2img in which you provide a seed image to guide the
|
||||
image creation. (inpainting & masking coming soon)
|
||||
# **Table of Contents**
|
||||
|
||||
4. A notebook for running the code on Google Colab.
|
||||
|
||||
5. Upscaling and face fixing using the optional ESRGAN and GFPGAN
|
||||
packages.
|
||||
|
||||
6. Weighted subprompts for prompt tuning.
|
||||
|
||||
7. [Image variations](VARIATIONS.md) which allow you to systematically
|
||||
generate variations of an image you like and combine two or more
|
||||
images together to combine the best features of both.
|
||||
|
||||
8. Textual inversion for customization of the prompt language and images.
|
||||
|
||||
8. ...and more!
|
||||
|
||||
This fork is rapidly evolving, so use the Issues panel to report bugs
|
||||
and make feature requests, and check back periodically for
|
||||
improvements and bug fixes.
|
||||
|
||||
# Table of Contents
|
||||
|
||||
1. [Major Features](#features)
|
||||
2. [Changelog](#latest-changes)
|
||||
3. [Installation](#installation)
|
||||
1. [Linux](#linux)
|
||||
1. [Windows](#windows)
|
||||
1. [MacOS](README-Mac-MPS.md)
|
||||
1. [Installation](#installation)
|
||||
2. [Major Features](#features)
|
||||
3. [Changelog](#latest-changes)
|
||||
4. [Troubleshooting](#troubleshooting)
|
||||
5. [Contributing](#contributing)
|
||||
6. [Support](#support)
|
||||
|
||||
# Features
|
||||
# Installation
|
||||
|
||||
## Interactive command-line interface similar to the Discord bot
|
||||
This fork is supported across multiple platforms. You can find individual installation instructions below.
|
||||
|
||||
The _dream.py_ script, located in scripts/dream.py,
|
||||
provides an interactive interface to image generation similar to
|
||||
the "dream mothership" bot that Stable AI provided on its Discord
|
||||
server. Unlike the txt2img.py and img2img.py scripts provided in the
|
||||
original CompViz/stable-diffusion source code repository, the
|
||||
time-consuming initialization of the AI model
|
||||
initialization only happens once. After that image generation
|
||||
from the command-line interface is very fast.
|
||||
- ## [Linux](docs/installation/INSTALL_LINUX.md)
|
||||
- ## [Windows](docs/installation/INSTALL_WINDOWS.md)
|
||||
- ## [Macintosh](docs/installation/INSTALL_MAC.md)
|
||||
|
||||
The script uses the readline library to allow for in-line editing,
|
||||
command history (up and down arrows), autocompletion, and more. To help
|
||||
keep track of which prompts generated which images, the script writes a
|
||||
log file of image names and prompts to the selected output directory.
|
||||
In addition, as of version 1.02, it also writes the prompt into the PNG
|
||||
file's metadata where it can be retrieved using scripts/images2prompt.py
|
||||
## **Hardware Requirements**
|
||||
|
||||
The script is confirmed to work on Linux and Windows systems. It should
|
||||
work on MacOSX as well, but this is not confirmed. Note that this script
|
||||
runs from the command-line (CMD or Terminal window), and does not have a GUI.
|
||||
**System**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
(ldm) ~/stable-diffusion$ python3 ./scripts/dream.py
|
||||
* Initializing, be patient...
|
||||
Loading model from models/ldm/text2img-large/model.ckpt
|
||||
(...more initialization messages...)
|
||||
You wil need one of the following:
|
||||
|
||||
* Initialization done! Awaiting your command...
|
||||
dream> ashley judd riding a camel -n2 -s150
|
||||
Outputs:
|
||||
outputs/img-samples/00009.png: "ashley judd riding a camel" -n2 -s150 -S 416354203
|
||||
outputs/img-samples/00010.png: "ashley judd riding a camel" -n2 -s150 -S 1362479620
|
||||
- An NVIDIA-based graphics card with 4 GB or more VRAM memory.
|
||||
- An Apple computer with an M1 chip.
|
||||
|
||||
dream> "there's a fly in my soup" -n6 -g
|
||||
outputs/img-samples/00011.png: "there's a fly in my soup" -n6 -g -S 2685670268
|
||||
seeds for individual rows: [2685670268, 1216708065, 2335773498, 822223658, 714542046, 3395302430]
|
||||
dream> q
|
||||
**Memory**
|
||||
|
||||
# this shows how to retrieve the prompt stored in the saved image's metadata
|
||||
(ldm) ~/stable-diffusion$ python3 ./scripts/images2prompt.py outputs/img_samples/*.png
|
||||
00009.png: "ashley judd riding a camel" -s150 -S 416354203
|
||||
00010.png: "ashley judd riding a camel" -s150 -S 1362479620
|
||||
00011.png: "there's a fly in my soup" -n6 -g -S 2685670268
|
||||
```
|
||||
- At least 12 GB Main Memory RAM.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align='center'>
|
||||
<img src="static/dream-py-demo.png"/>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
**Disk**
|
||||
|
||||
The dream> prompt's arguments are pretty much identical to those used
|
||||
in the Discord bot, except you don't need to type "!dream" (it doesn't
|
||||
hurt if you do). A significant change is that creation of individual
|
||||
images is now the default unless --grid (-g) is given. For backward
|
||||
compatibility, the -i switch is recognized. For command-line help
|
||||
type -h (or --help) at the dream> prompt.
|
||||
|
||||
The script itself also recognizes a series of command-line switches
|
||||
that will change important global defaults, such as the directory for
|
||||
image outputs and the location of the model weight files.
|
||||
|
||||
## Image-to-Image
|
||||
|
||||
This script also provides an img2img feature that lets you seed your
|
||||
creations with a drawing or photo. This is a really cool feature that tells
|
||||
stable diffusion to build the prompt on top of the image you provide, preserving
|
||||
the original's basic shape and layout. To use it, provide the --init_img
|
||||
option as shown here:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
dream> "waterfall and rainbow" --init_img=./init-images/crude_drawing.png --strength=0.5 -s100 -n4
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The --init_img (-I) option gives the path to the seed picture. --strength (-f) controls how much
|
||||
the original will be modified, ranging from 0.0 (keep the original intact), to 1.0 (ignore the original
|
||||
completely). The default is 0.75, and ranges from 0.25-0.75 give interesting results.
|
||||
|
||||
You may also pass a -v<count> option to generate count variants on the original image. This is done by
|
||||
passing the first generated image back into img2img the requested number of times. It generates interesting
|
||||
variants.
|
||||
|
||||
## GFPGAN and Real-ESRGAN Support
|
||||
|
||||
The script also provides the ability to do face restoration and
|
||||
upscaling with the help of GFPGAN and Real-ESRGAN respectively.
|
||||
|
||||
To use the ability, clone the **[GFPGAN
|
||||
repository](https://github.com/TencentARC/GFPGAN)** and follow their
|
||||
installation instructions. By default, we expect GFPGAN to be
|
||||
installed in a 'GFPGAN' sibling directory. Be sure that the `"ldm"`
|
||||
conda environment is active as you install GFPGAN.
|
||||
|
||||
You can use the `--gfpgan_dir` argument with `dream.py` to set a
|
||||
custom path to your GFPGAN directory. _There are other GFPGAN related
|
||||
boot arguments if you wish to customize further._
|
||||
|
||||
You can install **Real-ESRGAN** by typing the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
pip install realesrgan
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Note: Internet connection needed:**
|
||||
Users whose GPU machines are isolated from the Internet (e.g. on a
|
||||
University cluster) should be aware that the first time you run
|
||||
dream.py with GFPGAN and Real-ESRGAN turned on, it will try to
|
||||
download model files from the Internet. To rectify this, you may run
|
||||
`python3 scripts/preload_models.py` after you have installed GFPGAN
|
||||
and all its dependencies.
|
||||
|
||||
**Usage**
|
||||
|
||||
You will now have access to two new prompt arguments.
|
||||
|
||||
**Upscaling**
|
||||
|
||||
`-U : <upscaling_factor> <upscaling_strength>`
|
||||
|
||||
The upscaling prompt argument takes two values. The first value is a
|
||||
scaling factor and should be set to either `2` or `4` only. This will
|
||||
either scale the image 2x or 4x respectively using different models.
|
||||
|
||||
You can set the scaling stength between `0` and `1.0` to control
|
||||
intensity of the of the scaling. This is handy because AI upscalers
|
||||
generally tend to smooth out texture details. If you wish to retain
|
||||
some of those for natural looking results, we recommend using values
|
||||
between `0.5 to 0.8`.
|
||||
|
||||
If you do not explicitly specify an upscaling_strength, it will
|
||||
default to 0.75.
|
||||
|
||||
**Face Restoration**
|
||||
|
||||
`-G : <gfpgan_strength>`
|
||||
|
||||
This prompt argument controls the strength of the face restoration
|
||||
that is being applied. Similar to upscaling, values between `0.5 to 0.8` are recommended.
|
||||
|
||||
You can use either one or both without any conflicts. In cases where
|
||||
you use both, the image will be first upscaled and then the face
|
||||
restoration process will be executed to ensure you get the highest
|
||||
quality facial features.
|
||||
|
||||
`--save_orig`
|
||||
|
||||
When you use either `-U` or `-G`, the final result you get is upscaled
|
||||
or face modified. If you want to save the original Stable Diffusion
|
||||
generation, you can use the `-save_orig` prompt argument to save the
|
||||
original unaffected version too.
|
||||
|
||||
**Example Usage**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
dream > superman dancing with a panda bear -U 2 0.6 -G 0.4
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This also works with img2img:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
dream> a man wearing a pineapple hat -I path/to/your/file.png -U 2 0.5 -G 0.6
|
||||
```
|
||||
- At least 6 GB of free disk space for the machine learning model, Python, and all its dependencies.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**
|
||||
|
||||
GFPGAN and Real-ESRGAN are both memory intensive. In order to avoid
|
||||
crashes and memory overloads during the Stable Diffusion process,
|
||||
these effects are applied after Stable Diffusion has completed its
|
||||
work.
|
||||
If you are have a Nvidia 10xx series card (e.g. the 1080ti), please
|
||||
run the dream script in full-precision mode as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
In single image generations, you will see the output right away but
|
||||
when you are using multiple iterations, the images will first be
|
||||
generated and then upscaled and face restored after that process is
|
||||
complete. While the image generation is taking place, you will still
|
||||
be able to preview the base images.
|
||||
Similarly, specify full-precision mode on Apple M1 hardware.
|
||||
|
||||
If you wish to stop during the image generation but want to upscale or
|
||||
face restore a particular generated image, pass it again with the same
|
||||
prompt and generated seed along with the `-U` and `-G` prompt
|
||||
arguments to perform those actions.
|
||||
|
||||
## Google Colab
|
||||
|
||||
Stable Diffusion AI Notebook: <a href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/lstein/stable-diffusion/blob/main/Stable_Diffusion_AI_Notebook.ipynb" target="_parent"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"/></a> <br>
|
||||
Open and follow instructions to use an isolated environment running Dream.<br>
|
||||
|
||||
Output example:
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Barebones Web Server
|
||||
|
||||
As of version 1.10, this distribution comes with a bare bones web
|
||||
server (see screenshot). To use it, run the _dream.py_ script by
|
||||
adding the **--web** option.
|
||||
To run in full-precision mode, start `dream.py` with the
|
||||
`--full_precision` flag:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
(ldm) ~/stable-diffusion$ python3 scripts/dream.py --web
|
||||
(ldm) ~/stable-diffusion$ python scripts/dream.py --full_precision
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can then connect to the server by pointing your web browser at
|
||||
http://localhost:9090, or to the network name or IP address of the server.
|
||||
# Features
|
||||
|
||||
Kudos to [Tesseract Cat](https://github.com/TesseractCat) for
|
||||
contributing this code, and to [dagf2101](https://github.com/dagf2101)
|
||||
for refining it.
|
||||
## **Major Features**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
- ## [Interactive Command Line Interface](docs/features/CLI.md)
|
||||
|
||||
## Reading Prompts from a File
|
||||
- ## [Image To Image](docs/features/IMG2IMG.md)
|
||||
|
||||
You can automate dream.py by providing a text file with the prompts
|
||||
you want to run, one line per prompt. The text file must be composed
|
||||
with a text editor (e.g. Notepad) and not a word processor. Each line
|
||||
should look like what you would type at the dream> prompt:
|
||||
- ## [Inpainting Support](docs/features/INPAINTING.md)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
a beautiful sunny day in the park, children playing -n4 -C10
|
||||
stormy weather on a mountain top, goats grazing -s100
|
||||
innovative packaging for a squid's dinner -S137038382
|
||||
```
|
||||
- ## [GFPGAN and Real-ESRGAN Support](docs/features/UPSCALE.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Then pass this file's name to dream.py when you invoke it:
|
||||
- ## [Seamless Tiling](docs/features/OTHER.md#seamless-tiling)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
(ldm) ~/stable-diffusion$ python3 scripts/dream.py --from_file "path/to/prompts.txt"
|
||||
```
|
||||
- ## [Google Colab](docs/features/OTHER.md#google-colab)
|
||||
|
||||
You may read a series of prompts from standard input by providing a filename of "-":
|
||||
- ## [Web Server](docs/features/WEB.md)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
(ldm) ~/stable-diffusion$ echo "a beautiful day" | python3 scripts/dream.py --from_file -
|
||||
```
|
||||
- ## [Reading Prompts From File](docs/features/OTHER.md#reading-prompts-from-a-file)
|
||||
|
||||
## Shortcut for reusing seeds from the previous command
|
||||
- ## [Shortcut: Reusing Seeds](docs/features/OTHER.md#shortcuts-reusing-seeds)
|
||||
|
||||
Since it is so common to reuse seeds while refining a prompt, there is
|
||||
now a shortcut as of version 1.11. Provide a **-S** (or **--seed**)
|
||||
switch of -1 to use the seed of the most recent image generated. If
|
||||
you produced multiple images with the **-n** switch, then you can go
|
||||
back further using -2, -3, etc. up to the first image generated by the
|
||||
previous command. Sorry, but you can't go back further than one
|
||||
command.
|
||||
- ## [Weighted Prompts](docs/features/OTHER.md#weighted-prompts)
|
||||
|
||||
Here's an example of using this to do a quick refinement. It also
|
||||
illustrates using the new **-G** switch to turn on upscaling and
|
||||
face enhancement (see previous section):
|
||||
- ## [Variations](docs/features/VARIATIONS.md)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
dream> a cute child playing hopscotch -G0.5
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
outputs/img-samples/000039.3498014304.png: "a cute child playing hopscotch" -s50 -W512 -H512 -C7.5 -mk_lms -S3498014304
|
||||
- ## [Personalizing Text-to-Image Generation](docs/features/TEXTUAL_INVERSION.md)
|
||||
|
||||
# I wonder what it will look like if I bump up the steps and set facial enhancement to full strength?
|
||||
dream> a cute child playing hopscotch -G1.0 -s100 -S -1
|
||||
reusing previous seed 3498014304
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
outputs/img-samples/000040.3498014304.png: "a cute child playing hopscotch" -G1.0 -s100 -W512 -H512 -C7.5 -mk_lms -S3498014304
|
||||
```
|
||||
- ## [Simplified API for text to image generation](docs/features/OTHER.md#simplified-api)
|
||||
|
||||
## Weighted Prompts
|
||||
## **Other Features**
|
||||
|
||||
You may weight different sections of the prompt to tell the sampler to attach different levels of
|
||||
priority to them, by adding :(number) to the end of the section you wish to up- or downweight.
|
||||
For example consider this prompt:
|
||||
- ### [Creating Transparent Regions for Inpainting](docs/features/INPAINTING.md#creating-transparent-regions-for-inpainting)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
tabby cat:0.25 white duck:0.75 hybrid
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will tell the sampler to invest 25% of its effort on the tabby
|
||||
cat aspect of the image and 75% on the white duck aspect
|
||||
(surprisingly, this example actually works). The prompt weights can
|
||||
use any combination of integers and floating point numbers, and they
|
||||
do not need to add up to 1.
|
||||
|
||||
## Personalizing Text-to-Image Generation
|
||||
|
||||
You may personalize the generated images to provide your own styles or objects by training a new LDM checkpoint
|
||||
and introducing a new vocabulary to the fixed model.
|
||||
|
||||
To train, prepare a folder that contains images sized at 512x512 and execute the following:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
WINDOWS: As the default backend is not available on Windows, if you're using that platform, set the environment variable `PL_TORCH_DISTRIBUTED_BACKEND=gloo`
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
(ldm) ~/stable-diffusion$ python3 ./main.py --base ./configs/stable-diffusion/v1-finetune.yaml \
|
||||
-t \
|
||||
--actual_resume ./models/ldm/stable-diffusion-v1/model.ckpt \
|
||||
-n my_cat \
|
||||
--gpus 0, \
|
||||
--data_root D:/textual-inversion/my_cat \
|
||||
--init_word 'cat'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
During the training process, files will be created in /logs/[project][time][project]/
|
||||
where you can see the process.
|
||||
|
||||
conditioning\* contains the training prompts
|
||||
inputs, reconstruction the input images for the training epoch
|
||||
samples, samples scaled for a sample of the prompt and one with the init word provided
|
||||
|
||||
On a RTX3090, the process for SD will take ~1h @1.6 iterations/sec.
|
||||
|
||||
Note: According to the associated paper, the optimal number of images
|
||||
is 3-5. Your model may not converge if you use more images than that.
|
||||
|
||||
Training will run indefinately, but you may wish to stop it before the
|
||||
heat death of the universe, when you find a low loss epoch or around
|
||||
~5000 iterations.
|
||||
|
||||
Once the model is trained, specify the trained .pt file when starting
|
||||
dream using
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
(ldm) ~/stable-diffusion$ python3 ./scripts/dream.py --embedding_path /path/to/embedding.pt --full_precision
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then, to utilize your subject at the dream prompt
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
dream> "a photo of *"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
this also works with image2image
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
dream> "waterfall and rainbow in the style of *" --init_img=./init-images/crude_drawing.png --strength=0.5 -s100 -n4
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
It's also possible to train multiple tokens (modify the placeholder string in configs/stable-diffusion/v1-finetune.yaml) and combine LDM checkpoints using:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
(ldm) ~/stable-diffusion$ python3 ./scripts/merge_embeddings.py \
|
||||
--manager_ckpts /path/to/first/embedding.pt /path/to/second/embedding.pt [...] \
|
||||
--output_path /path/to/output/embedding.pt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Credit goes to @rinongal and the repository located at
|
||||
https://github.com/rinongal/textual_inversion Please see the
|
||||
repository and associated paper for details and limitations.
|
||||
- ### [Preload Models](docs/features/OTHER.md#preload-models)
|
||||
|
||||
# Latest Changes
|
||||
|
||||
- v1.13 (3 September 2022)
|
||||
- v1.14 (11 September 2022)
|
||||
|
||||
- Support image variations (see [VARIATIONS](VARIATIONS.md) ([Kevin Gibbons](https://github.com/bakkot) and many contributors and reviewers)
|
||||
- Memory optimizations for small-RAM cards. 512x512 now possible on 4 GB GPUs.
|
||||
- Full support for Apple hardware with M1 or M2 chips.
|
||||
- Add "seamless mode" for circular tiling of image. Generates beautiful effects. ([prixt](https://github.com/prixt)).
|
||||
- Inpainting support.
|
||||
- Improved web server GUI.
|
||||
- Lots of code and documentation cleanups.
|
||||
|
||||
- v1.13 (3 September 2022
|
||||
|
||||
- Support image variations (see [VARIATIONS](docs/features/VARIATIONS.md) ([Kevin Gibbons](https://github.com/bakkot) and many contributors and reviewers)
|
||||
- Supports a Google Colab notebook for a standalone server running on Google hardware [Arturo Mendivil](https://github.com/artmen1516)
|
||||
- WebUI supports GFPGAN/ESRGAN facial reconstruction and upscaling [Kevin Gibbons](https://github.com/bakkot)
|
||||
- WebUI supports incremental display of in-progress images during generation [Kevin Gibbons](https://github.com/bakkot)
|
||||
@ -413,369 +134,22 @@ repository and associated paper for details and limitations.
|
||||
- Works on M1 Apple hardware.
|
||||
- Multiple bug fixes.
|
||||
|
||||
For older changelogs, please visit **[CHANGELOGS](CHANGELOG.md)**.
|
||||
|
||||
# Installation
|
||||
|
||||
There are separate installation walkthroughs for [Linux](#linux), [Windows](#windows) and [Macintosh](#Macintosh)
|
||||
|
||||
## Linux
|
||||
|
||||
1. You will need to install the following prerequisites if they are not already available. Use your
|
||||
operating system's preferred installer
|
||||
|
||||
- Python (version 3.8.5 recommended; higher may work)
|
||||
- git
|
||||
|
||||
2. Install the Python Anaconda environment manager.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
~$ wget https://repo.anaconda.com/archive/Anaconda3-2022.05-Linux-x86_64.sh
|
||||
~$ chmod +x Anaconda3-2022.05-Linux-x86_64.sh
|
||||
~$ ./Anaconda3-2022.05-Linux-x86_64.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
After installing anaconda, you should log out of your system and log back in. If the installation
|
||||
worked, your command prompt will be prefixed by the name of the current anaconda environment, "(base)".
|
||||
|
||||
3. Copy the stable-diffusion source code from GitHub:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
(base) ~$ git clone https://github.com/lstein/stable-diffusion.git
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will create stable-diffusion folder where you will follow the rest of the steps.
|
||||
|
||||
4. Enter the newly-created stable-diffusion folder. From this step forward make sure that you are working in the stable-diffusion directory!
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
(base) ~$ cd stable-diffusion
|
||||
(base) ~/stable-diffusion$
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
5. Use anaconda to copy necessary python packages, create a new python environment named "ldm",
|
||||
and activate the environment.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
(base) ~/stable-diffusion$ conda env create -f environment.yaml
|
||||
(base) ~/stable-diffusion$ conda activate ldm
|
||||
(ldm) ~/stable-diffusion$
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
After these steps, your command prompt will be prefixed by "(ldm)" as shown above.
|
||||
|
||||
6. Load a couple of small machine-learning models required by stable diffusion:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
(ldm) ~/stable-diffusion$ python3 scripts/preload_models.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note that this step is necessary because I modified the original
|
||||
just-in-time model loading scheme to allow the script to work on GPU
|
||||
machines that are not internet connected. See [Workaround for machines with limited internet connectivity](#workaround-for-machines-with-limited-internet-connectivity)
|
||||
|
||||
7. Now you need to install the weights for the stable diffusion model.
|
||||
|
||||
For running with the released weights, you will first need to set up an acount with Hugging Face (https://huggingface.co).
|
||||
Use your credentials to log in, and then point your browser at https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion-v-1-4-original.
|
||||
You may be asked to sign a license agreement at this point.
|
||||
|
||||
Click on "Files and versions" near the top of the page, and then click on the file named "sd-v1-4.ckpt". You'll be taken
|
||||
to a page that prompts you to click the "download" link. Save the file somewhere safe on your local machine.
|
||||
|
||||
Now run the following commands from within the stable-diffusion directory. This will create a symbolic
|
||||
link from the stable-diffusion model.ckpt file, to the true location of the sd-v1-4.ckpt file.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
(ldm) ~/stable-diffusion$ mkdir -p models/ldm/stable-diffusion-v1
|
||||
(ldm) ~/stable-diffusion$ ln -sf /path/to/sd-v1-4.ckpt models/ldm/stable-diffusion-v1/model.ckpt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
8. Start generating images!
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# for the pre-release weights use the -l or --liaon400m switch
|
||||
(ldm) ~/stable-diffusion$ python3 scripts/dream.py -l
|
||||
|
||||
# for the post-release weights do not use the switch
|
||||
(ldm) ~/stable-diffusion$ python3 scripts/dream.py
|
||||
|
||||
# for additional configuration switches and arguments, use -h or --help
|
||||
(ldm) ~/stable-diffusion$ python3 scripts/dream.py -h
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
9. Subsequently, to relaunch the script, be sure to run "conda activate ldm" (step 5, second command), enter the "stable-diffusion"
|
||||
directory, and then launch the dream script (step 8). If you forget to activate the ldm environment, the script will fail with multiple ModuleNotFound errors.
|
||||
|
||||
### Updating to newer versions of the script
|
||||
|
||||
This distribution is changing rapidly. If you used the "git clone" method (step 5) to download the stable-diffusion directory, then to update to the latest and greatest version, launch the Anaconda window, enter "stable-diffusion", and type:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
(ldm) ~/stable-diffusion$ git pull
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will bring your local copy into sync with the remote one.
|
||||
|
||||
## Windows
|
||||
|
||||
### Notebook install (semi-automated)
|
||||
|
||||
We have a
|
||||
[Jupyter notebook](https://github.com/lstein/stable-diffusion/blob/main/Stable-Diffusion-local-Windows.ipynb)
|
||||
with cell-by-cell installation steps. It will download the code in this repo as
|
||||
one of the steps, so instead of cloning this repo, simply download the notebook
|
||||
from the link above and load it up in VSCode (with the
|
||||
appropriate extensions installed)/Jupyter/JupyterLab and start running the cells one-by-one.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that you will need NVIDIA drivers, Python 3.10, and Git installed
|
||||
beforehand - simplified
|
||||
[step-by-step instructions](https://github.com/lstein/stable-diffusion/wiki/Easy-peasy-Windows-install)
|
||||
are available in the wiki (you'll only need steps 1, 2, & 3 ).
|
||||
|
||||
### Manual installs
|
||||
|
||||
#### pip
|
||||
|
||||
See
|
||||
[Easy-peasy Windows install](https://github.com/lstein/stable-diffusion/wiki/Easy-peasy-Windows-install)
|
||||
in the wiki
|
||||
|
||||
#### Conda
|
||||
|
||||
1. Install Anaconda3 (miniconda3 version) from here: https://docs.anaconda.com/anaconda/install/windows/
|
||||
|
||||
2. Install Git from here: https://git-scm.com/download/win
|
||||
|
||||
3. Launch Anaconda from the Windows Start menu. This will bring up a command window. Type all the remaining commands in this window.
|
||||
|
||||
4. Run the command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/lstein/stable-diffusion.git
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will create stable-diffusion folder where you will follow the rest of the steps.
|
||||
|
||||
5. Enter the newly-created stable-diffusion folder. From this step forward make sure that you are working in the stable-diffusion directory!
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
cd stable-diffusion
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
6. Run the following two commands:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
conda env create -f environment.yaml (step 6a)
|
||||
conda activate ldm (step 6b)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will install all python requirements and activate the "ldm" environment which sets PATH and other environment variables properly.
|
||||
|
||||
7. Run the command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
python scripts\preload_models.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This installs several machine learning models that stable diffusion
|
||||
requires. (Note that this step is required. I created it because some people
|
||||
are using GPU systems that are behind a firewall and the models can't be
|
||||
downloaded just-in-time)
|
||||
|
||||
8. Now you need to install the weights for the big stable diffusion model.
|
||||
|
||||
For running with the released weights, you will first need to set up
|
||||
an acount with Hugging Face (https://huggingface.co). Use your
|
||||
credentials to log in, and then point your browser at
|
||||
https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion-v-1-4-original. You
|
||||
may be asked to sign a license agreement at this point.
|
||||
|
||||
Click on "Files and versions" near the top of the page, and then click
|
||||
on the file named "sd-v1-4.ckpt". You'll be taken to a page that
|
||||
prompts you to click the "download" link. Now save the file somewhere
|
||||
safe on your local machine. The weight file is >4 GB in size, so
|
||||
downloading may take a while.
|
||||
|
||||
Now run the following commands from **within the stable-diffusion
|
||||
directory** to copy the weights file to the right place:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
mkdir -p models\ldm\stable-diffusion-v1
|
||||
copy C:\path\to\sd-v1-4.ckpt models\ldm\stable-diffusion-v1\model.ckpt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Please replace "C:\path\to\sd-v1.4.ckpt" with the correct path to wherever
|
||||
you stashed this file. If you prefer not to copy or move the .ckpt file,
|
||||
you may instead create a shortcut to it from within
|
||||
"models\ldm\stable-diffusion-v1\".
|
||||
|
||||
9. Start generating images!
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# for the pre-release weights
|
||||
python scripts\dream.py -l
|
||||
|
||||
# for the post-release weights
|
||||
python scripts\dream.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
10. Subsequently, to relaunch the script, first activate the Anaconda
|
||||
command window (step 3), enter the stable-diffusion directory (step 5,
|
||||
"cd \path\to\stable-diffusion"), run "conda activate ldm" (step 6b),
|
||||
and then launch the dream script (step 9).
|
||||
|
||||
**Note:** Tildebyte has written an alternative ["Easy peasy Windows
|
||||
install"](https://github.com/lstein/stable-diffusion/wiki/Easy-peasy-Windows-install)
|
||||
which uses the Windows Powershell and pew. If you are having trouble
|
||||
with Anaconda on Windows, give this a try (or try it first!)
|
||||
|
||||
### Updating to newer versions of the script
|
||||
|
||||
This distribution is changing rapidly. If you used the "git clone"
|
||||
method (step 5) to download the stable-diffusion directory, then to
|
||||
update to the latest and greatest version, launch the Anaconda window,
|
||||
enter "stable-diffusion", and type:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
git pull
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will bring your local copy into sync with the remote one.
|
||||
|
||||
## Macintosh
|
||||
|
||||
See [README-Mac-MPS](README-Mac-MPS.md) for instructions.
|
||||
|
||||
# Simplified API for text to image generation
|
||||
|
||||
For programmers who wish to incorporate stable-diffusion into other
|
||||
products, this repository includes a simplified API for text to image
|
||||
generation, which lets you create images from a prompt in just three
|
||||
lines of code:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
from ldm.simplet2i import T2I
|
||||
model = T2I()
|
||||
outputs = model.txt2img("a unicorn in manhattan")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Outputs is a list of lists in the format [[filename1,seed1],[filename2,seed2]...]
|
||||
Please see ldm/simplet2i.py for more information. A set of example scripts is
|
||||
coming RSN.
|
||||
|
||||
# Workaround for machines with limited internet connectivity
|
||||
|
||||
My development machine is a GPU node in a high-performance compute
|
||||
cluster which has no connection to the internet. During model
|
||||
initialization, stable-diffusion tries to download the Bert tokenizer
|
||||
and a file needed by the kornia library. This obviously didn't work
|
||||
for me.
|
||||
|
||||
To work around this, I have modified ldm/modules/encoders/modules.py
|
||||
to look for locally cached Bert files rather than attempting to
|
||||
download them. For this to work, you must run
|
||||
"scripts/preload_models.py" once from an internet-connected machine
|
||||
prior to running the code on an isolated one. This assumes that both
|
||||
machines share a common network-mounted filesystem with a common
|
||||
.cache directory.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
(ldm) ~/stable-diffusion$ python3 ./scripts/preload_models.py
|
||||
preloading bert tokenizer...
|
||||
Downloading: 100%|██████████████████████████████████| 28.0/28.0 [00:00<00:00, 49.3kB/s]
|
||||
Downloading: 100%|██████████████████████████████████| 226k/226k [00:00<00:00, 2.79MB/s]
|
||||
Downloading: 100%|██████████████████████████████████| 455k/455k [00:00<00:00, 4.36MB/s]
|
||||
Downloading: 100%|██████████████████████████████████| 570/570 [00:00<00:00, 477kB/s]
|
||||
...success
|
||||
preloading kornia requirements...
|
||||
Downloading: "https://github.com/DagnyT/hardnet/raw/master/pretrained/train_liberty_with_aug/checkpoint_liberty_with_aug.pth" to /u/lstein/.cache/torch/hub/checkpoints/checkpoint_liberty_with_aug.pth
|
||||
100%|███████████████████████████████████████████████| 5.10M/5.10M [00:00<00:00, 101MB/s]
|
||||
...success
|
||||
```
|
||||
For older changelogs, please visit **[CHANGELOGS](docs/CHANGELOG.md)**.
|
||||
|
||||
# Troubleshooting
|
||||
|
||||
Here are a few common installation problems and their solutions. Often
|
||||
these are caused by incomplete installations or crashes during the
|
||||
install process.
|
||||
|
||||
- PROBLEM: During "conda env create -f environment.yaml", conda
|
||||
hangs indefinitely.
|
||||
|
||||
- SOLUTION: Enter the stable-diffusion directory and completely
|
||||
remove the "src" directory and all its contents. The safest way
|
||||
to do this is to enter the stable-diffusion directory and
|
||||
give the command "git clean -f". If this still doesn't fix
|
||||
the problem, try "conda clean -all" and then restart at the
|
||||
"conda env create" step.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
- PROBLEM: dream.py crashes with the complaint that it can't find
|
||||
ldm.simplet2i.py. Or it complains that function is being passed
|
||||
incorrect parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
- SOLUTION: Reinstall the stable diffusion modules. Enter the
|
||||
stable-diffusion directory and give the command "pip install -e ."
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
- PROBLEM: dream.py dies, complaining of various missing modules, none
|
||||
of which starts with "ldm".
|
||||
|
||||
- SOLUTION: From within the stable-diffusion directory, run "conda env
|
||||
update -f environment.yaml" This is also frequently the solution to
|
||||
complaints about an unknown function in a module.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
- PROBLEM: There's a feature or bugfix in the Stable Diffusion GitHub
|
||||
that you want to try out.
|
||||
|
||||
- SOLUTION: If the fix/feature is on the "main" branch, enter the stable-diffusion
|
||||
directory and do a "git pull". Usually this will be sufficient, but if
|
||||
you start to see errors about missing or incorrect modules, use the
|
||||
command "pip install -e ." and/or "conda env update -f environment.yaml"
|
||||
(These commands won't break anything.)
|
||||
|
||||
- If the feature/fix is on a branch (e.g. "foo-bugfix"), the recipe is similar, but
|
||||
do a "git pull <name of branch>".
|
||||
|
||||
- If the feature/fix is in a pull request that has not yet been made
|
||||
part of the main branch or a feature/bugfix branch, then from the page
|
||||
for the desired pull request, look for the line at the top that reads
|
||||
"xxxx wants to merge xx commits into lstein:main from YYYYYY". Copy
|
||||
the URL in YYYY. It should have the format
|
||||
https://github.com/<name of contributor>/stable-diffusion/tree/<name
|
||||
of branch>
|
||||
|
||||
- Then **go to the directory above stable-diffusion**, and rename the
|
||||
directory to "stable-diffusion.lstein", "stable-diffusion.old", or
|
||||
whatever. You can then git clone the branch that contains the
|
||||
pull request:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/<name of contributor>/stable-diffusion/tree/<name
|
||||
of branch>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You will need to go through the install procedure again, but it should
|
||||
be fast because all the dependencies are already loaded.
|
||||
Please check out our **[Q&A](docs/help/TROUBLESHOOT.md)** to get solutions for common installation problems and other issues.
|
||||
|
||||
# Contributing
|
||||
|
||||
Anyone who wishes to contribute to this project, whether
|
||||
documentation, features, bug fixes, code cleanup, testing, or code
|
||||
reviews, is very much encouraged to do so. If you are unfamiliar with
|
||||
how to contribute to GitHub projects, here is a [Getting Started
|
||||
Guide](https://opensource.com/article/19/7/create-pull-request-github).
|
||||
Anyone who wishes to contribute to this project, whether documentation, features, bug fixes, code cleanup, testing, or code reviews, is very much encouraged to do so. If you are unfamiliar with
|
||||
how to contribute to GitHub projects, here is a [Getting Started Guide](https://opensource.com/article/19/7/create-pull-request-github).
|
||||
|
||||
A full set of contribution guidelines, along with templates, are in
|
||||
progress, but for now the most important thing is to **make your pull
|
||||
request against the "development" branch**, and not against
|
||||
"main". This will help keep public breakage to a minimum and will
|
||||
allow you to propose more radical changes.
|
||||
A full set of contribution guidelines, along with templates, are in progress, but for now the most important thing is to **make your pull request against the "development" branch**, and not against "main". This will help keep public breakage to a minimum and will allow you to propose more radical changes.
|
||||
|
||||
## **Contributors**
|
||||
|
||||
This fork is a combined effort of various people from across the world. [Check out the list of all these amazing people](docs/CONTRIBUTORS.md). We thank them for their time, hard work and effort.
|
||||
|
||||
# Support
|
||||
|
||||
@ -783,22 +157,9 @@ For support,
|
||||
please use this repository's GitHub Issues tracking service. Feel free
|
||||
to send me an email if you use and like the script.
|
||||
|
||||
_Original Author:_ Lincoln D. Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
|
||||
|
||||
_Contributions by:_
|
||||
[Peter Kowalczyk](https://github.com/slix), [Henry Harrison](https://github.com/hwharrison),
|
||||
[xraxra](https://github.com/xraxra), [bmaltais](https://github.com/bmaltais), [Sean McLellan](https://github.com/Oceanswave),
|
||||
[nicolai256](https://github.com/nicolai256), [Benjamin Warner](https://github.com/warner-benjamin),
|
||||
[tildebyte](https://github.com/tildebyte),[yunsaki](https://github.com/yunsaki), [James Reynolds][https://github.com/magnusviri],
|
||||
[Tesseract Cat](https://github.com/TesseractCat), and many more!
|
||||
|
||||
(If you have contributed and don't see your name on the list of
|
||||
contributors, please let lstein know about the omission, or make a
|
||||
pull request)
|
||||
|
||||
Original portions of the software are Copyright (c) 2020 Lincoln D. Stein (https://github.com/lstein)
|
||||
|
||||
# Further Reading
|
||||
|
||||
Please see the original README for more information on this software
|
||||
and underlying algorithm, located in the file [README-CompViz.md](README-CompViz.md).
|
||||
and underlying algorithm, located in the file [README-CompViz.md](docs/README-CompViz.md).
|
||||
|
||||
@ -105,5 +105,6 @@ lightning:
|
||||
|
||||
trainer:
|
||||
benchmark: True
|
||||
max_steps: 4000
|
||||
max_steps: 4000000
|
||||
# max_steps: 4000
|
||||
|
||||
@ -134,4 +134,4 @@
|
||||
|
||||
## Links
|
||||
|
||||
- **[Read Me](readme.md)**
|
||||
- **[Read Me](../readme.md)**
|
||||
61
docs/CONTRIBUTORS.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
|
||||
# Contributors
|
||||
|
||||
The list of all the amazing people who have contributed to the various features that you get to experience in this fork.
|
||||
|
||||
We thank them for all of their time and hard work.
|
||||
|
||||
_Original Author:_
|
||||
|
||||
- Lincoln D. Stein <lincoln.stein@gmail.com>
|
||||
|
||||
_Contributions by:_
|
||||
|
||||
- [Sean McLellan](https://github.com/Oceanswave)
|
||||
- [Kevin Gibbons](https://github.com/bakkot)
|
||||
- [Tesseract Cat](https://github.com/TesseractCat)
|
||||
- [blessedcoolant](https://github.com/blessedcoolant)
|
||||
- [David Ford](https://github.com/david-ford)
|
||||
- [yunsaki](https://github.com/yunsaki)
|
||||
- [James Reynolds](https://github.com/magnusviri)
|
||||
- [David Wager](https://github.com/maddavid123)
|
||||
- [Jason Toffaletti](https://github.com/toffaletti)
|
||||
- [tildebyte](https://github.com/tildebyte)
|
||||
- [Cragin Godley](https://github.com/cgodley)
|
||||
- [BlueAmulet](https://github.com/BlueAmulet)
|
||||
- [Benjamin Warner](https://github.com/warner-benjamin)
|
||||
- [Cora Johnson-Roberson](https://github.com/corajr)
|
||||
- [veprogames](https://github.com/veprogames)
|
||||
- [JigenD](https://github.com/JigenD)
|
||||
- [Niek van der Maas](https://github.com/Niek)
|
||||
- [Henry van Megen](https://github.com/hvanmegen)
|
||||
- [Håvard Gulldahl](https://github.com/havardgulldahl)
|
||||
- [greentext2](https://github.com/greentext2)
|
||||
- [Simon Vans-Colina](https://github.com/simonvc)
|
||||
- [Gabriel Rotbart](https://github.com/gabrielrotbart)
|
||||
- [Eric Khun](https://github.com/erickhun)
|
||||
- [Brent Ozar](https://github.com/BrentOzar)
|
||||
- [nderscore](https://github.com/nderscore)
|
||||
- [Mikhail Tishin](https://github.com/tishin)
|
||||
- [Tom Elovi Spruce](https://github.com/ilovecomputers)
|
||||
- [spezialspezial](https://github.com/spezialspezial)
|
||||
- [Yosuke Shinya](https://github.com/shinya7y)
|
||||
- [Andy Pilate](https://github.com/Cubox)
|
||||
- [Muhammad Usama](https://github.com/SMUsamaShah)
|
||||
- [Arturo Mendivil](https://github.com/artmen1516)
|
||||
- [Paul Sajna](https://github.com/sajattack)
|
||||
- [Samuel Husso](https://github.com/shusso)
|
||||
- [nicolai256](https://github.com/nicolai256)
|
||||
|
||||
_Original CompVis Authors:_
|
||||
|
||||
- [Robin Rombach](https://github.com/rromb)
|
||||
- [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten)
|
||||
- [ablattmann](https://github.com/ablattmann)
|
||||
- [Patrick Esser](https://github.com/pesser)
|
||||
- [owenvincent](https://github.com/owenvincent)
|
||||
- [apolinario](https://github.com/apolinario)
|
||||
- [Charles Packer](https://github.com/cpacker)
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
_If you have contributed and don't see your name on the list of contributors, please let one of the collaborators know about the omission, or feel free to make a pull request._
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,6 @@
|
||||
# Original README from CompViz/stable-diffusion
|
||||
*Stable Diffusion was made possible thanks to a collaboration with [Stability AI](https://stability.ai/) and [Runway](https://runwayml.com/) and builds upon our previous work:*
|
||||
|
||||
_Stable Diffusion was made possible thanks to a collaboration with [Stability AI](https://stability.ai/) and [Runway](https://runwayml.com/) and builds upon our previous work:_
|
||||
|
||||
[**High-Resolution Image Synthesis with Latent Diffusion Models**](https://ommer-lab.com/research/latent-diffusion-models/)<br/>
|
||||
[Robin Rombach](https://github.com/rromb)\*,
|
||||
@ -12,7 +13,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
which is available on [GitHub](https://github.com/CompVis/latent-diffusion). PDF at [arXiv](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.10752). Please also visit our [Project page](https://ommer-lab.com/research/latent-diffusion-models/).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
[Stable Diffusion](#stable-diffusion-v1) is a latent text-to-image diffusion
|
||||
model.
|
||||
Thanks to a generous compute donation from [Stability AI](https://stability.ai/) and support from [LAION](https://laion.ai/), we were able to train a Latent Diffusion Model on 512x512 images from a subset of the [LAION-5B](https://laion.ai/blog/laion-5b/) database.
|
||||
@ -21,7 +22,6 @@ this model uses a frozen CLIP ViT-L/14 text encoder to condition the model on te
|
||||
With its 860M UNet and 123M text encoder, the model is relatively lightweight and runs on a GPU with at least 10GB VRAM.
|
||||
See [this section](#stable-diffusion-v1) below and the [model card](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Requirements
|
||||
|
||||
A suitable [conda](https://conda.io/) environment named `ldm` can be created
|
||||
@ -47,11 +47,11 @@ architecture that uses a downsampling-factor 8 autoencoder with an 860M UNet
|
||||
and CLIP ViT-L/14 text encoder for the diffusion model. The model was pretrained on 256x256 images and
|
||||
then finetuned on 512x512 images.
|
||||
|
||||
*Note: Stable Diffusion v1 is a general text-to-image diffusion model and therefore mirrors biases and (mis-)conceptions that are present
|
||||
\*Note: Stable Diffusion v1 is a general text-to-image diffusion model and therefore mirrors biases and (mis-)conceptions that are present
|
||||
in its training data.
|
||||
Details on the training procedure and data, as well as the intended use of the model can be found in the corresponding [model card](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion).
|
||||
Research into the safe deployment of general text-to-image models is an ongoing effort. To prevent misuse and harm, we currently provide access to the checkpoints only for [academic research purposes upon request](https://stability.ai/academia-access-form).
|
||||
**This is an experiment in safe and community-driven publication of a capable and general text-to-image model. We are working on a public release with a more permissive license that also incorporates ethical considerations.***
|
||||
**This is an experiment in safe and community-driven publication of a capable and general text-to-image model. We are working on a public release with a more permissive license that also incorporates ethical considerations.\***
|
||||
|
||||
[Request access to Stable Diffusion v1 checkpoints for academic research](https://stability.ai/academia-access-form)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -70,25 +70,26 @@ filtered to images with an original size `>= 512x512`, estimated aesthetics scor
|
||||
Evaluations with different classifier-free guidance scales (1.5, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0,
|
||||
5.0, 6.0, 7.0, 8.0) and 50 PLMS sampling
|
||||
steps show the relative improvements of the checkpoints:
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Text-to-Image with Stable Diffusion
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Stable Diffusion is a latent diffusion model conditioned on the (non-pooled) text embeddings of a CLIP ViT-L/14 text encoder.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Sampling Script
|
||||
|
||||
After [obtaining the weights](#weights), link them
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
mkdir -p models/ldm/stable-diffusion-v1/
|
||||
ln -s <path/to/model.ckpt> models/ldm/stable-diffusion-v1/model.ckpt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
and sample with
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
python scripts/txt2img.py --prompt "a photograph of an astronaut riding a horse" --plms
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -131,15 +132,16 @@ optional arguments:
|
||||
evaluate at this precision
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note: The inference config for all v1 versions is designed to be used with EMA-only checkpoints.
|
||||
For this reason `use_ema=False` is set in the configuration, otherwise the code will try to switch from
|
||||
non-EMA to EMA weights. If you want to examine the effect of EMA vs no EMA, we provide "full" checkpoints
|
||||
which contain both types of weights. For these, `use_ema=False` will load and use the non-EMA weights.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Diffusers Integration
|
||||
|
||||
Another way to download and sample Stable Diffusion is by using the [diffusers library](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main#new--stable-diffusion-is-now-fully-compatible-with-diffusers)
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
# make sure you're logged in with `huggingface-cli login`
|
||||
from torch import autocast
|
||||
@ -157,8 +159,6 @@ with autocast("cuda"):
|
||||
image.save("astronaut_rides_horse.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Image Modification with Stable Diffusion
|
||||
|
||||
By using a diffusion-denoising mechanism as first proposed by [SDEdit](https://arxiv.org/abs/2108.01073), the model can be used for different
|
||||
@ -166,24 +166,25 @@ tasks such as text-guided image-to-image translation and upscaling. Similar to t
|
||||
we provide a script to perform image modification with Stable Diffusion.
|
||||
|
||||
The following describes an example where a rough sketch made in [Pinta](https://www.pinta-project.com/) is converted into a detailed artwork.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
python scripts/img2img.py --prompt "A fantasy landscape, trending on artstation" --init-img <path-to-img.jpg> --strength 0.8
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here, strength is a value between 0.0 and 1.0, that controls the amount of noise that is added to the input image.
|
||||
Values that approach 1.0 allow for lots of variations but will also produce images that are not semantically consistent with the input. See the following example.
|
||||
|
||||
**Input**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Outputs**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
This procedure can, for example, also be used to upscale samples from the base model.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Comments
|
||||
|
||||
- Our codebase for the diffusion models builds heavily on [OpenAI's ADM codebase](https://github.com/openai/guided-diffusion)
|
||||
@ -192,7 +193,6 @@ Thanks for open-sourcing!
|
||||
|
||||
- The implementation of the transformer encoder is from [x-transformers](https://github.com/lucidrains/x-transformers) by [lucidrains](https://github.com/lucidrains?tab=repositories).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## BibTeX
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -206,5 +206,3 @@ Thanks for open-sourcing!
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
Before 
(image error) Size: 799 KiB After 
(image error) Size: 799 KiB 

|
|
Before 
(image error) Size: 499 KiB After 
(image error) Size: 499 KiB 

|
|
Before 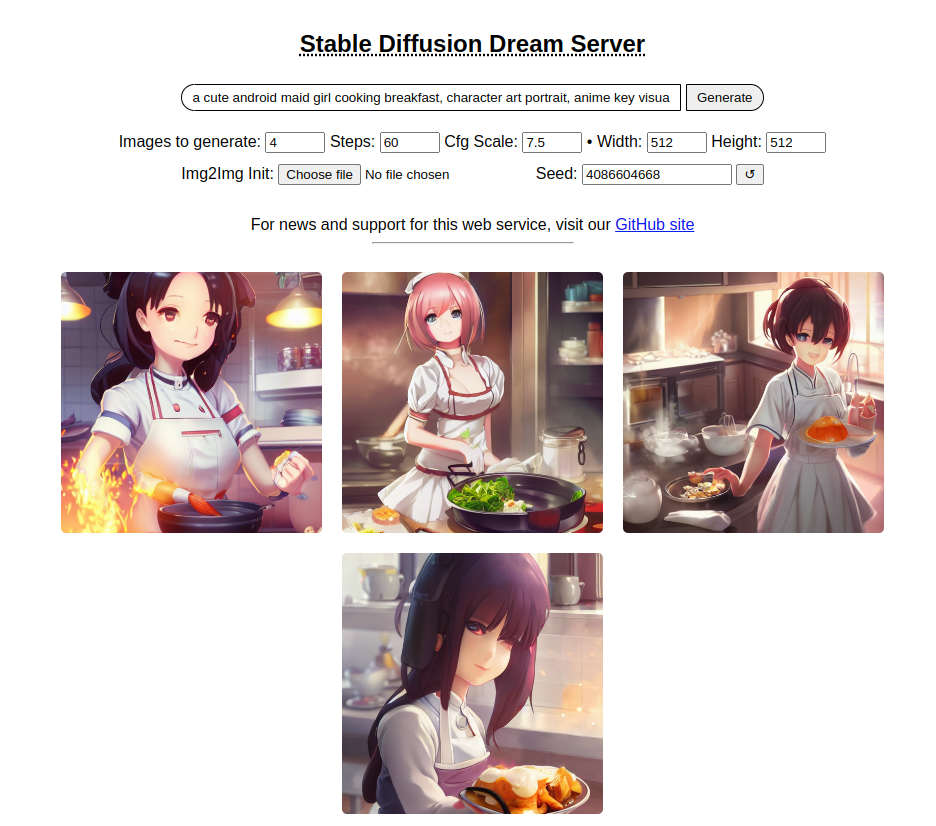
(image error) Size: 536 KiB After 
(image error) Size: 536 KiB 

|
BIN
docs/assets/logo.png
Normal file
|
After 
(image error) Size: 22 KiB |
|
Before 
(image error) Size: 429 KiB After 
(image error) Size: 429 KiB 

|
|
Before 
(image error) Size: 445 KiB After 
(image error) Size: 445 KiB 

|
|
Before 
(image error) Size: 426 KiB After 
(image error) Size: 426 KiB 

|
|
Before 
(image error) Size: 427 KiB After 
(image error) Size: 427 KiB 

|
|
Before 
(image error) Size: 424 KiB After 
(image error) Size: 424 KiB 

|
228
docs/features/CLI.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,228 @@
|
||||
# **Interactive Command-Line Interface**
|
||||
|
||||
The `dream.py` script, located in `scripts/dream.py`, provides an interactive interface to image generation similar to the "dream mothership" bot that Stable AI provided on its Discord server.
|
||||
|
||||
Unlike the txt2img.py and img2img.py scripts provided in the original CompViz/stable-diffusion source code repository, the time-consuming initialization of the AI model initialization only happens once. After that image generation
|
||||
from the command-line interface is very fast.
|
||||
|
||||
The script uses the readline library to allow for in-line editing, command history (up and down arrows), autocompletion, and more. To help keep track of which prompts generated which images, the script writes a log file of image names and prompts to the selected output directory.
|
||||
|
||||
In addition, as of version 1.02, it also writes the prompt into the PNG file's metadata where it can be retrieved using scripts/images2prompt.py
|
||||
|
||||
The script is confirmed to work on Linux, Windows and Mac systems.
|
||||
|
||||
_Note:_ This script runs from the command-line or can be used as a Web application. The Web GUI is currently rudimentary, but a much better replacement is on its way.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
(ldm) ~/stable-diffusion$ python3 ./scripts/dream.py
|
||||
* Initializing, be patient...
|
||||
Loading model from models/ldm/text2img-large/model.ckpt
|
||||
(...more initialization messages...)
|
||||
|
||||
* Initialization done! Awaiting your command...
|
||||
dream> ashley judd riding a camel -n2 -s150
|
||||
Outputs:
|
||||
outputs/img-samples/00009.png: "ashley judd riding a camel" -n2 -s150 -S 416354203
|
||||
outputs/img-samples/00010.png: "ashley judd riding a camel" -n2 -s150 -S 1362479620
|
||||
|
||||
dream> "there's a fly in my soup" -n6 -g
|
||||
outputs/img-samples/00011.png: "there's a fly in my soup" -n6 -g -S 2685670268
|
||||
seeds for individual rows: [2685670268, 1216708065, 2335773498, 822223658, 714542046, 3395302430]
|
||||
dream> q
|
||||
|
||||
# this shows how to retrieve the prompt stored in the saved image's metadata
|
||||
(ldm) ~/stable-diffusion$ python ./scripts/images2prompt.py outputs/img_samples/*.png
|
||||
00009.png: "ashley judd riding a camel" -s150 -S 416354203
|
||||
00010.png: "ashley judd riding a camel" -s150 -S 1362479620
|
||||
00011.png: "there's a fly in my soup" -n6 -g -S 2685670268
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<p align='center'>
|
||||
<img src="../assets/dream-py-demo.png"/>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
The `dream>` prompt's arguments are pretty much identical to those
|
||||
used in the Discord bot, except you don't need to type "!dream" (it
|
||||
doesn't hurt if you do). A significant change is that creation of
|
||||
individual images is now the default unless --grid (-g) is given. A
|
||||
full list is given in [List of prompt arguments]
|
||||
(#list-of-prompt-arguments).
|
||||
|
||||
# Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
The script itself also recognizes a series of command-line switches
|
||||
that will change important global defaults, such as the directory for
|
||||
image outputs and the location of the model weight files.
|
||||
|
||||
## List of arguments recognized at the command line:
|
||||
|
||||
These command-line arguments can be passed to dream.py when you first
|
||||
run it from the Windows, Mac or Linux command line. Some set defaults
|
||||
that can be overridden on a per-prompt basis (see [List of prompt
|
||||
arguments] (#list-of-prompt-arguments). Others
|
||||
|
||||
| Argument | Shortcut | Default | Description |
|
||||
|--------------------|------------|---------------------|--------------|
|
||||
| --help | -h | | Print a concise help message. |
|
||||
| --outdir <path> | -o<path> | outputs/img_samples | Location for generated images. |
|
||||
| --prompt_as_dir | -p | False | Name output directories using the prompt text. |
|
||||
| --from_file <path> | | None | Read list of prompts from a file. Use "-" to read from standard input |
|
||||
| --model <modelname>| | stable-diffusion-1.4| Loads model specified in configs/models.yaml. Currently one of "stable-diffusion-1.4" or "laion400m"|
|
||||
| --full_precision | -F | False | Run in slower full-precision mode. Needed for Macintosh M1/M2 hardware and some older video cards. |
|
||||
| --web | | False | Start in web server mode |
|
||||
| --host <ip addr> | | localhost | Which network interface web server should listen on. Set to 0.0.0.0 to listen on any. |
|
||||
| --port <port> | | 9090 | Which port web server should listen for requests on. |
|
||||
| --config <path> | | configs/models.yaml | Configuration file for models and their weights. |
|
||||
| --iterations <int> | -n<int> | 1 | How many images to generate per prompt. |
|
||||
| --grid | -g | False | Save all image series as a grid rather than individually. |
|
||||
| --sampler <sampler>| -A<sampler>| k_lms | Sampler to use. Use -h to get list of available samplers. |
|
||||
| --seamless | | False | Create interesting effects by tiling elements of the image. |
|
||||
| --embedding_path <path>| | None | Path to pre-trained embedding manager checkpoints, for custom models |
|
||||
| --gfpgan_dir | | src/gfpgan | Path to where GFPGAN is installed. |
|
||||
| --gfpgan_model_path| | experiments/pretrained_models/GFPGANv1.3.pth| Path to GFPGAN model file, relative to --gfpgan_dir. |
|
||||
| --device <device> | -d<device>| torch.cuda.current_device() | Device to run SD on, e.g. "cuda:0" |
|
||||
|
||||
These arguments are deprecated but still work:
|
||||
|
||||
| Argument | Shortcut | Default | Description |
|
||||
|--------------------|------------|---------------------|--------------|
|
||||
| --weights <path> | | None | Pth to weights file; use `--model stable-diffusion-1.4` instead |
|
||||
| --laion400m | -l | False | Use older LAION400m weights; use `--model=laion400m` instead |
|
||||
|
||||
**A note on path names:** On Windows systems, you may run into
|
||||
problems when passing the dream script standard backslashed path
|
||||
names because the Python interpreter treats "\" as an escape.
|
||||
You can either double your slashes (ick): C:\\\\path\\\\to\\\\my\\\\file, or
|
||||
use Linux/Mac style forward slashes (better): C:/path/to/my/file.
|
||||
|
||||
## List of prompt arguments
|
||||
|
||||
After the dream.py script initializes, it will present you with a
|
||||
**dream>** prompt. Here you can enter information to generate images
|
||||
from text (txt2img), to embellish an existing image or sketch
|
||||
(img2img), or to selectively alter chosen regions of the image
|
||||
(inpainting).
|
||||
|
||||
### This is an example of txt2img:
|
||||
|
||||
~~~~
|
||||
dream> waterfall and rainbow -W640 -H480
|
||||
~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
This will create the requested image with the dimensions 640 (width)
|
||||
and 480 (height).
|
||||
|
||||
Here are the dream> command that apply to txt2img:
|
||||
|
||||
| Argument | Shortcut | Default | Description |
|
||||
|--------------------|------------|---------------------|--------------|
|
||||
| "my prompt" | | | Text prompt to use. The quotation marks are optional. |
|
||||
| --width <int> | -W<int> | 512 | Width of generated image |
|
||||
| --height <int> | -H<int> | 512 | Height of generated image |
|
||||
| --iterations <int> | -n<int> | 1 | How many images to generate from this prompt |
|
||||
| --steps <int> | -s<int> | 50 | How many steps of refinement to apply |
|
||||
| --cfg_scale <float>| -C<float> | 7.5 | How hard to try to match the prompt to the generated image; any number greater than 0.0 works, but the useful range is roughly 5.0 to 20.0 |
|
||||
| --seed <int> | -S<int> | None | Set the random seed for the next series of images. This can be used to recreate an image generated previously.|
|
||||
| --sampler <sampler>| -A<sampler>| k_lms | Sampler to use. Use -h to get list of available samplers. |
|
||||
| --grid | -g | False | Turn on grid mode to return a single image combining all the images generated by this prompt |
|
||||
| --individual | -i | True | Turn off grid mode (deprecated; leave off --grid instead) |
|
||||
| --outdir <path> | -o<path> | outputs/img_samples | Temporarily change the location of these images |
|
||||
| --seamless | | False | Activate seamless tiling for interesting effects |
|
||||
| --log_tokenization | -t | False | Display a color-coded list of the parsed tokens derived from the prompt |
|
||||
| --skip_normalization| -x | False | Weighted subprompts will not be normalized. See [Weighted Prompts](./OTHER.md#weighted-prompts) |
|
||||
| --upscale <int> <float> | -U <int> <float> | -U 1 0.75| Upscale image by magnification factor (2, 4), and set strength of upscaling (0.0-1.0). If strength not set, will default to 0.75. |
|
||||
| --gfpgan_strength <float> | -G <float> | -G0 | Fix faces using the GFPGAN algorithm; argument indicates how hard the algorithm should try (0.0-1.0) |
|
||||
| --save_original | -save_orig| False | When upscaling or fixing faces, this will cause the original image to be saved rather than replaced. |
|
||||
| --variation <float> |-v<float>| 0.0 | Add a bit of noise (0.0=none, 1.0=high) to the image in order to generate a series of variations. Usually used in combination with -S<seed> and -n<int> to generate a series a riffs on a starting image. See [Variations](./VARIATIONS.md). |
|
||||
| --with_variations <pattern> | -V<pattern>| None | Combine two or more variations. See [Variations](./VARIATIONS.md) for now to use this. |
|
||||
|
||||
Note that the width and height of the image must be multiples of
|
||||
64. You can provide different values, but they will be rounded down to
|
||||
the nearest multiple of 64.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### This is an example of img2img:
|
||||
|
||||
~~~~
|
||||
dream> waterfall and rainbow -I./vacation-photo.png -W640 -H480 --fit
|
||||
~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
This will modify the indicated vacation photograph by making it more
|
||||
like the prompt. Results will vary greatly depending on what is in the
|
||||
image. We also ask to --fit the image into a box no bigger than
|
||||
640x480. Otherwise the image size will be identical to the provided
|
||||
photo and you may run out of memory if it is large.
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to the command-line options recognized by txt2img, img2img
|
||||
accepts additional options:
|
||||
|
||||
| Argument | Shortcut | Default | Description |
|
||||
|--------------------|------------|---------------------|--------------|
|
||||
| --init_img <path> | -I<path> | None | Path to the initialization image |
|
||||
| --fit | -F | False | Scale the image to fit into the specified -H and -W dimensions |
|
||||
| --strength <float> | -s<float> | 0.75 | How hard to try to match the prompt to the initial image. Ranges from 0.0-0.99, with higher values replacing the initial image completely.|
|
||||
|
||||
### This is an example of inpainting:
|
||||
|
||||
~~~~
|
||||
dream> waterfall and rainbow -I./vacation-photo.png -M./vacation-mask.png -W640 -H480 --fit
|
||||
~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
This will do the same thing as img2img, but image alterations will
|
||||
only occur within transparent areas defined by the mask file specified
|
||||
by -M. You may also supply just a single initial image with the areas
|
||||
to overpaint made transparent, but you must be careful not to destroy
|
||||
the pixels underneath when you create the transparent areas. See
|
||||
[Inpainting](./INPAINTING.md) for details.
|
||||
|
||||
inpainting accepts all the arguments used for txt2img and img2img, as
|
||||
well as the --mask (-M) argument:
|
||||
|
||||
| Argument | Shortcut | Default | Description |
|
||||
|--------------------|------------|---------------------|--------------|
|
||||
| --init_mask <path> | -M<path> | None |Path to an image the same size as the initial_image, with areas for inpainting made transparent.|
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Command-line editing and completion
|
||||
|
||||
If you are on a Macintosh or Linux machine, the command-line offers
|
||||
convenient history tracking, editing, and command completion.
|
||||
|
||||
- To scroll through previous commands and potentially edit/reuse them, use the up and down cursor keys.
|
||||
- To edit the current command, use the left and right cursor keys to position the cursor, and then backspace, delete or insert characters.
|
||||
- To move to the very beginning of the command, type CTRL-A (or command-A on the Mac)
|
||||
- To move to the end of the command, type CTRL-E.
|
||||
- To cut a section of the command, position the cursor where you want to start cutting and type CTRL-K.
|
||||
- To paste a cut section back in, position the cursor where you want to paste, and type CTRL-Y
|
||||
|
||||
Windows users can get similar, but more limited, functionality if they
|
||||
launch dream.py with the "winpty" program:
|
||||
|
||||
~~~
|
||||
> winpty python scripts\dream.py
|
||||
~~~
|
||||
|
||||
On the Mac and Linux platforms, when you exit dream.py, the last 1000
|
||||
lines of your command-line history will be saved. When you restart
|
||||
dream.py, you can access the saved history using the up-arrow key.
|
||||
|
||||
In addition, limited command-line completion is installed. In various
|
||||
contexts, you can start typing your command and press tab. A list of
|
||||
potential completions will be presented to you. You can then type a
|
||||
little more, hit tab again, and eventually autocomplete what you want.
|
||||
|
||||
When specifying file paths using the one-letter shortcuts, the CLI
|
||||
will attempt to complete pathnames for you. This is most handy for the
|
||||
-I (init image) and -M (init mask) paths. To initiate completion, start
|
||||
the path with a slash ("/") or "./". For example:
|
||||
|
||||
~~~
|
||||
dream> zebra with a mustache -I./test-pictures<TAB>
|
||||
-I./test-pictures/Lincoln-and-Parrot.png -I./test-pictures/zebra.jpg -I./test-pictures/madonna.png
|
||||
-I./test-pictures/bad-sketch.png -I./test-pictures/man_with_eagle/
|
||||
~~~
|
||||
|
||||
You can then type "z", hit tab again, and it will autofill to "zebra.jpg".
|
||||
|
||||
More text completion features (such as autocompleting seeds) are on their way.
|
||||
|
||||
30
docs/features/IMG2IMG.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
|
||||
# **Image-to-Image**
|
||||
|
||||
This script also provides an img2img feature that lets you seed your
|
||||
creations with an initial drawing or photo. This is a really cool
|
||||
feature that tells stable diffusion to build the prompt on top of the
|
||||
image you provide, preserving the original's basic shape and
|
||||
layout. To use it, provide the `--init_img` option as shown here:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
dream> "waterfall and rainbow" --init_img=./init-images/crude_drawing.png --strength=0.5 -s100 -n4
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The `--init_img (-I)` option gives the path to the seed
|
||||
picture. `--strength (-f)` controls how much the original will be
|
||||
modified, ranging from `0.0` (keep the original intact), to `1.0`
|
||||
(ignore the original completely). The default is `0.75`, and ranges
|
||||
from `0.25-0.75` give interesting results.
|
||||
|
||||
You may also pass a `-v<count>` option to generate count variants on
|
||||
the original image. This is done by passing the first generated image
|
||||
back into img2img the requested number of times. It generates
|
||||
interesting variants.
|
||||
|
||||
If the initial image contains transparent regions, then Stable
|
||||
Diffusion will only draw within the transparent regions, a process
|
||||
called "inpainting". However, for this to work correctly, the color
|
||||
information underneath the transparent needs to be preserved, not
|
||||
erased. See [Creating Transparent Images For
|
||||
Inpainting](./INPAINTING.md#creating-transparent-regions-for-inpainting)
|
||||
for details.
|
||||
41
docs/features/INPAINTING.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
|
||||
# **Creating Transparent Regions for Inpainting**
|
||||
|
||||
Inpainting is really cool. To do it, you start with an initial image
|
||||
and use a photoeditor to make one or more regions transparent
|
||||
(i.e. they have a "hole" in them). You then provide the path to this
|
||||
image at the dream> command line using the `-I` switch. Stable
|
||||
Diffusion will only paint within the transparent region.
|
||||
|
||||
There's a catch. In the current implementation, you have to prepare
|
||||
the initial image correctly so that the underlying colors are
|
||||
preserved under the transparent area. Many imaging editing
|
||||
applications will by default erase the color information under the
|
||||
transparent pixels and replace them with white or black, which will
|
||||
lead to suboptimal inpainting. You also must take care to export the
|
||||
PNG file in such a way that the color information is preserved.
|
||||
|
||||
If your photoeditor is erasing the underlying color information,
|
||||
`dream.py` will give you a big fat warning. If you can't find a way to
|
||||
coax your photoeditor to retain color values under transparent areas,
|
||||
then you can combine the `-I` and `-M` switches to provide both the
|
||||
original unedited image and the masked (partially transparent) image:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
dream> man with cat on shoulder -I./images/man.png -M./images/man-transparent.png
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We are hoping to get rid of the need for this workaround in an upcoming release.
|
||||
|
||||
## Recipe for GIMP
|
||||
|
||||
[GIMP](https://www.gimp.org/) is a popular Linux photoediting tool.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Open image in GIMP.
|
||||
2. Layer->Transparency->Add Alpha Channel
|
||||
3. Use lasoo tool to select region to mask
|
||||
4. Choose Select -> Float to create a floating selection
|
||||
5. Open the Layers toolbar (^L) and select "Floating Selection"
|
||||
6. Set opacity to 0%
|
||||
7. Export as PNG
|
||||
8. In the export dialogue, Make sure the "Save colour values from
|
||||
transparent pixels" checkbox is selected.
|
||||
133
docs/features/OTHER.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,133 @@
|
||||
## **Google Colab**
|
||||
|
||||
Stable Diffusion AI Notebook: <a
|
||||
href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/lstein/stable-diffusion/blob/main/notebooks/Stable_Diffusion_AI_Notebook.ipynb"
|
||||
target="_parent"><img
|
||||
src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg"
|
||||
alt="Open In Colab"/></a> <br> Open and follow instructions to use an
|
||||
isolated environment running Dream.<br>
|
||||
|
||||
Output Example:
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## **Seamless Tiling**
|
||||
|
||||
The seamless tiling mode causes generated images to seamlessly tile
|
||||
with itself. To use it, add the `--seamless` option when starting the
|
||||
script which will result in all generated images to tile, or for each
|
||||
`dream>` prompt as shown here:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
dream> "pond garden with lotus by claude monet" --seamless -s100 -n4
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## **Reading Prompts from a File**
|
||||
|
||||
You can automate `dream.py` by providing a text file with the prompts
|
||||
you want to run, one line per prompt. The text file must be composed
|
||||
with a text editor (e.g. Notepad) and not a word processor. Each line
|
||||
should look like what you would type at the dream> prompt:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
a beautiful sunny day in the park, children playing -n4 -C10
|
||||
stormy weather on a mountain top, goats grazing -s100
|
||||
innovative packaging for a squid's dinner -S137038382
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then pass this file's name to `dream.py` when you invoke it:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
(ldm) ~/stable-diffusion$ python3 scripts/dream.py --from_file "path/to/prompts.txt"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You may read a series of prompts from standard input by providing a filename of `-`:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
(ldm) ~/stable-diffusion$ echo "a beautiful day" | python3 scripts/dream.py --from_file -
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## **Shortcuts: Reusing Seeds**
|
||||
|
||||
Since it is so common to reuse seeds while refining a prompt, there is now a shortcut as of version 1.11. Provide a `**-S**` (or `**--seed**`)
|
||||
switch of `-1` to use the seed of the most recent image generated. If you produced multiple images with the `**-n**` switch, then you can go back further using -2, -3, etc. up to the first image generated by the previous command. Sorry, but you can't go back further than one command.
|
||||
|
||||
Here's an example of using this to do a quick refinement. It also illustrates using the new `**-G**` switch to turn on upscaling and face enhancement (see previous section):
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
dream> a cute child playing hopscotch -G0.5
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
outputs/img-samples/000039.3498014304.png: "a cute child playing hopscotch" -s50 -W512 -H512 -C7.5 -mk_lms -S3498014304
|
||||
|
||||
# I wonder what it will look like if I bump up the steps and set facial enhancement to full strength?
|
||||
dream> a cute child playing hopscotch -G1.0 -s100 -S -1
|
||||
reusing previous seed 3498014304
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
outputs/img-samples/000040.3498014304.png: "a cute child playing hopscotch" -G1.0 -s100 -W512 -H512 -C7.5 -mk_lms -S3498014304
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## **Weighted Prompts**
|
||||
|
||||
You may weight different sections of the prompt to tell the sampler to attach different levels of
|
||||
priority to them, by adding `:(number)` to the end of the section you wish to up- or downweight.
|
||||
For example consider this prompt:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
tabby cat:0.25 white duck:0.75 hybrid
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will tell the sampler to invest 25% of its effort on the tabby
|
||||
cat aspect of the image and 75% on the white duck aspect
|
||||
(surprisingly, this example actually works). The prompt weights can
|
||||
use any combination of integers and floating point numbers, and they
|
||||
do not need to add up to 1.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## **Simplified API**
|
||||
|
||||
For programmers who wish to incorporate stable-diffusion into other products, this repository includes a simplified API for text to image generation, which lets you create images from a prompt in just three lines of code:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
from ldm.generate import Generate
|
||||
g = Generate()
|
||||
outputs = g.txt2img("a unicorn in manhattan")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Outputs is a list of lists in the format [filename1,seed1],[filename2,seed2]...].
|
||||
|
||||
Please see ldm/generate.py for more information. A set of example scripts is coming RSN.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## **Preload Models**
|
||||
|
||||
In situations where you have limited internet connectivity or are
|
||||
blocked behind a firewall, you can use the preload script to preload
|
||||
the required files for Stable Diffusion to run.
|
||||
|
||||
The preload script `scripts/preload_models.py` needs to be run once at
|
||||
least while connected to the internet. In the following runs, it will
|
||||
load up the cached versions of the required files from the `.cache`
|
||||
directory of the system.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
(ldm) ~/stable-diffusion$ python3 ./scripts/preload_models.py
|
||||
preloading bert tokenizer...
|
||||
Downloading: 100%|██████████████████████████████████| 28.0/28.0 [00:00<00:00, 49.3kB/s]
|
||||
Downloading: 100%|██████████████████████████████████| 226k/226k [00:00<00:00, 2.79MB/s]
|
||||
Downloading: 100%|██████████████████████████████████| 455k/455k [00:00<00:00, 4.36MB/s]
|
||||
Downloading: 100%|██████████████████████████████████| 570/570 [00:00<00:00, 477kB/s]
|
||||
...success
|
||||
preloading kornia requirements...
|
||||
Downloading: "https://github.com/DagnyT/hardnet/raw/master/pretrained/train_liberty_with_aug/checkpoint_liberty_with_aug.pth" to /u/lstein/.cache/torch/hub/checkpoints/checkpoint_liberty_with_aug.pth
|
||||
100%|███████████████████████████████████████████████| 5.10M/5.10M [00:00<00:00, 101MB/s]
|
||||
...success
|
||||
```
|
||||
70
docs/features/TEXTUAL_INVERSION.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
|
||||
# **Personalizing Text-to-Image Generation**
|
||||
|
||||
You may personalize the generated images to provide your own styles or objects by training a new LDM checkpoint and introducing a new vocabulary to the fixed model as a (.pt) embeddings file. Alternatively, you may use or train HuggingFace Concepts embeddings files (.bin) from https://huggingface.co/sd-concepts-library and its associated notebooks.
|
||||
|
||||
**Training**
|
||||
|
||||
To train, prepare a folder that contains images sized at 512x512 and execute the following:
|
||||
|
||||
**WINDOWS**: As the default backend is not available on Windows, if you're using that platform, set the environment variable `PL_TORCH_DISTRIBUTED_BACKEND=gloo`
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
(ldm) ~/stable-diffusion$ python3 ./main.py --base ./configs/stable-diffusion/v1-finetune.yaml \
|
||||
-t \
|
||||
--actual_resume ./models/ldm/stable-diffusion-v1/model.ckpt \
|
||||
-n my_cat \
|
||||
--gpus 0, \
|
||||
--data_root D:/textual-inversion/my_cat \
|
||||
--init_word 'cat'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
During the training process, files will be created in
|
||||
/logs/[project][time][project]/ where you can see the process.
|
||||
|
||||
Conditioning contains the training prompts inputs, reconstruction the
|
||||
input images for the training epoch samples, samples scaled for a
|
||||
sample of the prompt and one with the init word provided.
|
||||
|
||||
On a RTX3090, the process for SD will take ~1h @1.6 iterations/sec.
|
||||
|
||||
_Note_: According to the associated paper, the optimal number of
|
||||
images is 3-5. Your model may not converge if you use more images than
|
||||
that.
|
||||
|
||||
Training will run indefinitely, but you may wish to stop it (with
|
||||
ctrl-c) before the heat death of the universe, when you find a low
|
||||
loss epoch or around ~5000 iterations. Note that you can set a fixed
|
||||
limit on the number of training steps by decreasing the "max_steps"
|
||||
option in configs/stable_diffusion/v1-finetune.yaml (currently set to
|
||||
4000000)
|
||||
|
||||
**Running**
|
||||
|
||||
Once the model is trained, specify the trained .pt or .bin file when
|
||||
starting dream using
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
(ldm) ~/stable-diffusion$ python3 ./scripts/dream.py --embedding_path /path/to/embedding.pt --full_precision
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then, to utilize your subject at the dream prompt
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
dream> "a photo of *"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This also works with image2image
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
dream> "waterfall and rainbow in the style of *" --init_img=./init-images/crude_drawing.png --strength=0.5 -s100 -n4
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For .pt files it's also possible to train multiple tokens (modify the placeholder string in `configs/stable-diffusion/v1-finetune.yaml`) and combine LDM checkpoints using:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
(ldm) ~/stable-diffusion$ python3 ./scripts/merge_embeddings.py \
|
||||
--manager_ckpts /path/to/first/embedding.pt /path/to/second/embedding.pt [...] \
|
||||
--output_path /path/to/output/embedding.pt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Credit goes to rinongal and the repository located at https://github.com/rinongal/textual_inversion Please see the repository and associated paper for details and limitations.
|
||||
105
docs/features/UPSCALE.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,105 @@
|
||||
# **GFPGAN and Real-ESRGAN Support**
|
||||
|
||||
The script also provides the ability to do face restoration and
|
||||
upscaling with the help of GFPGAN and Real-ESRGAN respectively.
|
||||
|
||||
As of version 1.14, environment.yaml will install the Real-ESRGAN package into the
|
||||
standard install location for python packages, and will put GFPGAN into a subdirectory of "src"
|
||||
in the stable-diffusion directory.
|
||||
(The reason for this is that the standard GFPGAN distribution has a minor bug that adversely affects image
|
||||
color.) Upscaling with Real-ESRGAN should "just work" without further intervention. Simply pass the --upscale (-U)
|
||||
option on the dream> command line, or indicate the desired scale on the popup in the Web GUI.
|
||||
|
||||
For **GFPGAN** to work, there is one additional step needed. You will need to download and
|
||||
copy the GFPGAN [models file](https://github.com/TencentARC/GFPGAN/releases/download/v1.3.0/GFPGANv1.3.pth)
|
||||
into **src/gfpgan/experiments/pretrained_models**. On Mac and Linux systems, here's how you'd do it using
|
||||
**wget**:
|
||||
~~~~
|
||||
> wget https://github.com/TencentARC/GFPGAN/releases/download/v1.3.0/GFPGANv1.3.pth src/gfpgan/experiments/pretrained_models/
|
||||
~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure that you're in the stable-diffusion directory when you do this.
|
||||
|
||||
Alternatively, if you have GFPGAN installed elsewhere, or if you are using
|
||||
an earlier version of this package which asked you to install GFPGAN in a
|
||||
sibling directory, you may use the `--gfpgan_dir` argument with `dream.py` to set a
|
||||
custom path to your GFPGAN directory. _There are other GFPGAN related
|
||||
boot arguments if you wish to customize further._
|
||||
|
||||
**Note: Internet connection needed:**
|
||||
Users whose GPU machines are isolated from the Internet (e.g. on a
|
||||
University cluster) should be aware that the first time you run
|
||||
dream.py with GFPGAN and Real-ESRGAN turned on, it will try to
|
||||
download model files from the Internet. To rectify this, you may run
|
||||
`python3 scripts/preload_models.py` after you have installed GFPGAN
|
||||
and all its dependencies.
|
||||
|
||||
**Usage**
|
||||
|
||||
You will now have access to two new prompt arguments.
|
||||
|
||||
**Upscaling**
|
||||
|
||||
`-U : <upscaling_factor> <upscaling_strength>`
|
||||
|
||||
The upscaling prompt argument takes two values. The first value is a
|
||||
scaling factor and should be set to either `2` or `4` only. This will
|
||||
either scale the image 2x or 4x respectively using different models.
|
||||
|
||||
You can set the scaling stength between `0` and `1.0` to control
|
||||
intensity of the of the scaling. This is handy because AI upscalers
|
||||
generally tend to smooth out texture details. If you wish to retain
|
||||
some of those for natural looking results, we recommend using values
|
||||
between `0.5 to 0.8`.
|
||||
|
||||
If you do not explicitly specify an upscaling_strength, it will
|
||||
default to 0.75.
|
||||
|
||||
**Face Restoration**
|
||||
|
||||
`-G : <gfpgan_strength>`
|
||||
|
||||
This prompt argument controls the strength of the face restoration
|
||||
that is being applied. Similar to upscaling, values between `0.5 to 0.8` are recommended.
|
||||
|
||||
You can use either one or both without any conflicts. In cases where
|
||||
you use both, the image will be first upscaled and then the face
|
||||
restoration process will be executed to ensure you get the highest
|
||||
quality facial features.
|
||||
|
||||
`--save_orig`
|
||||
|
||||
When you use either `-U` or `-G`, the final result you get is upscaled
|
||||
or face modified. If you want to save the original Stable Diffusion
|
||||
generation, you can use the `-save_orig` prompt argument to save the
|
||||
original unaffected version too.
|
||||
|
||||
**Example Usage**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
dream > superman dancing with a panda bear -U 2 0.6 -G 0.4
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This also works with img2img:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
dream> a man wearing a pineapple hat -I path/to/your/file.png -U 2 0.5 -G 0.6
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**
|
||||
|
||||
GFPGAN and Real-ESRGAN are both memory intensive. In order to avoid
|
||||
crashes and memory overloads during the Stable Diffusion process,
|
||||
these effects are applied after Stable Diffusion has completed its
|
||||
work.
|
||||
|
||||
In single image generations, you will see the output right away but
|
||||
when you are using multiple iterations, the images will first be
|
||||
generated and then upscaled and face restored after that process is
|
||||
complete. While the image generation is taking place, you will still
|
||||
be able to preview the base images.
|
||||
|
||||
If you wish to stop during the image generation but want to upscale or
|
||||
face restore a particular generated image, pass it again with the same
|
||||
prompt and generated seed along with the `-U` and `-G` prompt
|
||||
arguments to perform those actions.
|
||||
@ -1,28 +1,28 @@
|
||||
# Cheat Sheat for Generating Variations
|
||||
# **Variations**
|
||||
|
||||
Release 1.13 of SD-Dream adds support for image variations. There are two things that you can do:
|
||||
Release 1.13 of SD-Dream adds support for image variations.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Generate a series of systematic variations of an image, given a
|
||||
prompt. The amount of variation from one image to the next can be
|
||||
controlled.
|
||||
You are able to do the following:
|
||||
|
||||
2. Given two or more variations that you like, you can combine them in
|
||||
a weighted fashion
|
||||
1. Generate a series of systematic variations of an image, given a prompt. The amount of variation from one image to the next can be controlled.
|
||||
|
||||
This cheat sheet provides a quick guide for how this works in
|
||||
practice, using variations to create the desired image of Xena,
|
||||
Warrior Princess.
|
||||
2. Given two or more variations that you like, you can combine them in a weighted fashion.
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 1 -- find a base image that you like
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
The prompt we will use throughout is "lucy lawless as xena, warrior
|
||||
princess, character portrait, high resolution." This will be indicated
|
||||
as "prompt" in the examples below.
|
||||
This cheat sheet provides a quick guide for how this works in practice, using variations to create the desired image of Xena, Warrior Princess.
|
||||
|
||||
First we let SD create a series of images in the usual way, in this case
|
||||
requesting six iterations:
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
~~~
|
||||
## Step 1 -- Find a base image that you like
|
||||
|
||||
The prompt we will use throughout is `lucy lawless as xena, warrior princess, character portrait, high resolution.`
|
||||
|
||||
This will be indicated as `prompt` in the examples below.
|
||||
|
||||
First we let SD create a series of images in the usual way, in this case requesting six iterations:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
dream> lucy lawless as xena, warrior princess, character portrait, high resolution -n6
|
||||
...
|
||||
Outputs:
|
||||
@ -32,19 +32,21 @@ Outputs:
|
||||
./outputs/Xena/000001.2224800325.png: "prompt" -s50 -W512 -H512 -C7.5 -Ak_lms -S2224800325
|
||||
./outputs/Xena/000001.465250761.png: "prompt" -s50 -W512 -H512 -C7.5 -Ak_lms -S465250761
|
||||
./outputs/Xena/000001.3357757885.png: "prompt" -s50 -W512 -H512 -C7.5 -Ak_lms -S3357757885
|
||||
~~~
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The one with seed 3357757885 looks nice:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="static/variation_walkthru/000001.3357757885.png"/>
|
||||
<img src="assets/variation_walkthru/000001.3357757885.png"/>
|
||||
|
||||
Let's try to generate some variations. Using the same seed, we pass
|
||||
the argument -v0.1 (or --variant_amount), which generates a series of
|
||||
variations each differing by a variation amount of 0.2. This number
|
||||
ranges from 0 to 1.0, with higher numbers being larger amounts of
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 2 - Generating Variations
|
||||
|
||||
Let's try to generate some variations. Using the same seed, we pass the argument `-v0.1` (or --variant_amount), which generates a series of
|
||||
variations each differing by a variation amount of 0.2. This number ranges from `0` to `1.0`, with higher numbers being larger amounts of
|
||||
variation.
|
||||
|
||||
~~~
|
||||
```
|
||||
dream> "prompt" -n6 -S3357757885 -v0.2
|
||||
...
|
||||
Outputs:
|
||||
@ -54,45 +56,36 @@ Outputs:
|
||||
./outputs/Xena/000002.4116285959.png: "prompt" -s50 -W512 -H512 -C7.5 -Ak_lms -V 4116285959:0.2 -S3357757885
|
||||
./outputs/Xena/000002.1614299449.png: "prompt" -s50 -W512 -H512 -C7.5 -Ak_lms -V 1614299449:0.2 -S3357757885
|
||||
./outputs/Xena/000002.1335553075.png: "prompt" -s50 -W512 -H512 -C7.5 -Ak_lms -V 1335553075:0.2 -S3357757885
|
||||
~~~
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note that the output for each image has a -V option giving the
|
||||
"variant subseed" for that image, consisting of a seed followed by the
|
||||
### **Variation Sub Seeding**
|
||||
|
||||
Note that the output for each image has a `-V` option giving the "variant subseed" for that image, consisting of a seed followed by the
|
||||
variation amount used to generate it.
|
||||
|
||||
This gives us a series of closely-related variations, including the
|
||||
two shown here.
|
||||
This gives us a series of closely-related variations, including the two shown here.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="static/variation_walkthru/000002.3647897225.png">
|
||||
<img src="static/variation_walkthru/000002.1614299449.png">
|
||||
<img src="assets/variation_walkthru/000002.3647897225.png">
|
||||
<img src="assets/variation_walkthru/000002.1614299449.png">
|
||||
|
||||
I like the expression on Xena's face in the first one (subseed 3647897225), and the armor on her shoulder in the second one (subseed 1614299449). Can we combine them to get the best of both worlds?
|
||||
|
||||
I like the expression on Xena's face in the first one (subseed
|
||||
3647897225), and the armor on her shoulder in the second one (subseed
|
||||
1614299449). Can we combine them to get the best of both worlds?
|
||||
|
||||
We combine the two variations using -V (--with_variations). Again, we
|
||||
must provide the seed for the originally-chosen image in order for
|
||||
We combine the two variations using `-V` (--with_variations). Again, we must provide the seed for the originally-chosen image in order for
|
||||
this to work.
|
||||
|
||||
~~~
|
||||
```
|
||||
dream> "prompt" -S3357757885 -V3647897225,0.1;1614299449,0.1
|
||||
Outputs:
|
||||
./outputs/Xena/000003.1614299449.png: "prompt" -s50 -W512 -H512 -C7.5 -Ak_lms -V 3647897225:0.1,1614299449:0.1 -S3357757885
|
||||
~~~
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here we are providing equal weights (0.1 and 0.1) for both the
|
||||
subseeds. The resulting image is close, but not exactly what I
|
||||
wanted:
|
||||
Here we are providing equal weights (0.1 and 0.1) for both the subseeds. The resulting image is close, but not exactly what I wanted:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="static/variation_walkthru/000003.1614299449.png">
|
||||
<img src="assets/variation_walkthru/000003.1614299449.png">
|
||||
|
||||
We could either try combining the images with different weights, or we
|
||||
can generate more variations around the almost-but-not-quite image. We
|
||||
do the latter, using both the -V (combining) and -v (variation
|
||||
strength) options. Note that we use -n6 to generate 6 variations:
|
||||
We could either try combining the images with different weights, or we can generate more variations around the almost-but-not-quite image. We do the latter, using both the `-V` (combining) and `-v` (variation strength) options. Note that we use `-n6` to generate 6 variations:
|
||||
|
||||
~~~~
|
||||
```
|
||||
dream> "prompt" -S3357757885 -V3647897225,0.1;1614299449,0.1 -v0.05 -n6
|
||||
Outputs:
|
||||
./outputs/Xena/000004.3279757577.png: "prompt" -s50 -W512 -H512 -C7.5 -Ak_lms -V 3647897225:0.1,1614299449:0.1,3279757577:0.05 -S3357757885
|
||||
@ -101,13 +94,11 @@ Outputs:
|
||||
./outputs/Xena/000004.2664260391.png: "prompt" -s50 -W512 -H512 -C7.5 -Ak_lms -V 3647897225:0.1,1614299449:0.1,2664260391:0.05 -S3357757885
|
||||
./outputs/Xena/000004.1642517170.png: "prompt" -s50 -W512 -H512 -C7.5 -Ak_lms -V 3647897225:0.1,1614299449:0.1,1642517170:0.05 -S3357757885
|
||||
./outputs/Xena/000004.2183375608.png: "prompt" -s50 -W512 -H512 -C7.5 -Ak_lms -V 3647897225:0.1,1614299449:0.1,2183375608:0.05 -S3357757885
|
||||
~~~~
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This produces six images, all slight variations on the combination of
|
||||
the chosen two images. Here's the one I like best:
|
||||
This produces six images, all slight variations on the combination of the chosen two images. Here's the one I like best:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="static/variation_walkthru/000004.3747154981.png">
|
||||
<img src="assets/variation_walkthru/000004.3747154981.png">
|
||||
|
||||
As you can see, this is a very powerful too, which when combined with
|
||||
subprompt weighting, gives you great control over the content and
|
||||
As you can see, this is a very powerful tool, which when combined with subprompt weighting, gives you great control over the content and
|
||||
quality of your generated images.
|
||||
13
docs/features/WEB.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
|
||||
# Barebones Web Server
|
||||
|
||||
As of version 1.10, this distribution comes with a bare bones web server (see screenshot). To use it, run the `dream.py` script by adding the `**--web**` option.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
(ldm) ~/stable-diffusion$ python3 scripts/dream.py --web
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can then connect to the server by pointing your web browser at http://localhost:9090, or to the network name or IP address of the server.
|
||||
|
||||
Kudos to [Tesseract Cat](https://github.com/TesseractCat) for contributing this code, and to [dagf2101](https://github.com/dagf2101) for refining it.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
68
docs/help/TROUBLESHOOT.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
|
||||
# **Frequently Asked Questions**
|
||||
|
||||
Here are a few common installation problems and their solutions. Often these are caused by incomplete installations or crashes during the
|
||||
install process.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
**QUESTION**
|
||||
|
||||
During `conda env create -f environment.yaml`, conda hangs indefinitely.
|
||||
|
||||
**SOLUTION**
|
||||
|
||||
Enter the stable-diffusion directory and completely remove the `src` directory and all its contents. The safest way to do this is to enter the stable-diffusion directory and give the command `git clean -f`. If this still doesn't fix the problem, try "conda clean -all" and then restart at the `conda env create` step.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
**QUESTION**
|
||||
|
||||
`dream.py` crashes with the complaint that it can't find `ldm.simplet2i.py`. Or it complains that function is being passed incorrect parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
**SOLUTION**
|
||||
|
||||
Reinstall the stable diffusion modules. Enter the `stable-diffusion` directory and give the command `pip install -e .`
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
**QUESTION**
|
||||
|
||||
`dream.py` dies, complaining of various missing modules, none of which starts with `ldm``.
|
||||
|
||||
**SOLUTION**
|
||||
|
||||
From within the `stable-diffusion` directory, run `conda env update -f environment.yaml` This is also frequently the solution to
|
||||
complaints about an unknown function in a module.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
**QUESTION**
|
||||
|
||||
There's a feature or bugfix in the Stable Diffusion GitHub that you want to try out.
|
||||
|
||||
**SOLUTION**
|
||||
|
||||
**Main Branch**
|
||||
|
||||
If the fix/feature is on the `main` branch, enter the stable-diffusion directory and do a `git pull`.
|
||||
|
||||
Usually this will be sufficient, but if you start to see errors about missing or incorrect modules, use the command `pip install -e .` and/or `conda env update -f environment.yaml` (These commands won't break anything.)
|
||||
|
||||
**Sub Branch**
|
||||
|
||||
If the feature/fix is on a branch (e.g. "_foo-bugfix_"), the recipe is similar, but do a `git pull <name of branch>`.
|
||||
|
||||
**Not Committed**
|
||||
|
||||
If the feature/fix is in a pull request that has not yet been made part of the main branch or a feature/bugfix branch, then from the page for the desired pull request, look for the line at the top that reads "_xxxx wants to merge xx commits into lstein:main from YYYYYY_". Copy the URL in YYYY. It should have the format `https://github.com/<name of contributor>/stable-diffusion/tree/<name of branch>`
|
||||
|
||||
Then **go to the directory above stable-diffusion** and rename the directory to "_stable-diffusion.lstein_", "_stable-diffusion.old_", or anything else. You can then git clone the branch that contains the pull request:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/<name of contributor>/stable-diffusion/tree/<name
|
||||
of branch>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You will need to go through the install procedure again, but it should be fast because all the dependencies are already loaded.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
89
docs/installation/INSTALL_LINUX.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,89 @@
|
||||
# **Linux Installation**
|
||||
|
||||
1. You will need to install the following prerequisites if they are not already available. Use your operating system's preferred installer
|
||||
|
||||
- Python (version 3.8.5 recommended; higher may work)
|
||||
- git
|
||||
|
||||
2. Install the Python Anaconda environment manager.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
~$ wget https://repo.anaconda.com/archive/Anaconda3-2022.05-Linux-x86_64.sh
|
||||
~$ chmod +x Anaconda3-2022.05-Linux-x86_64.sh
|
||||
~$ ./Anaconda3-2022.05-Linux-x86_64.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
After installing anaconda, you should log out of your system and log back in. If the installation
|
||||
worked, your command prompt will be prefixed by the name of the current anaconda environment - `(base)`.
|
||||
|
||||
3. Copy the stable-diffusion source code from GitHub:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
(base) ~$ git clone https://github.com/lstein/stable-diffusion.git
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will create stable-diffusion folder where you will follow the rest of the steps.
|
||||
|
||||
4. Enter the newly-created stable-diffusion folder. From this step forward make sure that you are working in the stable-diffusion directory!
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
(base) ~$ cd stable-diffusion
|
||||
(base) ~/stable-diffusion$
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
5. Use anaconda to copy necessary python packages, create a new python environment named `ldm` and activate the environment.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
(base) ~/stable-diffusion$ conda env create -f environment.yaml
|
||||
(base) ~/stable-diffusion$ conda activate ldm
|
||||
(ldm) ~/stable-diffusion$
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
After these steps, your command prompt will be prefixed by `(ldm)` as shown above.
|
||||
|
||||
6. Load a couple of small machine-learning models required by stable diffusion:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
(ldm) ~/stable-diffusion$ python3 scripts/preload_models.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note that this step is necessary because I modified the original just-in-time model loading scheme to allow the script to work on GPU machines that are not internet connected. See [Preload Models](../features/OTHER.md#preload-models)
|
||||
|
||||
7. Now you need to install the weights for the stable diffusion model.
|
||||
|
||||
- For running with the released weights, you will first need to set up an acount with Hugging Face (https://huggingface.co).
|
||||
- Use your credentials to log in, and then point your browser at https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion-v-1-4-original.
|
||||
- You may be asked to sign a license agreement at this point.
|
||||
- Click on "Files and versions" near the top of the page, and then click on the file named "sd-v1-4.ckpt". You'll be taken to a page that prompts you to click the "download" link. Save the file somewhere safe on your local machine.
|
||||
|
||||
Now run the following commands from within the stable-diffusion directory. This will create a symbolic link from the stable-diffusion model.ckpt file, to the true location of the sd-v1-4.ckpt file.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
(ldm) ~/stable-diffusion$ mkdir -p models/ldm/stable-diffusion-v1
|
||||
(ldm) ~/stable-diffusion$ ln -sf /path/to/sd-v1-4.ckpt models/ldm/stable-diffusion-v1/model.ckpt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
8. Start generating images!
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# for the pre-release weights use the -l or --liaon400m switch
|
||||
(ldm) ~/stable-diffusion$ python3 scripts/dream.py -l
|
||||
|
||||
# for the post-release weights do not use the switch
|
||||
(ldm) ~/stable-diffusion$ python3 scripts/dream.py
|
||||
|
||||
# for additional configuration switches and arguments, use -h or --help
|
||||
(ldm) ~/stable-diffusion$ python3 scripts/dream.py -h
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
9. Subsequently, to relaunch the script, be sure to run "conda activate ldm" (step 5, second command), enter the `stable-diffusion` directory, and then launch the dream script (step 8). If you forget to activate the ldm environment, the script will fail with multiple `ModuleNotFound` errors.
|
||||
|
||||
### Updating to newer versions of the script
|
||||
|
||||
This distribution is changing rapidly. If you used the `git clone` method (step 5) to download the stable-diffusion directory, then to update to the latest and greatest version, launch the Anaconda window, enter `stable-diffusion` and type:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
(ldm) ~/stable-diffusion$ git pull
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will bring your local copy into sync with the remote one.
|
||||
@ -1,21 +1,20 @@
|
||||
# macOS Instructions
|
||||
# **macOS Instructions**
|
||||
|
||||
Requirements
|
||||
|
||||
- macOS 12.3 Monterey or later
|
||||
- Python
|
||||
- Patience
|
||||
- Apple Silicon*
|
||||
- Apple Silicon\*
|
||||
|
||||
*I haven't tested any of this on Intel Macs but I have read that one person got
|
||||
it to work, so Apple Silicon might not be requried.
|
||||
\*I haven't tested any of this on Intel Macs but I have read that one person got it to work, so Apple Silicon might not be requried.
|
||||
|
||||
Things have moved really fast and so these instructions change often and are
|
||||
often out-of-date. One of the problems is that there are so many different ways to
|
||||
run this.
|
||||
Things have moved really fast and so these instructions change often
|
||||
and are often out-of-date. One of the problems is that there are so
|
||||
many different ways to run this.
|
||||
|
||||
We are trying to build a testing setup so that when we make changes it doesn't
|
||||
always break.
|
||||
We are trying to build a testing setup so that when we make changes it
|
||||
doesn't always break.
|
||||
|
||||
How to (this hasn't been 100% tested yet):
|
||||
|
||||
@ -38,7 +37,6 @@ While that is downloading, open Terminal and run the following commands one at a
|
||||
# 2. No pyenv
|
||||
#
|
||||
# If you don't know what we are talking about, choose 2.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# NOW EITHER DO
|
||||
# 1. Installing alongside pyenv
|
||||
|
||||
@ -93,11 +91,11 @@ The original scripts should work as well.
|
||||
python scripts/orig_scripts/txt2img.py --prompt "a photograph of an astronaut riding a horse" --plms
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note, `export PIP_EXISTS_ACTION=w` is a precaution to fix `conda env create -f environment-mac.yaml`
|
||||
never finishing in some situations. So it isn't required but wont hurt.
|
||||
Note, `export PIP_EXISTS_ACTION=w` is a precaution to fix `conda env
|
||||
create -f environment-mac.yaml` never finishing in some situations. So
|
||||
it isn't required but wont hurt.
|
||||
|
||||
After you follow all the instructions and run dream.py you might get several
|
||||
errors. Here's the errors I've seen and found solutions for.
|
||||
After you follow all the instructions and run dream.py you might get several errors. Here's the errors I've seen and found solutions for.
|
||||
|
||||
### Is it slow?
|
||||
|
||||
@ -107,12 +105,7 @@ Be sure to specify 1 sample and 1 iteration.
|
||||
|
||||
### Doesn't work anymore?
|
||||
|
||||
PyTorch nightly includes support for MPS. Because of this, this setup is
|
||||
inherently unstable. One morning I woke up and it no longer worked no matter
|
||||
what I did until I switched to miniforge. However, I have another Mac that works
|
||||
just fine with Anaconda. If you can't get it to work, please search a little
|
||||
first because many of the errors will get posted and solved. If you can't find
|
||||
a solution please [create an issue](https://github.com/lstein/stable-diffusion/issues).
|
||||
PyTorch nightly includes support for MPS. Because of this, this setup is inherently unstable. One morning I woke up and it no longer worked no matter what I did until I switched to miniforge. However, I have another Mac that works just fine with Anaconda. If you can't get it to work, please search a little first because many of the errors will get posted and solved. If you can't find a solution please [create an issue](https://github.com/lstein/stable-diffusion/issues).
|
||||
|
||||
One debugging step is to update to the latest version of PyTorch nightly.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -148,10 +141,7 @@ environment.
|
||||
conda env remove -n ldm
|
||||
conda env create -f environment-mac.yaml
|
||||
|
||||
Fourth, If you have activated the ldm virtual environment and tried rebuilding
|
||||
it, maybe the problem could be that I have something installed that
|
||||
you don't and you'll just need to manually install it. Make sure you
|
||||
activate the virtual environment so it installs there instead of
|
||||
Fourth, If you have activated the ldm virtual environment and tried rebuilding it, maybe the problem could be that I have something installed that you don't and you'll just need to manually install it. Make sure you activate the virtual environment so it installs there instead of
|
||||
globally.
|
||||
|
||||
conda activate ldm
|
||||
@ -244,9 +234,9 @@ I have not seen this error because I had Rust installed on my computer before I
|
||||
First this:
|
||||
|
||||
> Completely reproducible results are not guaranteed across PyTorch
|
||||
releases, individual commits, or different platforms. Furthermore,
|
||||
results may not be reproducible between CPU and GPU executions, even
|
||||
when using identical seeds.
|
||||
> releases, individual commits, or different platforms. Furthermore,
|
||||
> results may not be reproducible between CPU and GPU executions, even
|
||||
> when using identical seeds.
|
||||
|
||||
[PyTorch docs](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/notes/randomness.html)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -267,7 +257,7 @@ a dependency. [nomkl](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/66224879/what-is-the-n
|
||||
is a metapackage designed to prevent this, by making it impossible to install
|
||||
`mkl`, but if your environment is already broken it may not work.
|
||||
|
||||
Do *not* use `os.environ['KMP_DUPLICATE_LIB_OK']='True'` or equivalents as this
|
||||
Do _not_ use `os.environ['KMP_DUPLICATE_LIB_OK']='True'` or equivalents as this
|
||||
masks the underlying issue of using Intel packages.
|
||||
|
||||
### Not enough memory.
|
||||
@ -282,7 +272,7 @@ affect the quality of the images though.
|
||||
|
||||
See [this issue](https://github.com/CompVis/stable-diffusion/issues/71).
|
||||
|
||||
### "Error: product of dimension sizes > 2**31'"
|
||||
### "Error: product of dimension sizes > 2\*\*31'"
|
||||
|
||||
This error happens with img2img, which I haven't played with too much
|
||||
yet. But I know it's because your image is too big or the resolution
|
||||
@ -292,7 +282,7 @@ output size (which is the default). However, if you're using that size
|
||||
and you get the above error, try 256 x 256 or 512 x 256 or something
|
||||
as the source image.
|
||||
|
||||
BTW, 2**31-1 = [2,147,483,647](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/2,147,483,647#In_computing), which is also 32-bit signed [LONG_MAX](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/C_data_types) in C.
|
||||
BTW, 2\*\*31-1 = [2,147,483,647](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/2,147,483,647#In_computing), which is also 32-bit signed [LONG_MAX](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/C_data_types) in C.
|
||||
|
||||
### I just got Rickrolled! Do I have a virus?
|
||||
|
||||
@ -342,3 +332,20 @@ something that depends on it-- Rosetta can translate some Intel instructions but
|
||||
not the specialized ones here. To avoid this, make sure to use the environment
|
||||
variable `CONDA_SUBDIR=osx-arm64`, which restricts the Conda environment to only
|
||||
use ARM packages, and use `nomkl` as described above.
|
||||
|
||||
### input types 'tensor<2x1280xf32>' and 'tensor<\*xf16>' are not broadcast compatible
|
||||
|
||||
May appear when just starting to generate, e.g.:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
dream> clouds
|
||||
Generating: 0%| | 0/1 [00:00<?, ?it/s]/Users/[...]/dev/stable-diffusion/ldm/modules/embedding_manager.py:152: UserWarning: The operator 'aten::nonzero' is not currently supported on the MPS backend and will fall back to run on the CPU. This may have performance implications. (Triggered internally at /Users/runner/work/_temp/anaconda/conda-bld/pytorch_1662016319283/work/aten/src/ATen/mps/MPSFallback.mm:11.)
|
||||
placeholder_idx = torch.where(
|
||||
loc("mps_add"("(mpsFileLoc): /AppleInternal/Library/BuildRoots/20d6c351-ee94-11ec-bcaf-7247572f23b4/Library/Caches/com.apple.xbs/Sources/MetalPerformanceShadersGraph/mpsgraph/MetalPerformanceShadersGraph/Core/Files/MPSGraphUtilities.mm":219:0)): error: input types 'tensor<2x1280xf32>' and 'tensor<*xf16>' are not broadcast compatible
|
||||
LLVM ERROR: Failed to infer result type(s).
|
||||
Abort trap: 6
|
||||
/Users/[...]/opt/anaconda3/envs/ldm/lib/python3.9/multiprocessing/resource_tracker.py:216: UserWarning: resource_tracker: There appear to be 1 leaked semaphore objects to clean up at shutdown
|
||||
warnings.warn('resource_tracker: There appear to be %d '
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Macs do not support autocast/mixed-precision. Supply `--full_precision` to use float32 everywhere.
|
||||
112
docs/installation/INSTALL_WINDOWS.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,112 @@
|
||||
# **Windows Installation**
|
||||
|
||||
## **Notebook install (semi-automated)**
|
||||
|
||||
We have a [Jupyter
|
||||
notebook](https://github.com/lstein/stable-diffusion/blob/main/notebooks/Stable-Diffusion-local-Windows.ipynb)
|
||||
with cell-by-cell installation steps. It will download the code in
|
||||
this repo as one of the steps, so instead of cloning this repo, simply
|
||||
download the notebook from the link above and load it up in VSCode
|
||||
(with the appropriate extensions installed)/Jupyter/JupyterLab and
|
||||
start running the cells one-by-one.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that you will need NVIDIA drivers, Python 3.10, and Git installed
|
||||
beforehand - simplified [step-by-step
|
||||
instructions](https://github.com/lstein/stable-diffusion/wiki/Easy-peasy-Windows-install)
|
||||
are available in the wiki (you'll only need steps 1, 2, & 3 ).
|
||||
|
||||
## **Manual Install**
|
||||
|
||||
### **pip**
|
||||
|
||||
See [Easy-peasy Windows install](https://github.com/lstein/stable-diffusion/wiki/Easy-peasy-Windows-install)
|
||||
in the wiki
|
||||
|
||||
### **Conda**
|
||||
|
||||
1. Install Anaconda3 (miniconda3 version) from here: https://docs.anaconda.com/anaconda/install/windows/
|
||||
|
||||
2. Install Git from here: https://git-scm.com/download/win
|
||||
|
||||
3. Launch Anaconda from the Windows Start menu. This will bring up a command window. Type all the remaining commands in this window.
|
||||
|
||||
4. Run the command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/lstein/stable-diffusion.git
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will create stable-diffusion folder where you will follow the rest of the steps.
|
||||
|
||||
5. Enter the newly-created stable-diffusion folder. From this step forward make sure that you are working in the stable-diffusion directory!
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
cd stable-diffusion
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
6. Run the following two commands:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
conda env create -f environment.yaml (step 6a)
|
||||
conda activate ldm (step 6b)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will install all python requirements and activate the "ldm"
|
||||
environment which sets PATH and other environment variables properly.
|
||||
|
||||
7. Run the command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
python scripts\preload_models.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This installs several machine learning models that stable diffusion requires.
|
||||
|
||||
Note: This step is required. This was done because some users may might be blocked by firewalls or have limited internet connectivity for the models to be downloaded just-in-time.
|
||||
|
||||
8. Now you need to install the weights for the big stable diffusion model.
|
||||
|
||||
- For running with the released weights, you will first need to set up an acount with Hugging Face (https://huggingface.co).
|
||||
- Use your credentials to log in, and then point your browser at https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion-v-1-4-original.
|
||||
- You may be asked to sign a license agreement at this point.
|
||||
- Click on "Files and versions" near the top of the page, and then click on the file named `sd-v1-4.ckpt`. You'll be taken to a page that
|
||||
prompts you to click the "download" link. Now save the file somewhere safe on your local machine.
|
||||
- The weight file is >4 GB in size, so
|
||||
downloading may take a while.
|
||||
|
||||
Now run the following commands from **within the stable-diffusion directory** to copy the weights file to the right place:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
mkdir -p models\ldm\stable-diffusion-v1
|
||||
copy C:\path\to\sd-v1-4.ckpt models\ldm\stable-diffusion-v1\model.ckpt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Please replace `C:\path\to\sd-v1.4.ckpt` with the correct path to wherever you stashed this file. If you prefer not to copy or move the .ckpt file,
|
||||
you may instead create a shortcut to it from within `models\ldm\stable-diffusion-v1\`.
|
||||
|
||||
9. Start generating images!
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# for the pre-release weights
|
||||
python scripts\dream.py -l
|
||||
|
||||
# for the post-release weights
|
||||
python scripts\dream.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
10. Subsequently, to relaunch the script, first activate the Anaconda command window (step 3),enter the stable-diffusion directory (step 5, `cd \path\to\stable-diffusion`), run `conda activate ldm` (step 6b), and then launch the dream script (step 9).
|
||||
|
||||
**Note:** Tildebyte has written an alternative ["Easy peasy Windows
|
||||
install"](https://github.com/lstein/stable-diffusion/wiki/Easy-peasy-Windows-install)
|
||||
which uses the Windows Powershell and pew. If you are having trouble with Anaconda on Windows, give this a try (or try it first!)
|
||||
|
||||
### Updating to newer versions of the script
|
||||
|
||||
This distribution is changing rapidly. If you used the `git clone` method (step 5) to download the stable-diffusion directory, then to update to the latest and greatest version, launch the Anaconda window, enter `stable-diffusion`, and type:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
git pull
|
||||
conda env update -f environment.yaml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will bring your local copy into sync with the remote one.
|
||||
@ -1,33 +1,29 @@
|
||||
name: ldm
|
||||
channels:
|
||||
- pytorch-nightly
|
||||
- pytorch
|
||||
- conda-forge
|
||||
dependencies:
|
||||
- python==3.9.13
|
||||
- python==3.10.5
|
||||
- pip==22.2.2
|
||||
|
||||
# pytorch-nightly, left unpinned
|
||||
# pytorch left unpinned
|
||||
- pytorch
|
||||
- torchmetrics
|
||||
- torchvision
|
||||
|
||||
# I suggest to keep the other deps sorted for convenience.
|
||||
# If you wish to upgrade to 3.10, try to run this:
|
||||
# To determine what the latest versions should be, run:
|
||||
#
|
||||
# ```shell
|
||||
# CONDA_CMD=conda
|
||||
# sed -E 's/python==3.9.13/python==3.10.5/;s/ldm/ldm-3.10/;21,99s/- ([^=]+)==.+/- \1/' environment-mac.yaml > /tmp/environment-mac-updated.yml
|
||||
# CONDA_SUBDIR=osx-arm64 $CONDA_CMD env create -f /tmp/environment-mac-updated.yml && $CONDA_CMD list -n ldm-3.10 | awk ' {print " - " $1 "==" $2;} '
|
||||
# sed -E 's/ldm/ldm-updated/;20,99s/- ([^=]+)==.+/- \1/' environment-mac.yaml > environment-mac-updated.yml
|
||||
# CONDA_SUBDIR=osx-arm64 conda env create -f environment-mac-updated.yml && conda list -n ldm-updated | awk ' {print " - " $1 "==" $2;} '
|
||||
# ```
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unfortunately, as of 2022-08-31, this fails at the pip stage.
|
||||
- albumentations==1.2.1
|
||||
- coloredlogs==15.0.1
|
||||
- einops==0.4.1
|
||||
- grpcio==1.46.4
|
||||
- humanfriendly
|
||||
- imageio-ffmpeg==0.4.7
|
||||
- humanfriendly==10.0
|
||||
- imageio==2.21.2
|
||||
- imageio-ffmpeg==0.4.7
|
||||
- imgaug==0.4.0
|
||||
- kornia==0.6.7
|
||||
- mpmath==1.2.1
|
||||
@ -36,23 +32,23 @@ dependencies:
|
||||
- omegaconf==2.1.1
|
||||
- onnx==1.12.0
|
||||
- onnxruntime==1.12.1
|
||||
- opencv==4.6.0
|
||||
- pudb==2022.1
|
||||
- pytorch-lightning==1.6.5
|
||||
- scipy==1.9.1
|
||||
- streamlit==1.12.2
|
||||
- sympy==1.10.1
|
||||
- tensorboard==2.9.0
|
||||
- transformers==4.21.2
|
||||
- torchmetrics==0.9.3
|
||||
- pip:
|
||||
- invisible-watermark
|
||||
- test-tube
|
||||
- tokenizers
|
||||
- torch-fidelity
|
||||
- -e git+https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers.git@v0.2.4#egg=diffusers
|
||||
- opencv-python==4.6.0
|
||||
- realesrgan==0.2.5.0
|
||||
- test-tube==0.7.5
|
||||
- transformers==4.21.2
|
||||
- torch-fidelity==0.3.0
|
||||
- -e git+https://github.com/CompVis/taming-transformers.git@master#egg=taming-transformers
|
||||
- -e git+https://github.com/openai/CLIP.git@main#egg=clip
|
||||
- -e git+https://github.com/Birch-san/k-diffusion.git@mps#egg=k_diffusion
|
||||
- -e git+https://github.com/lstein/GFPGAN@fix-dark-cast-images#egg=gfpgan
|
||||
- -e .
|
||||
variables:
|
||||
PYTORCH_ENABLE_MPS_FALLBACK: 1
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
name: ldm
|
||||
name: sd-ldm
|
||||
channels:
|
||||
- pytorch
|
||||
- defaults
|
||||
@ -11,12 +11,13 @@ dependencies:
|
||||
- numpy=1.19.2
|
||||
- pip:
|
||||
- albumentations==0.4.3
|
||||
- opencv-python==4.1.2.30
|
||||
- opencv-python==4.5.5.64
|
||||
- pudb==2019.2
|
||||
- imageio==2.9.0
|
||||
- imageio-ffmpeg==0.4.2
|
||||
- pytorch-lightning==1.4.2
|
||||
- omegaconf==2.1.1
|
||||
- realesrgan==0.2.5.0
|
||||
- test-tube>=0.7.5
|
||||
- streamlit==1.12.0
|
||||
- pillow==9.2.0
|
||||
@ -28,4 +29,5 @@ dependencies:
|
||||
- -e git+https://github.com/openai/CLIP.git@main#egg=clip
|
||||
- -e git+https://github.com/CompVis/taming-transformers.git@master#egg=taming-transformers
|
||||
- -e git+https://github.com/lstein/k-diffusion.git@master#egg=k-diffusion
|
||||
- -e git+https://github.com/lstein/GFPGAN@fix-dark-cast-images#egg=gfpgan
|
||||
- -e .
|
||||
|
||||
96
ldm/dream/conditioning.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,96 @@
|
||||
'''
|
||||
This module handles the generation of the conditioning tensors, including management of
|
||||
weighted subprompts.
|
||||
|
||||
Useful function exports:
|
||||
|
||||
get_uc_and_c() get the conditioned and unconditioned latent
|
||||
split_weighted_subpromopts() split subprompts, normalize and weight them
|
||||
log_tokenization() print out colour-coded tokens and warn if truncated
|
||||
|
||||
'''
|
||||
import re
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
def get_uc_and_c(prompt, model, log_tokens=False, skip_normalize=False):
|
||||
uc = model.get_learned_conditioning([''])
|
||||
|
||||
# get weighted sub-prompts
|
||||
weighted_subprompts = split_weighted_subprompts(
|
||||
prompt, skip_normalize
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if len(weighted_subprompts) > 1:
|
||||
# i dont know if this is correct.. but it works
|
||||
c = torch.zeros_like(uc)
|
||||
# normalize each "sub prompt" and add it
|
||||
for subprompt, weight in weighted_subprompts:
|
||||
log_tokenization(subprompt, model, log_tokens)
|
||||
c = torch.add(
|
||||
c,
|
||||
model.get_learned_conditioning([subprompt]),
|
||||
alpha=weight,
|
||||
)
|
||||
else: # just standard 1 prompt
|
||||
log_tokenization(prompt, model, log_tokens)
|
||||
c = model.get_learned_conditioning([prompt])
|
||||
return (uc, c)
|
||||
|
||||
def split_weighted_subprompts(text, skip_normalize=False)->list:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
grabs all text up to the first occurrence of ':'
|
||||
uses the grabbed text as a sub-prompt, and takes the value following ':' as weight
|
||||
if ':' has no value defined, defaults to 1.0
|
||||
repeats until no text remaining
|
||||
"""
|
||||
prompt_parser = re.compile("""
|
||||
(?P<prompt> # capture group for 'prompt'
|
||||
(?:\\\:|[^:])+ # match one or more non ':' characters or escaped colons '\:'
|
||||
) # end 'prompt'
|
||||
(?: # non-capture group
|
||||
:+ # match one or more ':' characters
|
||||
(?P<weight> # capture group for 'weight'
|
||||
-?\d+(?:\.\d+)? # match positive or negative integer or decimal number
|
||||
)? # end weight capture group, make optional
|
||||
\s* # strip spaces after weight
|
||||
| # OR
|
||||
$ # else, if no ':' then match end of line
|
||||
) # end non-capture group
|
||||
""", re.VERBOSE)
|
||||
parsed_prompts = [(match.group("prompt").replace("\\:", ":"), float(
|
||||
match.group("weight") or 1)) for match in re.finditer(prompt_parser, text)]
|
||||
if skip_normalize:
|
||||
return parsed_prompts
|
||||
weight_sum = sum(map(lambda x: x[1], parsed_prompts))
|
||||
if weight_sum == 0:
|
||||
print(
|
||||
"Warning: Subprompt weights add up to zero. Discarding and using even weights instead.")
|
||||
equal_weight = 1 / len(parsed_prompts)
|
||||
return [(x[0], equal_weight) for x in parsed_prompts]
|
||||
return [(x[0], x[1] / weight_sum) for x in parsed_prompts]
|
||||
|
||||
# shows how the prompt is tokenized
|
||||
# usually tokens have '</w>' to indicate end-of-word,
|
||||
# but for readability it has been replaced with ' '
|
||||
def log_tokenization(text, model, log=False):
|
||||
if not log:
|
||||
return
|
||||
tokens = model.cond_stage_model.tokenizer._tokenize(text)
|
||||
tokenized = ""
|
||||
discarded = ""
|
||||
usedTokens = 0
|
||||
totalTokens = len(tokens)
|
||||
for i in range(0, totalTokens):
|
||||
token = tokens[i].replace('</w>', ' ')
|
||||
# alternate color
|
||||
s = (usedTokens % 6) + 1
|
||||
if i < model.cond_stage_model.max_length:
|
||||
tokenized = tokenized + f"\x1b[0;3{s};40m{token}"
|
||||
usedTokens += 1
|
||||
else: # over max token length
|
||||
discarded = discarded + f"\x1b[0;3{s};40m{token}"
|
||||
print(f"\n>> Tokens ({usedTokens}):\n{tokenized}\x1b[0m")
|
||||
if discarded != "":
|
||||
print(
|
||||
f">> Tokens Discarded ({totalTokens-usedTokens}):\n{discarded}\x1b[0m"
|
||||
)
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,6 @@
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from torch import autocast
|
||||
from contextlib import contextmanager, nullcontext
|
||||
|
||||
def choose_torch_device() -> str:
|
||||
'''Convenience routine for guessing which GPU device to run model on'''
|
||||
@ -8,10 +10,11 @@ def choose_torch_device() -> str:
|
||||
return 'mps'
|
||||
return 'cpu'
|
||||
|
||||
def choose_autocast_device(device) -> str:
|
||||
def choose_autocast_device(device):
|
||||
'''Returns an autocast compatible device from a torch device'''
|
||||
device_type = device.type # this returns 'mps' on M1
|
||||
# autocast only supports cuda or cpu
|
||||
if device_type not in ('cuda','cpu'):
|
||||
return 'cpu'
|
||||
return device_type
|
||||
if device_type in ('cuda','cpu'):
|
||||
return device_type,autocast
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return 'cpu',nullcontext
|
||||
|
||||
4
ldm/dream/generator/__init__.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,4 @@
|
||||
'''
|
||||
Initialization file for the ldm.dream.generator package
|
||||
'''
|
||||
from .base import Generator
|
||||
158
ldm/dream/generator/base.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,158 @@
|
||||
'''
|
||||
Base class for ldm.dream.generator.*
|
||||
including img2img, txt2img, and inpaint
|
||||
'''
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import random
|
||||
from tqdm import tqdm, trange
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
from einops import rearrange, repeat
|
||||
from pytorch_lightning import seed_everything
|
||||
from ldm.dream.devices import choose_autocast_device
|
||||
|
||||
downsampling = 8
|
||||
|
||||
class Generator():
|
||||
def __init__(self,model):
|
||||
self.model = model
|
||||
self.seed = None
|
||||
self.latent_channels = model.channels
|
||||
self.downsampling_factor = downsampling # BUG: should come from model or config
|
||||
self.variation_amount = 0
|
||||
self.with_variations = []
|
||||
|
||||
# this is going to be overridden in img2img.py, txt2img.py and inpaint.py
|
||||
def get_make_image(self,prompt,**kwargs):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns a function returning an image derived from the prompt and the initial image
|
||||
Return value depends on the seed at the time you call it
|
||||
"""
|
||||
raise NotImplementedError("image_iterator() must be implemented in a descendent class")
|
||||
|
||||
def set_variation(self, seed, variation_amount, with_variations):
|
||||
self.seed = seed
|
||||
self.variation_amount = variation_amount
|
||||
self.with_variations = with_variations
|
||||
|
||||
def generate(self,prompt,init_image,width,height,iterations=1,seed=None,
|
||||
image_callback=None, step_callback=None,
|
||||
**kwargs):
|
||||
device_type,scope = choose_autocast_device(self.model.device)
|
||||
make_image = self.get_make_image(
|
||||
prompt,
|
||||
init_image = init_image,
|
||||
width = width,
|
||||
height = height,
|
||||
step_callback = step_callback,
|
||||
**kwargs
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
results = []
|
||||
seed = seed if seed else self.new_seed()
|
||||
seed, initial_noise = self.generate_initial_noise(seed, width, height)
|
||||
with scope(device_type), self.model.ema_scope():
|
||||
for n in trange(iterations, desc='Generating'):
|
||||
x_T = None
|
||||
if self.variation_amount > 0:
|
||||
seed_everything(seed)
|
||||
target_noise = self.get_noise(width,height)
|
||||
x_T = self.slerp(self.variation_amount, initial_noise, target_noise)
|
||||
elif initial_noise is not None:
|
||||
# i.e. we specified particular variations
|
||||
x_T = initial_noise
|
||||
else:
|
||||
seed_everything(seed)
|
||||
if self.model.device.type == 'mps':
|
||||
x_T = self.get_noise(width,height)
|
||||
|
||||
# make_image will do the equivalent of get_noise itself
|
||||
image = make_image(x_T)
|
||||
results.append([image, seed])
|
||||
if image_callback is not None:
|
||||
image_callback(image, seed)
|
||||
seed = self.new_seed()
|
||||
return results
|
||||
|
||||
def sample_to_image(self,samples):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns a function returning an image derived from the prompt and the initial image
|
||||
Return value depends on the seed at the time you call it
|
||||
"""
|
||||
x_samples = self.model.decode_first_stage(samples)
|
||||
x_samples = torch.clamp((x_samples + 1.0) / 2.0, min=0.0, max=1.0)
|
||||
if len(x_samples) != 1:
|
||||
raise Exception(
|
||||
f'>> expected to get a single image, but got {len(x_samples)}')
|
||||
x_sample = 255.0 * rearrange(
|
||||
x_samples[0].cpu().numpy(), 'c h w -> h w c'
|
||||
)
|
||||
return Image.fromarray(x_sample.astype(np.uint8))
|
||||
|
||||
def generate_initial_noise(self, seed, width, height):
|
||||
initial_noise = None
|
||||
if self.variation_amount > 0 or len(self.with_variations) > 0:
|
||||
# use fixed initial noise plus random noise per iteration
|
||||
seed_everything(seed)
|
||||
initial_noise = self.get_noise(width,height)
|
||||
for v_seed, v_weight in self.with_variations:
|
||||
seed = v_seed
|
||||
seed_everything(seed)
|
||||
next_noise = self.get_noise(width,height)
|
||||
initial_noise = self.slerp(v_weight, initial_noise, next_noise)
|
||||
if self.variation_amount > 0:
|
||||
random.seed() # reset RNG to an actually random state, so we can get a random seed for variations
|
||||
seed = random.randrange(0,np.iinfo(np.uint32).max)
|
||||
return (seed, initial_noise)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return (seed, None)
|
||||
|
||||
# returns a tensor filled with random numbers from a normal distribution
|
||||
def get_noise(self,width,height):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns a tensor filled with random numbers, either form a normal distribution
|
||||
(txt2img) or from the latent image (img2img, inpaint)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
raise NotImplementedError("get_noise() must be implemented in a descendent class")
|
||||
|
||||
def new_seed(self):
|
||||
self.seed = random.randrange(0, np.iinfo(np.uint32).max)
|
||||
return self.seed
|
||||
|
||||
def slerp(self, t, v0, v1, DOT_THRESHOLD=0.9995):
|
||||
'''
|
||||
Spherical linear interpolation
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
t (float/np.ndarray): Float value between 0.0 and 1.0
|
||||
v0 (np.ndarray): Starting vector
|
||||
v1 (np.ndarray): Final vector
|
||||
DOT_THRESHOLD (float): Threshold for considering the two vectors as
|
||||
colineal. Not recommended to alter this.
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
v2 (np.ndarray): Interpolation vector between v0 and v1
|
||||
'''
|
||||
inputs_are_torch = False
|
||||
if not isinstance(v0, np.ndarray):
|
||||
inputs_are_torch = True
|
||||
v0 = v0.detach().cpu().numpy()
|
||||
if not isinstance(v1, np.ndarray):
|
||||
inputs_are_torch = True
|
||||
v1 = v1.detach().cpu().numpy()
|
||||
|
||||
dot = np.sum(v0 * v1 / (np.linalg.norm(v0) * np.linalg.norm(v1)))
|
||||
if np.abs(dot) > DOT_THRESHOLD:
|
||||
v2 = (1 - t) * v0 + t * v1
|
||||
else:
|
||||
theta_0 = np.arccos(dot)
|
||||
sin_theta_0 = np.sin(theta_0)
|
||||
theta_t = theta_0 * t
|
||||
sin_theta_t = np.sin(theta_t)
|
||||
s0 = np.sin(theta_0 - theta_t) / sin_theta_0
|
||||
s1 = sin_theta_t / sin_theta_0
|
||||
v2 = s0 * v0 + s1 * v1
|
||||
|
||||
if inputs_are_torch:
|
||||
v2 = torch.from_numpy(v2).to(self.model.device)
|
||||
|
||||
return v2
|
||||
|
||||
72
ldm/dream/generator/img2img.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
|
||||
'''
|
||||
ldm.dream.generator.txt2img descends from ldm.dream.generator
|
||||
'''
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
from ldm.dream.devices import choose_autocast_device
|
||||
from ldm.dream.generator.base import Generator
|
||||
from ldm.models.diffusion.ddim import DDIMSampler
|
||||
|
||||
class Img2Img(Generator):
|
||||
def __init__(self,model):
|
||||
super().__init__(model)
|
||||
self.init_latent = None # by get_noise()
|
||||
|
||||
@torch.no_grad()
|
||||
def get_make_image(self,prompt,sampler,steps,cfg_scale,ddim_eta,
|
||||
conditioning,init_image,strength,step_callback=None,**kwargs):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns a function returning an image derived from the prompt and the initial image
|
||||
Return value depends on the seed at the time you call it.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
# PLMS sampler not supported yet, so ignore previous sampler
|
||||
if not isinstance(sampler,DDIMSampler):
|
||||
print(
|
||||
f">> sampler '{sampler.__class__.__name__}' is not yet supported. Using DDIM sampler"
|
||||
)
|
||||
sampler = DDIMSampler(self.model, device=self.model.device)
|
||||
|
||||
sampler.make_schedule(
|
||||
ddim_num_steps=steps, ddim_eta=ddim_eta, verbose=False
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
device_type,scope = choose_autocast_device(self.model.device)
|
||||
with scope(device_type):
|
||||
self.init_latent = self.model.get_first_stage_encoding(
|
||||
self.model.encode_first_stage(init_image)
|
||||
) # move to latent space
|
||||
|
||||
t_enc = int(strength * steps)
|
||||
uc, c = conditioning
|
||||
|
||||
@torch.no_grad()
|
||||
def make_image(x_T):
|
||||
# encode (scaled latent)
|
||||
z_enc = sampler.stochastic_encode(
|
||||
self.init_latent,
|
||||
torch.tensor([t_enc]).to(self.model.device),
|
||||
noise=x_T
|
||||
)
|
||||
# decode it
|
||||
samples = sampler.decode(
|
||||
z_enc,
|
||||
c,
|
||||
t_enc,
|
||||
img_callback = step_callback,
|
||||
unconditional_guidance_scale=cfg_scale,
|
||||
unconditional_conditioning=uc,
|
||||
)
|
||||
return self.sample_to_image(samples)
|
||||
|
||||
return make_image
|
||||
|
||||
def get_noise(self,width,height):
|
||||
device = self.model.device
|
||||
init_latent = self.init_latent
|
||||
assert init_latent is not None,'call to get_noise() when init_latent not set'
|
||||
if device.type == 'mps':
|
||||
return torch.randn_like(init_latent, device='cpu').to(device)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return torch.randn_like(init_latent, device=device)
|
||||
77
ldm/dream/generator/inpaint.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,77 @@
|
||||
'''
|
||||
ldm.dream.generator.inpaint descends from ldm.dream.generator
|
||||
'''
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
from einops import rearrange, repeat
|
||||
from ldm.dream.devices import choose_autocast_device
|
||||
from ldm.dream.generator.img2img import Img2Img
|
||||
from ldm.models.diffusion.ddim import DDIMSampler
|
||||
|
||||
class Inpaint(Img2Img):
|
||||
def __init__(self,model):
|
||||
self.init_latent = None
|
||||
super().__init__(model)
|
||||
|
||||
@torch.no_grad()
|
||||
def get_make_image(self,prompt,sampler,steps,cfg_scale,ddim_eta,
|
||||
conditioning,init_image,mask_image,strength,
|
||||
step_callback=None,**kwargs):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns a function returning an image derived from the prompt and
|
||||
the initial image + mask. Return value depends on the seed at
|
||||
the time you call it. kwargs are 'init_latent' and 'strength'
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
mask_image = mask_image[0][0].unsqueeze(0).repeat(4,1,1).unsqueeze(0)
|
||||
mask_image = repeat(mask_image, '1 ... -> b ...', b=1)
|
||||
|
||||
# PLMS sampler not supported yet, so ignore previous sampler
|
||||
if not isinstance(sampler,DDIMSampler):
|
||||
print(
|
||||
f">> sampler '{sampler.__class__.__name__}' is not yet supported. Using DDIM sampler"
|
||||
)
|
||||
sampler = DDIMSampler(self.model, device=self.model.device)
|
||||
|
||||
sampler.make_schedule(
|
||||
ddim_num_steps=steps, ddim_eta=ddim_eta, verbose=False
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
device_type,scope = choose_autocast_device(self.model.device)
|
||||
with scope(device_type):
|
||||
self.init_latent = self.model.get_first_stage_encoding(
|
||||
self.model.encode_first_stage(init_image)
|
||||
) # move to latent space
|
||||
|
||||
t_enc = int(strength * steps)
|
||||
uc, c = conditioning
|
||||
|
||||
print(f">> target t_enc is {t_enc} steps")
|
||||
|
||||
@torch.no_grad()
|
||||
def make_image(x_T):
|
||||
# encode (scaled latent)
|
||||
z_enc = sampler.stochastic_encode(
|
||||
self.init_latent,
|
||||
torch.tensor([t_enc]).to(self.model.device),
|
||||
noise=x_T
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# decode it
|
||||
samples = sampler.decode(
|
||||
z_enc,
|
||||
c,
|
||||
t_enc,
|
||||
img_callback = step_callback,
|
||||
unconditional_guidance_scale = cfg_scale,
|
||||
unconditional_conditioning = uc,
|
||||
mask = mask_image,
|
||||
init_latent = self.init_latent
|
||||
)
|
||||
return self.sample_to_image(samples)
|
||||
|
||||
return make_image
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
61
ldm/dream/generator/txt2img.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
|
||||
'''
|
||||
ldm.dream.generator.txt2img inherits from ldm.dream.generator
|
||||
'''
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
from ldm.dream.generator.base import Generator
|
||||
|
||||
class Txt2Img(Generator):
|
||||
def __init__(self,model):
|
||||
super().__init__(model)
|
||||
|
||||
@torch.no_grad()
|
||||
def get_make_image(self,prompt,sampler,steps,cfg_scale,ddim_eta,
|
||||
conditioning,width,height,step_callback=None,**kwargs):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns a function returning an image derived from the prompt and the initial image
|
||||
Return value depends on the seed at the time you call it
|
||||
kwargs are 'width' and 'height'
|
||||
"""
|
||||
uc, c = conditioning
|
||||
|
||||
@torch.no_grad()
|
||||
def make_image(x_T):
|
||||
shape = [
|
||||
self.latent_channels,
|
||||
height // self.downsampling_factor,
|
||||
width // self.downsampling_factor,
|
||||
]
|
||||
samples, _ = sampler.sample(
|
||||
batch_size = 1,
|
||||
S = steps,
|
||||
x_T = x_T,
|
||||
conditioning = c,
|
||||
shape = shape,
|
||||
verbose = False,
|
||||
unconditional_guidance_scale = cfg_scale,
|
||||
unconditional_conditioning = uc,
|
||||
eta = ddim_eta,
|
||||
img_callback = step_callback
|
||||
)
|
||||
return self.sample_to_image(samples)
|
||||
|
||||
return make_image
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# returns a tensor filled with random numbers from a normal distribution
|
||||
def get_noise(self,width,height):
|
||||
device = self.model.device
|
||||
if device.type == 'mps':
|
||||
return torch.randn([1,
|
||||
self.latent_channels,
|
||||
height // self.downsampling_factor,
|
||||
width // self.downsampling_factor],
|
||||
device='cpu').to(device)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return torch.randn([1,
|
||||
self.latent_channels,
|
||||
height // self.downsampling_factor,
|
||||
width // self.downsampling_factor],
|
||||
device=device)
|
||||
@ -59,6 +59,10 @@ class PromptFormatter:
|
||||
switches.append(f'-H{opt.height or t2i.height}')
|
||||
switches.append(f'-C{opt.cfg_scale or t2i.cfg_scale}')
|
||||
switches.append(f'-A{opt.sampler_name or t2i.sampler_name}')
|
||||
# to do: put model name into the t2i object
|
||||
# switches.append(f'--model{t2i.model_name}')
|
||||
if opt.seamless or t2i.seamless:
|
||||
switches.append(f'--seamless')
|
||||
if opt.init_img:
|
||||
switches.append(f'-I{opt.init_img}')
|
||||
if opt.fit:
|
||||
@ -74,6 +78,4 @@ class PromptFormatter:
|
||||
if opt.with_variations:
|
||||
formatted_variations = ','.join(f'{seed}:{weight}' for seed, weight in opt.with_variations)
|
||||
switches.append(f'-V{formatted_variations}')
|
||||
if t2i.full_precision:
|
||||
switches.append('-F')
|
||||
return ' '.join(switches)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ class Completer:
|
||||
def complete(self, text, state):
|
||||
buffer = readline.get_line_buffer()
|
||||
|
||||
if text.startswith(('-I', '--init_img')):
|
||||
if text.startswith(('-I', '--init_img','-M','--init_mask')):
|
||||
return self._path_completions(text, state, ('.png','.jpg','.jpeg'))
|
||||
|
||||
if buffer.strip().endswith('cd') or text.startswith(('.', '/')):
|
||||
@ -48,10 +48,15 @@ class Completer:
|
||||
|
||||
def _path_completions(self, text, state, extensions):
|
||||
# get the path so far
|
||||
# TODO: replace this mess with a regular expression match
|
||||
if text.startswith('-I'):
|
||||
path = text.replace('-I', '', 1).lstrip()
|
||||
elif text.startswith('--init_img='):
|
||||
path = text.replace('--init_img=', '', 1).lstrip()
|
||||
elif text.startswith('--init_mask='):
|
||||
path = text.replace('--init_mask=', '', 1).lstrip()
|
||||
elif text.startswith('-M'):
|
||||
path = text.replace('-M', '', 1).lstrip()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
path = text
|
||||
|
||||
@ -94,6 +99,7 @@ if readline_available:
|
||||
'--grid','-g',
|
||||
'--individual','-i',
|
||||
'--init_img','-I',
|
||||
'--init_mask','-M',
|
||||
'--strength','-f',
|
||||
'--variants','-v',
|
||||
'--outdir','-o',
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,16 +1,65 @@
|
||||
import argparse
|
||||
import json
|
||||
import base64
|
||||
import mimetypes
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from http.server import BaseHTTPRequestHandler, ThreadingHTTPServer
|
||||
from ldm.dream.pngwriter import PngWriter
|
||||
from ldm.dream.pngwriter import PngWriter, PromptFormatter
|
||||
from threading import Event
|
||||
|
||||
def build_opt(post_data, seed, gfpgan_model_exists):
|
||||
opt = argparse.Namespace()
|
||||
setattr(opt, 'prompt', post_data['prompt'])
|
||||
setattr(opt, 'init_img', post_data['initimg'])
|
||||
setattr(opt, 'strength', float(post_data['strength']))
|
||||
setattr(opt, 'iterations', int(post_data['iterations']))
|
||||
setattr(opt, 'steps', int(post_data['steps']))
|
||||
setattr(opt, 'width', int(post_data['width']))
|
||||
setattr(opt, 'height', int(post_data['height']))
|
||||
setattr(opt, 'seamless', 'seamless' in post_data)
|
||||
setattr(opt, 'fit', 'fit' in post_data)
|
||||
setattr(opt, 'mask', 'mask' in post_data)
|
||||
setattr(opt, 'invert_mask', 'invert_mask' in post_data)
|
||||
setattr(opt, 'cfg_scale', float(post_data['cfg_scale']))
|
||||
setattr(opt, 'sampler_name', post_data['sampler_name'])
|
||||
setattr(opt, 'gfpgan_strength', float(post_data['gfpgan_strength']) if gfpgan_model_exists else 0)
|
||||
setattr(opt, 'upscale', [int(post_data['upscale_level']), float(post_data['upscale_strength'])] if post_data['upscale_level'] != '' else None)
|
||||
setattr(opt, 'progress_images', 'progress_images' in post_data)
|
||||
setattr(opt, 'seed', None if int(post_data['seed']) == -1 else int(post_data['seed']))
|
||||
setattr(opt, 'variation_amount', float(post_data['variation_amount']) if int(post_data['seed']) != -1 else 0)
|
||||
setattr(opt, 'with_variations', [])
|
||||
|
||||
broken = False
|
||||
if int(post_data['seed']) != -1 and post_data['with_variations'] != '':
|
||||
for part in post_data['with_variations'].split(','):
|
||||
seed_and_weight = part.split(':')
|
||||
if len(seed_and_weight) != 2:
|
||||
print(f'could not parse with_variation part "{part}"')
|
||||
broken = True
|
||||
break
|
||||
try:
|
||||
seed = int(seed_and_weight[0])
|
||||
weight = float(seed_and_weight[1])
|
||||
except ValueError:
|
||||
print(f'could not parse with_variation part "{part}"')
|
||||
broken = True
|
||||
break
|
||||
opt.with_variations.append([seed, weight])
|
||||
|
||||
if broken:
|
||||
raise CanceledException
|
||||
|
||||
if len(opt.with_variations) == 0:
|
||||
opt.with_variations = None
|
||||
|
||||
return opt
|
||||
|
||||
class CanceledException(Exception):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
class DreamServer(BaseHTTPRequestHandler):
|
||||
model = None
|
||||
outdir = None
|
||||
canceled = Event()
|
||||
|
||||
def do_GET(self):
|
||||
@ -30,6 +79,23 @@ class DreamServer(BaseHTTPRequestHandler):
|
||||
'gfpgan_model_exists': gfpgan_model_exists
|
||||
}
|
||||
self.wfile.write(bytes("let config = " + json.dumps(config) + ";\n", "utf-8"))
|
||||
elif self.path == "/run_log.json":
|
||||
self.send_response(200)
|
||||
self.send_header("Content-type", "application/json")
|
||||
self.end_headers()
|
||||
output = []
|
||||
|
||||
log_file = os.path.join(self.outdir, "dream_web_log.txt")
|
||||
if os.path.exists(log_file):
|
||||
with open(log_file, "r") as log:
|
||||
for line in log:
|
||||
url, config = line.split(": {", maxsplit=1)
|
||||
config = json.loads("{" + config)
|
||||
config["url"] = url.lstrip(".")
|
||||
if os.path.exists(url):
|
||||
output.append(config)
|
||||
|
||||
self.wfile.write(bytes(json.dumps({"run_log": output}), "utf-8"))
|
||||
elif self.path == "/cancel":
|
||||
self.canceled.set()
|
||||
self.send_response(200)
|
||||
@ -63,34 +129,19 @@ class DreamServer(BaseHTTPRequestHandler):
|
||||
|
||||
content_length = int(self.headers['Content-Length'])
|
||||
post_data = json.loads(self.rfile.read(content_length))
|
||||
prompt = post_data['prompt']
|
||||
initimg = post_data['initimg']
|
||||
strength = float(post_data['strength'])
|
||||
iterations = int(post_data['iterations'])
|
||||
steps = int(post_data['steps'])
|
||||
width = int(post_data['width'])
|
||||
height = int(post_data['height'])
|
||||
fit = 'fit' in post_data
|
||||
cfgscale = float(post_data['cfgscale'])
|
||||
sampler_name = post_data['sampler']
|
||||
gfpgan_strength = float(post_data['gfpgan_strength']) if gfpgan_model_exists else 0
|
||||
upscale_level = post_data['upscale_level']
|
||||
upscale_strength = post_data['upscale_strength']
|
||||
upscale = [int(upscale_level),float(upscale_strength)] if upscale_level != '' else None
|
||||
progress_images = 'progress_images' in post_data
|
||||
seed = self.model.seed if int(post_data['seed']) == -1 else int(post_data['seed'])
|
||||
opt = build_opt(post_data, self.model.seed, gfpgan_model_exists)
|
||||
|
||||
self.canceled.clear()
|
||||
print(f">> Request to generate with prompt: {prompt}")
|
||||
print(f">> Request to generate with prompt: {opt.prompt}")
|
||||
# In order to handle upscaled images, the PngWriter needs to maintain state
|
||||
# across images generated by each call to prompt2img(), so we define it in
|
||||
# the outer scope of image_done()
|
||||
config = post_data.copy() # Shallow copy
|
||||
config['initimg'] = ''
|
||||
config['initimg'] = config.pop('initimg_name', '')
|
||||
|
||||
images_generated = 0 # helps keep track of when upscaling is started
|
||||
images_upscaled = 0 # helps keep track of when upscaling is completed
|
||||
pngwriter = PngWriter("./outputs/img-samples/")
|
||||
pngwriter = PngWriter(self.outdir)
|
||||
|
||||
prefix = pngwriter.unique_prefix()
|
||||
# if upscaling is requested, then this will be called twice, once when
|
||||
@ -99,11 +150,24 @@ class DreamServer(BaseHTTPRequestHandler):
|
||||
# entry should not be inserted into the image list.
|
||||
def image_done(image, seed, upscaled=False):
|
||||
name = f'{prefix}.{seed}.png'
|
||||
path = pngwriter.save_image_and_prompt_to_png(image, f'{prompt} -S{seed}', name)
|
||||
iter_opt = argparse.Namespace(**vars(opt)) # copy
|
||||
if opt.variation_amount > 0:
|
||||
this_variation = [[seed, opt.variation_amount]]
|
||||
if opt.with_variations is None:
|
||||
iter_opt.with_variations = this_variation
|
||||
else:
|
||||
iter_opt.with_variations = opt.with_variations + this_variation
|
||||
iter_opt.variation_amount = 0
|
||||
elif opt.with_variations is None:
|
||||
iter_opt.seed = seed
|
||||
normalized_prompt = PromptFormatter(self.model, iter_opt).normalize_prompt()
|
||||
path = pngwriter.save_image_and_prompt_to_png(image, f'{normalized_prompt} -S{iter_opt.seed}', name)
|
||||
|
||||
if int(config['seed']) == -1:
|
||||
config['seed'] = seed
|
||||
# Append post_data to log, but only once!
|
||||
if not upscaled:
|
||||
with open("./outputs/img-samples/dream_web_log.txt", "a") as log:
|
||||
with open(os.path.join(self.outdir, "dream_web_log.txt"), "a") as log:
|
||||
log.write(f"{path}: {json.dumps(config)}\n")
|
||||
|
||||
self.wfile.write(bytes(json.dumps(
|
||||
@ -111,7 +175,7 @@ class DreamServer(BaseHTTPRequestHandler):
|
||||
) + '\n',"utf-8"))
|
||||
|
||||
# control state of the "postprocessing..." message
|
||||
upscaling_requested = upscale or gfpgan_strength>0
|
||||
upscaling_requested = opt.upscale or opt.gfpgan_strength > 0
|
||||
nonlocal images_generated # NB: Is this bad python style? It is typical usage in a perl closure.
|
||||
nonlocal images_upscaled # NB: Is this bad python style? It is typical usage in a perl closure.
|
||||
if upscaled:
|
||||
@ -120,18 +184,18 @@ class DreamServer(BaseHTTPRequestHandler):
|
||||
images_generated += 1
|
||||
if upscaling_requested:
|
||||
action = None
|
||||
if images_generated >= iterations:
|
||||
if images_upscaled < iterations:
|
||||
if images_generated >= opt.iterations:
|
||||
if images_upscaled < opt.iterations:
|
||||
action = 'upscaling-started'
|
||||
else:
|
||||
action = 'upscaling-done'
|
||||
if action:
|
||||
x = images_upscaled + 1
|
||||
self.wfile.write(bytes(json.dumps(
|
||||
{'event':action,'processed_file_cnt':f'{x}/{iterations}'}
|
||||
{'event': action, 'processed_file_cnt': f'{x}/{opt.iterations}'}
|
||||
) + '\n',"utf-8"))
|
||||
|
||||
step_writer = PngWriter('./outputs/intermediates/')
|
||||
step_writer = PngWriter(os.path.join(self.outdir, "intermediates"))
|
||||
step_index = 1
|
||||
def image_progress(sample, step):
|
||||
if self.canceled.is_set():
|
||||
@ -141,10 +205,10 @@ class DreamServer(BaseHTTPRequestHandler):
|
||||
# since rendering images is moderately expensive, only render every 5th image
|
||||
# and don't bother with the last one, since it'll render anyway
|
||||
nonlocal step_index
|
||||
if progress_images and step % 5 == 0 and step < steps - 1:
|
||||
image = self.model._sample_to_image(sample)
|
||||
name = f'{prefix}.{seed}.{step_index}.png'
|
||||
metadata = f'{prompt} -S{seed} [intermediate]'
|
||||
if opt.progress_images and step % 5 == 0 and step < opt.steps - 1:
|
||||
image = self.model.sample_to_image(sample)
|
||||
name = f'{prefix}.{opt.seed}.{step_index}.png'
|
||||
metadata = f'{opt.prompt} -S{opt.seed} [intermediate]'
|
||||
path = step_writer.save_image_and_prompt_to_png(image, metadata, name)
|
||||
step_index += 1
|
||||
self.wfile.write(bytes(json.dumps(
|
||||
@ -152,43 +216,20 @@ class DreamServer(BaseHTTPRequestHandler):
|
||||
) + '\n',"utf-8"))
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
if initimg is None:
|
||||
if opt.init_img is None:
|
||||
# Run txt2img
|
||||
self.model.prompt2image(prompt,
|
||||
iterations=iterations,
|
||||
cfg_scale = cfgscale,
|
||||
width = width,
|
||||
height = height,
|
||||
seed = seed,
|
||||
steps = steps,
|
||||
gfpgan_strength = gfpgan_strength,
|
||||
upscale = upscale,
|
||||
sampler_name = sampler_name,
|
||||
step_callback=image_progress,
|
||||
image_callback=image_done)
|
||||
self.model.prompt2image(**vars(opt), step_callback=image_progress, image_callback=image_done)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# Decode initimg as base64 to temp file
|
||||
with open("./img2img-tmp.png", "wb") as f:
|
||||
initimg = initimg.split(",")[1] # Ignore mime type
|
||||
initimg = opt.init_img.split(",")[1] # Ignore mime type
|
||||
f.write(base64.b64decode(initimg))
|
||||
opt1 = argparse.Namespace(**vars(opt))
|
||||
opt1.init_img = "./img2img-tmp.png"
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
# Run img2img
|
||||
self.model.prompt2image(prompt,
|
||||
init_img = "./img2img-tmp.png",
|
||||
strength = strength,
|
||||
iterations = iterations,
|
||||
cfg_scale = cfgscale,
|
||||
seed = seed,
|
||||
steps = steps,
|
||||
sampler_name = sampler_name,
|
||||
width = width,
|
||||
height = height,
|
||||
fit = fit,
|
||||
gfpgan_strength=gfpgan_strength,
|
||||
upscale = upscale,
|
||||
step_callback=image_progress,
|
||||
image_callback=image_done)
|
||||
self.model.prompt2image(**vars(opt1), step_callback=image_progress, image_callback=image_done)
|
||||
finally:
|
||||
# Remove the temp file
|
||||
os.remove("./img2img-tmp.png")
|
||||
|
||||
695
ldm/generate.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,695 @@
|
||||
# Copyright (c) 2022 Lincoln D. Stein (https://github.com/lstein)
|
||||
|
||||
# Derived from source code carrying the following copyrights
|
||||
# Copyright (c) 2022 Machine Vision and Learning Group, LMU Munich
|
||||
# Copyright (c) 2022 Robin Rombach and Patrick Esser and contributors
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import random
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import time
|
||||
import re
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import traceback
|
||||
import transformers
|
||||
|
||||
from omegaconf import OmegaConf
|
||||
from PIL import Image, ImageOps
|
||||
from torch import nn
|
||||
from pytorch_lightning import seed_everything
|
||||
|
||||
from ldm.util import instantiate_from_config
|
||||
from ldm.models.diffusion.ddim import DDIMSampler
|
||||
from ldm.models.diffusion.plms import PLMSSampler
|
||||
from ldm.models.diffusion.ksampler import KSampler
|
||||
from ldm.dream.pngwriter import PngWriter
|
||||
from ldm.dream.image_util import InitImageResizer
|
||||
from ldm.dream.devices import choose_torch_device
|
||||
from ldm.dream.conditioning import get_uc_and_c
|
||||
|
||||
"""Simplified text to image API for stable diffusion/latent diffusion
|
||||
|
||||
Example Usage:
|
||||
|
||||
from ldm.generate import Generate
|
||||
|
||||
# Create an object with default values
|
||||
gr = Generate()
|
||||
|
||||
# do the slow model initialization
|
||||
gr.load_model()
|
||||
|
||||
# Do the fast inference & image generation. Any options passed here
|
||||
# override the default values assigned during class initialization
|
||||
# Will call load_model() if the model was not previously loaded and so
|
||||
# may be slow at first.
|
||||
# The method returns a list of images. Each row of the list is a sub-list of [filename,seed]
|
||||
results = gr.prompt2png(prompt = "an astronaut riding a horse",
|
||||
outdir = "./outputs/samples",
|
||||
iterations = 3)
|
||||
|
||||
for row in results:
|
||||
print(f'filename={row[0]}')
|
||||
print(f'seed ={row[1]}')
|
||||
|
||||
# Same thing, but using an initial image.
|
||||
results = gr.prompt2png(prompt = "an astronaut riding a horse",
|
||||
outdir = "./outputs/,
|
||||
iterations = 3,
|
||||
init_img = "./sketches/horse+rider.png")
|
||||
|
||||
for row in results:
|
||||
print(f'filename={row[0]}')
|
||||
print(f'seed ={row[1]}')
|
||||
|
||||
# Same thing, but we return a series of Image objects, which lets you manipulate them,
|
||||
# combine them, and save them under arbitrary names
|
||||
|
||||
results = gr.prompt2image(prompt = "an astronaut riding a horse"
|
||||
outdir = "./outputs/")
|
||||
for row in results:
|
||||
im = row[0]
|
||||
seed = row[1]
|
||||
im.save(f'./outputs/samples/an_astronaut_riding_a_horse-{seed}.png')
|
||||
im.thumbnail(100,100).save('./outputs/samples/astronaut_thumb.jpg')
|
||||
|
||||
Note that the old txt2img() and img2img() calls are deprecated but will
|
||||
still work.
|
||||
|
||||
The full list of arguments to Generate() are:
|
||||
gr = Generate(
|
||||
weights = path to model weights ('models/ldm/stable-diffusion-v1/model.ckpt')
|
||||
config = path to model configuraiton ('configs/stable-diffusion/v1-inference.yaml')
|
||||
iterations = <integer> // how many times to run the sampling (1)
|
||||
steps = <integer> // 50
|
||||
seed = <integer> // current system time
|
||||
sampler_name= ['ddim', 'k_dpm_2_a', 'k_dpm_2', 'k_euler_a', 'k_euler', 'k_heun', 'k_lms', 'plms'] // k_lms
|
||||
grid = <boolean> // false
|
||||
width = <integer> // image width, multiple of 64 (512)
|
||||
height = <integer> // image height, multiple of 64 (512)
|
||||
cfg_scale = <float> // condition-free guidance scale (7.5)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Generate:
|
||||
"""Generate class
|
||||
Stores default values for multiple configuration items
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
iterations = 1,
|
||||
steps = 50,
|
||||
cfg_scale = 7.5,
|
||||
weights = 'models/ldm/stable-diffusion-v1/model.ckpt',
|
||||
config = 'configs/stable-diffusion/v1-inference.yaml',
|
||||
grid = False,
|
||||
width = 512,
|
||||
height = 512,
|
||||
sampler_name = 'k_lms',
|
||||
ddim_eta = 0.0, # deterministic
|
||||
precision = 'autocast',
|
||||
full_precision = False,
|
||||
strength = 0.75, # default in scripts/img2img.py
|
||||
seamless = False,
|
||||
embedding_path = None,
|
||||
device_type = 'cuda',
|
||||
ignore_ctrl_c = False,
|
||||
):
|
||||
self.iterations = iterations
|
||||
self.width = width
|
||||
self.height = height
|
||||
self.steps = steps
|
||||
self.cfg_scale = cfg_scale
|
||||
self.weights = weights
|
||||
self.config = config
|
||||
self.sampler_name = sampler_name
|
||||
self.grid = grid
|
||||
self.ddim_eta = ddim_eta
|
||||
self.precision = precision
|
||||
self.full_precision = True if choose_torch_device() == 'mps' else full_precision
|
||||
self.strength = strength
|
||||
self.seamless = seamless
|
||||
self.embedding_path = embedding_path
|
||||
self.device_type = device_type
|
||||
self.ignore_ctrl_c = ignore_ctrl_c # note, this logic probably doesn't belong here...
|
||||
self.model = None # empty for now
|
||||
self.sampler = None
|
||||
self.device = None
|
||||
self.generators = {}
|
||||
self.base_generator = None
|
||||
self.seed = None
|
||||
|
||||
if device_type == 'cuda' and not torch.cuda.is_available():
|
||||
device_type = choose_torch_device()
|
||||
print(">> cuda not available, using device", device_type)
|
||||
self.device = torch.device(device_type)
|
||||
|
||||
# for VRAM usage statistics
|
||||
device_type = choose_torch_device()
|
||||
self.session_peakmem = torch.cuda.max_memory_allocated() if device_type == 'cuda' else None
|
||||
transformers.logging.set_verbosity_error()
|
||||
|
||||
def prompt2png(self, prompt, outdir, **kwargs):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Takes a prompt and an output directory, writes out the requested number
|
||||
of PNG files, and returns an array of [[filename,seed],[filename,seed]...]
|
||||
Optional named arguments are the same as those passed to Generate and prompt2image()
|
||||
"""
|
||||
results = self.prompt2image(prompt, **kwargs)
|
||||
pngwriter = PngWriter(outdir)
|
||||
prefix = pngwriter.unique_prefix()
|
||||
outputs = []
|
||||
for image, seed in results:
|
||||
name = f'{prefix}.{seed}.png'
|
||||
path = pngwriter.save_image_and_prompt_to_png(
|
||||
image, f'{prompt} -S{seed}', name)
|
||||
outputs.append([path, seed])
|
||||
return outputs
|
||||
|
||||
def txt2img(self, prompt, **kwargs):
|
||||
outdir = kwargs.pop('outdir', 'outputs/img-samples')
|
||||
return self.prompt2png(prompt, outdir, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
def img2img(self, prompt, **kwargs):
|
||||
outdir = kwargs.pop('outdir', 'outputs/img-samples')
|
||||
assert (
|
||||
'init_img' in kwargs
|
||||
), 'call to img2img() must include the init_img argument'
|
||||
return self.prompt2png(prompt, outdir, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
def prompt2image(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
# these are common
|
||||
prompt,
|
||||
iterations = None,
|
||||
steps = None,
|
||||
seed = None,
|
||||
cfg_scale = None,
|
||||
ddim_eta = None,
|
||||
skip_normalize = False,
|
||||
image_callback = None,
|
||||
step_callback = None,
|
||||
width = None,
|
||||
height = None,
|
||||
sampler_name = None,
|
||||
seamless = False,
|
||||
log_tokenization= False,
|
||||
with_variations = None,
|
||||
variation_amount = 0.0,
|
||||
# these are specific to img2img and inpaint
|
||||
init_img = None,
|
||||
init_mask = None,
|
||||
fit = False,
|
||||
strength = None,
|
||||
# these are specific to GFPGAN/ESRGAN
|
||||
gfpgan_strength= 0,
|
||||
save_original = False,
|
||||
upscale = None,
|
||||
**args,
|
||||
): # eat up additional cruft
|
||||
"""
|
||||
ldm.generate.prompt2image() is the common entry point for txt2img() and img2img()
|
||||
It takes the following arguments:
|
||||
prompt // prompt string (no default)
|
||||
iterations // iterations (1); image count=iterations
|
||||
steps // refinement steps per iteration
|
||||
seed // seed for random number generator
|
||||
width // width of image, in multiples of 64 (512)
|
||||
height // height of image, in multiples of 64 (512)
|
||||
cfg_scale // how strongly the prompt influences the image (7.5) (must be >1)
|
||||
seamless // whether the generated image should tile
|
||||
init_img // path to an initial image
|
||||
strength // strength for noising/unnoising init_img. 0.0 preserves image exactly, 1.0 replaces it completely
|
||||
gfpgan_strength // strength for GFPGAN. 0.0 preserves image exactly, 1.0 replaces it completely
|
||||
ddim_eta // image randomness (eta=0.0 means the same seed always produces the same image)
|
||||
step_callback // a function or method that will be called each step
|
||||
image_callback // a function or method that will be called each time an image is generated
|
||||
with_variations // a weighted list [(seed_1, weight_1), (seed_2, weight_2), ...] of variations which should be applied before doing any generation
|
||||
variation_amount // optional 0-1 value to slerp from -S noise to random noise (allows variations on an image)
|
||||
|
||||
To use the step callback, define a function that receives two arguments:
|
||||
- Image GPU data
|
||||
- The step number
|
||||
|
||||
To use the image callback, define a function of method that receives two arguments, an Image object
|
||||
and the seed. You can then do whatever you like with the image, including converting it to
|
||||
different formats and manipulating it. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
def process_image(image,seed):
|
||||
image.save(f{'images/seed.png'})
|
||||
|
||||
The callback used by the prompt2png() can be found in ldm/dream_util.py. It contains code
|
||||
to create the requested output directory, select a unique informative name for each image, and
|
||||
write the prompt into the PNG metadata.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# TODO: convert this into a getattr() loop
|
||||
steps = steps or self.steps
|
||||
width = width or self.width
|
||||
height = height or self.height
|
||||
seamless = seamless or self.seamless
|
||||
cfg_scale = cfg_scale or self.cfg_scale
|
||||
ddim_eta = ddim_eta or self.ddim_eta
|
||||
iterations = iterations or self.iterations
|
||||
strength = strength or self.strength
|
||||
self.seed = seed
|
||||
self.log_tokenization = log_tokenization
|
||||
with_variations = [] if with_variations is None else with_variations
|
||||
|
||||
model = (
|
||||
self.load_model()
|
||||
) # will instantiate the model or return it from cache
|
||||
|
||||
for m in model.modules():
|
||||
if isinstance(m, (nn.Conv2d, nn.ConvTranspose2d)):
|
||||
m.padding_mode = 'circular' if seamless else m._orig_padding_mode
|
||||
|
||||
assert cfg_scale > 1.0, 'CFG_Scale (-C) must be >1.0'
|
||||
assert (
|
||||
0.0 < strength < 1.0
|
||||
), 'img2img and inpaint strength can only work with 0.0 < strength < 1.0'
|
||||
assert (
|
||||
0.0 <= variation_amount <= 1.0
|
||||
), '-v --variation_amount must be in [0.0, 1.0]'
|
||||
|
||||
# check this logic - doesn't look right
|
||||
if len(with_variations) > 0 or variation_amount > 1.0:
|
||||
assert seed is not None,\
|
||||
'seed must be specified when using with_variations'
|
||||
if variation_amount == 0.0:
|
||||
assert iterations == 1,\
|
||||
'when using --with_variations, multiple iterations are only possible when using --variation_amount'
|
||||
assert all(0 <= weight <= 1 for _, weight in with_variations),\
|
||||
f'variation weights must be in [0.0, 1.0]: got {[weight for _, weight in with_variations]}'
|
||||
|
||||
width, height, _ = self._resolution_check(width, height, log=True)
|
||||
|
||||
if sampler_name and (sampler_name != self.sampler_name):
|
||||
self.sampler_name = sampler_name
|
||||
self._set_sampler()
|
||||
|
||||
tic = time.time()
|
||||
if torch.cuda.is_available():
|
||||
torch.cuda.reset_peak_memory_stats()
|
||||
|
||||
results = list()
|
||||
init_image = None
|
||||
mask_image = None
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
uc, c = get_uc_and_c(
|
||||
prompt, model=self.model,
|
||||
skip_normalize=skip_normalize,
|
||||
log_tokens=self.log_tokenization
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
(init_image,mask_image) = self._make_images(init_img,init_mask, width, height, fit)
|
||||
|
||||
if (init_image is not None) and (mask_image is not None):
|
||||
generator = self._make_inpaint()
|
||||
elif init_image is not None:
|
||||
generator = self._make_img2img()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
generator = self._make_txt2img()
|
||||
|
||||
generator.set_variation(self.seed, variation_amount, with_variations)
|
||||
results = generator.generate(
|
||||
prompt,
|
||||
iterations = iterations,
|
||||
seed = self.seed,
|
||||
sampler = self.sampler,
|
||||
steps = steps,
|
||||
cfg_scale = cfg_scale,
|
||||
conditioning = (uc,c),
|
||||
ddim_eta = ddim_eta,
|
||||
image_callback = image_callback, # called after the final image is generated
|
||||
step_callback = step_callback, # called after each intermediate image is generated
|
||||
width = width,
|
||||
height = height,
|
||||
init_image = init_image, # notice that init_image is different from init_img
|
||||
mask_image = mask_image,
|
||||
strength = strength,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if upscale is not None or gfpgan_strength > 0:
|
||||
self.upscale_and_reconstruct(results,
|
||||
upscale = upscale,
|
||||
strength = gfpgan_strength,
|
||||
save_original = save_original,
|
||||
image_callback = image_callback)
|
||||
|
||||
except KeyboardInterrupt:
|
||||
print('*interrupted*')
|
||||
if not self.ignore_ctrl_c:
|
||||
raise KeyboardInterrupt
|
||||
print(
|
||||
'>> Partial results will be returned; if --grid was requested, nothing will be returned.'
|
||||
)
|
||||
except RuntimeError as e:
|
||||
print(traceback.format_exc(), file=sys.stderr)
|
||||
print('>> Could not generate image.')
|
||||
|
||||
toc = time.time()
|
||||
print('>> Usage stats:')
|
||||
print(
|
||||
f'>> {len(results)} image(s) generated in', '%4.2fs' % (toc - tic)
|
||||
)
|
||||
if torch.cuda.is_available() and self.device.type == 'cuda':
|
||||
print(
|
||||
f'>> Max VRAM used for this generation:',
|
||||
'%4.2fG.' % (torch.cuda.max_memory_allocated() / 1e9),
|
||||
'Current VRAM utilization:'
|
||||
'%4.2fG' % (torch.cuda.memory_allocated() / 1e9),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
self.session_peakmem = max(
|
||||
self.session_peakmem, torch.cuda.max_memory_allocated()
|
||||
)
|
||||
print(
|
||||
f'>> Max VRAM used since script start: ',
|
||||
'%4.2fG' % (self.session_peakmem / 1e9),
|
||||
)
|
||||
return results
|
||||
|
||||
def _make_images(self, img_path, mask_path, width, height, fit=False):
|
||||
init_image = None
|
||||
init_mask = None
|
||||
if not img_path:
|
||||
return None,None
|
||||
|
||||
image = self._load_img(img_path, width, height, fit=fit) # this returns an Image
|
||||
init_image = self._create_init_image(image) # this returns a torch tensor
|
||||
|
||||
if self._has_transparency(image) and not mask_path: # if image has a transparent area and no mask was provided, then try to generate mask
|
||||
print('>> Initial image has transparent areas. Will inpaint in these regions.')
|
||||
if self._check_for_erasure(image):
|
||||
print(
|
||||
'>> WARNING: Colors underneath the transparent region seem to have been erased.\n',
|
||||
'>> Inpainting will be suboptimal. Please preserve the colors when making\n',
|
||||
'>> a transparency mask, or provide mask explicitly using --init_mask (-M).'
|
||||
)
|
||||
init_mask = self._create_init_mask(image) # this returns a torch tensor
|
||||
|
||||
if mask_path:
|
||||
mask_image = self._load_img(mask_path, width, height, fit=fit) # this returns an Image
|
||||
init_mask = self._create_init_mask(mask_image)
|
||||
|
||||
return init_image,init_mask
|
||||
|
||||
def _make_img2img(self):
|
||||
if not self.generators.get('img2img'):
|
||||
from ldm.dream.generator.img2img import Img2Img
|
||||
self.generators['img2img'] = Img2Img(self.model)
|
||||
return self.generators['img2img']
|
||||
|
||||
def _make_txt2img(self):
|
||||
if not self.generators.get('txt2img'):
|
||||
from ldm.dream.generator.txt2img import Txt2Img
|
||||
self.generators['txt2img'] = Txt2Img(self.model)
|
||||
return self.generators['txt2img']
|
||||
|
||||
def _make_inpaint(self):
|
||||
if not self.generators.get('inpaint'):
|
||||
from ldm.dream.generator.inpaint import Inpaint
|
||||
self.generators['inpaint'] = Inpaint(self.model)
|
||||
return self.generators['inpaint']
|
||||
|
||||
def load_model(self):
|
||||
"""Load and initialize the model from configuration variables passed at object creation time"""
|
||||
if self.model is None:
|
||||
seed_everything(random.randrange(0, np.iinfo(np.uint32).max))
|
||||
try:
|
||||
config = OmegaConf.load(self.config)
|
||||
model = self._load_model_from_config(config, self.weights)
|
||||
if self.embedding_path is not None:
|
||||
model.embedding_manager.load(
|
||||
self.embedding_path, self.full_precision
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.model = model.to(self.device)
|
||||
# model.to doesn't change the cond_stage_model.device used to move the tokenizer output, so set it here
|
||||
self.model.cond_stage_model.device = self.device
|
||||
except AttributeError as e:
|
||||
print(f'>> Error loading model. {str(e)}', file=sys.stderr)
|
||||
print(traceback.format_exc(), file=sys.stderr)
|
||||
raise SystemExit from e
|
||||
|
||||
self._set_sampler()
|
||||
|
||||
for m in self.model.modules():
|
||||
if isinstance(m, (nn.Conv2d, nn.ConvTranspose2d)):
|
||||
m._orig_padding_mode = m.padding_mode
|
||||
|
||||
return self.model
|
||||
|
||||
def upscale_and_reconstruct(self,
|
||||
image_list,
|
||||
upscale = None,
|
||||
strength = 0.0,
|
||||
save_original = False,
|
||||
image_callback = None):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
if upscale is not None:
|
||||
from ldm.gfpgan.gfpgan_tools import real_esrgan_upscale
|
||||
if strength > 0:
|
||||
from ldm.gfpgan.gfpgan_tools import run_gfpgan
|
||||
except (ModuleNotFoundError, ImportError):
|
||||
print(traceback.format_exc(), file=sys.stderr)
|
||||
print('>> You may need to install the ESRGAN and/or GFPGAN modules')
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
for r in image_list:
|
||||
image, seed = r
|
||||
try:
|
||||
if upscale is not None:
|
||||
if len(upscale) < 2:
|
||||
upscale.append(0.75)
|
||||
image = real_esrgan_upscale(
|
||||
image,
|
||||
upscale[1],
|
||||
int(upscale[0]),
|
||||
seed,
|
||||
)
|
||||
if strength > 0:
|
||||
image = run_gfpgan(
|
||||
image, strength, seed, 1
|
||||
)
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
print(
|
||||
f'>> Error running RealESRGAN or GFPGAN. Your image was not upscaled.\n{e}'
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if image_callback is not None:
|
||||
image_callback(image, seed, upscaled=True)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
r[0] = image
|
||||
|
||||
# to help WebGUI - front end to generator util function
|
||||
def sample_to_image(self,samples):
|
||||
return self._sample_to_image(samples)
|
||||
|
||||
def _sample_to_image(self,samples):
|
||||
if not self.base_generator:
|
||||
from ldm.dream.generator import Generator
|
||||
self.base_generator = Generator(self.model)
|
||||
return self.base_generator.sample_to_image(samples)
|
||||
|
||||
def _set_sampler(self):
|
||||
msg = f'>> Setting Sampler to {self.sampler_name}'
|
||||
if self.sampler_name == 'plms':
|
||||
self.sampler = PLMSSampler(self.model, device=self.device)
|
||||
elif self.sampler_name == 'ddim':
|
||||
self.sampler = DDIMSampler(self.model, device=self.device)
|
||||
elif self.sampler_name == 'k_dpm_2_a':
|
||||
self.sampler = KSampler(
|
||||
self.model, 'dpm_2_ancestral', device=self.device
|
||||
)
|
||||
elif self.sampler_name == 'k_dpm_2':
|
||||
self.sampler = KSampler(self.model, 'dpm_2', device=self.device)
|
||||
elif self.sampler_name == 'k_euler_a':
|
||||
self.sampler = KSampler(
|
||||
self.model, 'euler_ancestral', device=self.device
|
||||
)
|
||||
elif self.sampler_name == 'k_euler':
|
||||
self.sampler = KSampler(self.model, 'euler', device=self.device)
|
||||
elif self.sampler_name == 'k_heun':
|
||||
self.sampler = KSampler(self.model, 'heun', device=self.device)
|
||||
elif self.sampler_name == 'k_lms':
|
||||
self.sampler = KSampler(self.model, 'lms', device=self.device)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
msg = f'>> Unsupported Sampler: {self.sampler_name}, Defaulting to plms'
|
||||
self.sampler = PLMSSampler(self.model, device=self.device)
|
||||
|
||||
print(msg)
|
||||
|
||||
def _load_model_from_config(self, config, ckpt):
|
||||
print(f'>> Loading model from {ckpt}')
|
||||
|
||||
# for usage statistics
|
||||
device_type = choose_torch_device()
|
||||
if device_type == 'cuda':
|
||||
torch.cuda.reset_peak_memory_stats()
|
||||
tic = time.time()
|
||||
|
||||
# this does the work
|
||||
pl_sd = torch.load(ckpt, map_location='cpu')
|
||||
sd = pl_sd['state_dict']
|
||||
model = instantiate_from_config(config.model)
|
||||
m, u = model.load_state_dict(sd, strict=False)
|
||||
|
||||
if self.full_precision:
|
||||
print(
|
||||
'>> Using slower but more accurate full-precision math (--full_precision)'
|
||||
)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print(
|
||||
'>> Using half precision math. Call with --full_precision to use more accurate but VRAM-intensive full precision.'
|
||||
)
|
||||
model.half()
|
||||
model.to(self.device)
|
||||
model.eval()
|
||||
|
||||
# usage statistics
|
||||
toc = time.time()
|
||||
print(
|
||||
f'>> Model loaded in', '%4.2fs' % (toc - tic)
|
||||
)
|
||||
if device_type == 'cuda':
|
||||
print(
|
||||
'>> Max VRAM used to load the model:',
|
||||
'%4.2fG' % (torch.cuda.max_memory_allocated() / 1e9),
|
||||
'\n>> Current VRAM usage:'
|
||||
'%4.2fG' % (torch.cuda.memory_allocated() / 1e9),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
return model
|
||||
|
||||
def _load_img(self, path, width, height, fit=False):
|
||||
assert os.path.exists(path), f'>> {path}: File not found'
|
||||
|
||||
# with Image.open(path) as img:
|
||||
# image = img.convert('RGBA')
|
||||
image = Image.open(path)
|
||||
print(
|
||||
f'>> loaded input image of size {image.width}x{image.height} from {path}'
|
||||
)
|
||||
if fit:
|
||||
image = self._fit_image(image,(width,height))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
image = self._squeeze_image(image)
|
||||
return image
|
||||
|
||||
def _create_init_image(self,image):
|
||||
image = image.convert('RGB')
|
||||
# print(
|
||||
# f'>> DEBUG: writing the image to img.png'
|
||||
# )
|
||||
# image.save('img.png')
|
||||
image = np.array(image).astype(np.float32) / 255.0
|
||||
image = image[None].transpose(0, 3, 1, 2)
|
||||
image = torch.from_numpy(image)
|
||||
image = 2.0 * image - 1.0
|
||||
return image.to(self.device)
|
||||
|
||||
def _create_init_mask(self, image):
|
||||
# convert into a black/white mask
|
||||
image = self._image_to_mask(image)
|
||||
image = image.convert('RGB')
|
||||
# BUG: We need to use the model's downsample factor rather than hardcoding "8"
|
||||
from ldm.dream.generator.base import downsampling
|
||||
image = image.resize((image.width//downsampling, image.height//downsampling), resample=Image.Resampling.LANCZOS)
|
||||
# print(
|
||||
# f'>> DEBUG: writing the mask to mask.png'
|
||||
# )
|
||||
# image.save('mask.png')
|
||||
image = np.array(image)
|
||||
image = image.astype(np.float32) / 255.0
|
||||
image = image[None].transpose(0, 3, 1, 2)
|
||||
image = torch.from_numpy(image)
|
||||
return image.to(self.device)
|
||||
|
||||
# The mask is expected to have the region to be inpainted
|
||||
# with alpha transparency. It converts it into a black/white
|
||||
# image with the transparent part black.
|
||||
def _image_to_mask(self, mask_image, invert=False) -> Image:
|
||||
# Obtain the mask from the transparency channel
|
||||
mask = Image.new(mode="L", size=mask_image.size, color=255)
|
||||
mask.putdata(mask_image.getdata(band=3))
|
||||
if invert:
|
||||
mask = ImageOps.invert(mask)
|
||||
return mask
|
||||
|
||||
def _has_transparency(self,image):
|
||||
if image.info.get("transparency", None) is not None:
|
||||
return True
|
||||
if image.mode == "P":
|
||||
transparent = image.info.get("transparency", -1)
|
||||
for _, index in image.getcolors():
|
||||
if index == transparent:
|
||||
return True
|
||||
elif image.mode == "RGBA":
|
||||
extrema = image.getextrema()
|
||||
if extrema[3][0] < 255:
|
||||
return True
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _check_for_erasure(self,image):
|
||||
width, height = image.size
|
||||
pixdata = image.load()
|
||||
colored = 0
|
||||
for y in range(height):
|
||||
for x in range(width):
|
||||
if pixdata[x, y][3] == 0:
|
||||
r, g, b, _ = pixdata[x, y]
|
||||
if (r, g, b) != (0, 0, 0) and \
|
||||
(r, g, b) != (255, 255, 255):
|
||||
colored += 1
|
||||
return colored == 0
|
||||
|
||||
def _squeeze_image(self,image):
|
||||
x,y,resize_needed = self._resolution_check(image.width,image.height)
|
||||
if resize_needed:
|
||||
return InitImageResizer(image).resize(x,y)
|
||||
return image
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _fit_image(self,image,max_dimensions):
|
||||
w,h = max_dimensions
|
||||
print(
|
||||
f'>> image will be resized to fit inside a box {w}x{h} in size.'
|
||||
)
|
||||
if image.width > image.height:
|
||||
h = None # by setting h to none, we tell InitImageResizer to fit into the width and calculate height
|
||||
elif image.height > image.width:
|
||||
w = None # ditto for w
|
||||
else:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
image = InitImageResizer(image).resize(w,h) # note that InitImageResizer does the multiple of 64 truncation internally
|
||||
print(
|
||||
f'>> after adjusting image dimensions to be multiples of 64, init image is {image.width}x{image.height}'
|
||||
)
|
||||
return image
|
||||
|
||||
def _resolution_check(self, width, height, log=False):
|
||||
resize_needed = False
|
||||
w, h = map(
|
||||
lambda x: x - x % 64, (width, height)
|
||||
) # resize to integer multiple of 64
|
||||
if h != height or w != width:
|
||||
if log:
|
||||
print(
|
||||
f'>> Provided width and height must be multiples of 64. Auto-resizing to {w}x{h}'
|
||||
)
|
||||
height = h
|
||||
width = w
|
||||
resize_needed = True
|
||||
|
||||
if (width * height) > (self.width * self.height):
|
||||
print(">> This input is larger than your defaults. If you run out of memory, please use a smaller image.")
|
||||
|
||||
return width, height, resize_needed
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -9,12 +9,11 @@ from scripts.dream import create_argv_parser
|
||||
|
||||
arg_parser = create_argv_parser()
|
||||
opt = arg_parser.parse_args()
|
||||
|
||||
model_path = os.path.join(opt.gfpgan_dir, opt.gfpgan_model_path)
|
||||
gfpgan_model_exists = os.path.isfile(model_path)
|
||||
|
||||
def _run_gfpgan(image, strength, prompt, seed, upsampler_scale=4):
|
||||
print(f'>> GFPGAN - Restoring Faces: {prompt} : seed:{seed}')
|
||||
def run_gfpgan(image, strength, seed, upsampler_scale=4):
|
||||
print(f'>> GFPGAN - Restoring Faces for image seed:{seed}')
|
||||
gfpgan = None
|
||||
with warnings.catch_warnings():
|
||||
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore', category=DeprecationWarning)
|
||||
@ -46,7 +45,10 @@ def _run_gfpgan(image, strength, prompt, seed, upsampler_scale=4):
|
||||
|
||||
if gfpgan is None:
|
||||
print(
|
||||
f'>> GFPGAN not initialized, it must be loaded via the --gfpgan argument'
|
||||
f'>> WARNING: GFPGAN not initialized.'
|
||||
)
|
||||
print(
|
||||
f'>> Download https://github.com/TencentARC/GFPGAN/releases/download/v1.3.0/GFPGANv1.3.pth to {model_path}, \nor change GFPGAN directory with --gfpgan_dir.'
|
||||
)
|
||||
return image
|
||||
|
||||
@ -75,13 +77,11 @@ def _run_gfpgan(image, strength, prompt, seed, upsampler_scale=4):
|
||||
|
||||
def _load_gfpgan_bg_upsampler(bg_upsampler, upsampler_scale, bg_tile=400):
|
||||
if bg_upsampler == 'realesrgan':
|
||||
if not torch.cuda.is_available(): # CPU
|
||||
warnings.warn(
|
||||
'The unoptimized RealESRGAN is slow on CPU. We do not use it. '
|
||||
'If you really want to use it, please modify the corresponding codes.'
|
||||
)
|
||||
bg_upsampler = None
|
||||
if not torch.cuda.is_available(): # CPU or MPS on M1
|
||||
use_half_precision = False
|
||||
else:
|
||||
use_half_precision = True
|
||||
|
||||
model_path = {
|
||||
2: 'https://github.com/xinntao/Real-ESRGAN/releases/download/v0.2.1/RealESRGAN_x2plus.pth',
|
||||
4: 'https://github.com/xinntao/Real-ESRGAN/releases/download/v0.1.0/RealESRGAN_x4plus.pth',
|
||||
@ -119,17 +119,17 @@ def _load_gfpgan_bg_upsampler(bg_upsampler, upsampler_scale, bg_tile=400):
|
||||
tile=bg_tile,
|
||||
tile_pad=10,
|
||||
pre_pad=0,
|
||||
half=True,
|
||||
) # need to set False in CPU mode
|
||||
half=use_half_precision,
|
||||
)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
bg_upsampler = None
|
||||
|
||||
return bg_upsampler
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def real_esrgan_upscale(image, strength, upsampler_scale, prompt, seed):
|
||||
def real_esrgan_upscale(image, strength, upsampler_scale, seed):
|
||||
print(
|
||||
f'>> Real-ESRGAN Upscaling: {prompt} : seed:{seed} : scale:{upsampler_scale}x'
|
||||
f'>> Real-ESRGAN Upscaling seed:{seed} : scale:{upsampler_scale}x'
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
with warnings.catch_warnings():
|
||||
|
||||
@ -171,6 +171,7 @@ class DDIMSampler(object):
|
||||
)
|
||||
return samples, intermediates
|
||||
|
||||
# This routine gets called from img2img
|
||||
@torch.no_grad()
|
||||
def ddim_sampling(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
@ -270,6 +271,7 @@ class DDIMSampler(object):
|
||||
|
||||
return img, intermediates
|
||||
|
||||
# This routine gets called from ddim_sampling() and decode()
|
||||
@torch.no_grad()
|
||||
def p_sample_ddim(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
@ -380,6 +382,8 @@ class DDIMSampler(object):
|
||||
unconditional_guidance_scale=1.0,
|
||||
unconditional_conditioning=None,
|
||||
use_original_steps=False,
|
||||
init_latent = None,
|
||||
mask = None,
|
||||
):
|
||||
|
||||
timesteps = (
|
||||
@ -395,6 +399,8 @@ class DDIMSampler(object):
|
||||
|
||||
iterator = tqdm(time_range, desc='Decoding image', total=total_steps)
|
||||
x_dec = x_latent
|
||||
x0 = init_latent
|
||||
|
||||
for i, step in enumerate(iterator):
|
||||
index = total_steps - i - 1
|
||||
ts = torch.full(
|
||||
@ -403,6 +409,14 @@ class DDIMSampler(object):
|
||||
device=x_latent.device,
|
||||
dtype=torch.long,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if mask is not None:
|
||||
assert x0 is not None
|
||||
xdec_orig = self.model.q_sample(
|
||||
x0, ts
|
||||
) # TODO: deterministic forward pass?
|
||||
x_dec = xdec_orig * mask + (1.0 - mask) * x_dec
|
||||
|
||||
x_dec, _ = self.p_sample_ddim(
|
||||
x_dec,
|
||||
cond,
|
||||
@ -412,6 +426,7 @@ class DDIMSampler(object):
|
||||
unconditional_guidance_scale=unconditional_guidance_scale,
|
||||
unconditional_conditioning=unconditional_conditioning,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if img_callback:
|
||||
img_callback(x_dec, i)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -7,6 +7,7 @@ from einops import rearrange, repeat
|
||||
|
||||
from ldm.modules.diffusionmodules.util import checkpoint
|
||||
|
||||
import psutil
|
||||
|
||||
def exists(val):
|
||||
return val is not None
|
||||
@ -45,18 +46,19 @@ class GEGLU(nn.Module):
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class FeedForward(nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self, dim, dim_out=None, mult=4, glu=False, dropout=0.0):
|
||||
def __init__(self, dim, dim_out=None, mult=4, glu=False, dropout=0.):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
inner_dim = int(dim * mult)
|
||||
dim_out = default(dim_out, dim)
|
||||
project_in = (
|
||||
nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(dim, inner_dim), nn.GELU())
|
||||
if not glu
|
||||
else GEGLU(dim, inner_dim)
|
||||
)
|
||||
project_in = nn.Sequential(
|
||||
nn.Linear(dim, inner_dim),
|
||||
nn.GELU()
|
||||
) if not glu else GEGLU(dim, inner_dim)
|
||||
|
||||
self.net = nn.Sequential(
|
||||
project_in, nn.Dropout(dropout), nn.Linear(inner_dim, dim_out)
|
||||
project_in,
|
||||
nn.Dropout(dropout),
|
||||
nn.Linear(inner_dim, dim_out)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, x):
|
||||
@ -73,9 +75,7 @@ def zero_module(module):
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def Normalize(in_channels):
|
||||
return torch.nn.GroupNorm(
|
||||
num_groups=32, num_channels=in_channels, eps=1e-6, affine=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
return torch.nn.GroupNorm(num_groups=32, num_channels=in_channels, eps=1e-6, affine=True)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class LinearAttention(nn.Module):
|
||||
@ -89,22 +89,11 @@ class LinearAttention(nn.Module):
|
||||
def forward(self, x):
|
||||
b, c, h, w = x.shape
|
||||
qkv = self.to_qkv(x)
|
||||
q, k, v = rearrange(
|
||||
qkv,
|
||||
'b (qkv heads c) h w -> qkv b heads c (h w)',
|
||||
heads=self.heads,
|
||||
qkv=3,
|
||||
)
|
||||
q, k, v = rearrange(qkv, 'b (qkv heads c) h w -> qkv b heads c (h w)', heads = self.heads, qkv=3)
|
||||
k = k.softmax(dim=-1)
|
||||
context = torch.einsum('bhdn,bhen->bhde', k, v)
|
||||
out = torch.einsum('bhde,bhdn->bhen', context, q)
|
||||
out = rearrange(
|
||||
out,
|
||||
'b heads c (h w) -> b (heads c) h w',
|
||||
heads=self.heads,
|
||||
h=h,
|
||||
w=w,
|
||||
)
|
||||
out = rearrange(out, 'b heads c (h w) -> b (heads c) h w', heads=self.heads, h=h, w=w)
|
||||
return self.to_out(out)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -114,18 +103,26 @@ class SpatialSelfAttention(nn.Module):
|
||||
self.in_channels = in_channels
|
||||
|
||||
self.norm = Normalize(in_channels)
|
||||
self.q = torch.nn.Conv2d(
|
||||
in_channels, in_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.k = torch.nn.Conv2d(
|
||||
in_channels, in_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.v = torch.nn.Conv2d(
|
||||
in_channels, in_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.proj_out = torch.nn.Conv2d(
|
||||
in_channels, in_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.q = torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels,
|
||||
in_channels,
|
||||
kernel_size=1,
|
||||
stride=1,
|
||||
padding=0)
|
||||
self.k = torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels,
|
||||
in_channels,
|
||||
kernel_size=1,
|
||||
stride=1,
|
||||
padding=0)
|
||||
self.v = torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels,
|
||||
in_channels,
|
||||
kernel_size=1,
|
||||
stride=1,
|
||||
padding=0)
|
||||
self.proj_out = torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels,
|
||||
in_channels,
|
||||
kernel_size=1,
|
||||
stride=1,
|
||||
padding=0)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, x):
|
||||
h_ = x
|
||||
@ -154,9 +151,7 @@ class SpatialSelfAttention(nn.Module):
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class CrossAttention(nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self, query_dim, context_dim=None, heads=8, dim_head=64, dropout=0.0
|
||||
):
|
||||
def __init__(self, query_dim, context_dim=None, heads=8, dim_head=64, dropout=0.):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
inner_dim = dim_head * heads
|
||||
context_dim = default(context_dim, query_dim)
|
||||
@ -169,69 +164,136 @@ class CrossAttention(nn.Module):
|
||||
self.to_v = nn.Linear(context_dim, inner_dim, bias=False)
|
||||
|
||||
self.to_out = nn.Sequential(
|
||||
nn.Linear(inner_dim, query_dim), nn.Dropout(dropout)
|
||||
nn.Linear(inner_dim, query_dim),
|
||||
nn.Dropout(dropout)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if not torch.cuda.is_available():
|
||||
mem_av = psutil.virtual_memory().available / (1024**3)
|
||||
if mem_av > 32:
|
||||
self.einsum_op = self.einsum_op_v1
|
||||
elif mem_av > 12:
|
||||
self.einsum_op = self.einsum_op_v2
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.einsum_op = self.einsum_op_v3
|
||||
del mem_av
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.einsum_op = self.einsum_op_v4
|
||||
|
||||
# mps 64-128 GB
|
||||
def einsum_op_v1(self, q, k, v, r1):
|
||||
if q.shape[1] <= 4096: # for 512x512: the max q.shape[1] is 4096
|
||||
s1 = einsum('b i d, b j d -> b i j', q, k) * self.scale # aggressive/faster: operation in one go
|
||||
s2 = s1.softmax(dim=-1, dtype=q.dtype)
|
||||
del s1
|
||||
r1 = einsum('b i j, b j d -> b i d', s2, v)
|
||||
del s2
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# q.shape[0] * q.shape[1] * slice_size >= 2**31 throws err
|
||||
# needs around half of that slice_size to not generate noise
|
||||
slice_size = math.floor(2**30 / (q.shape[0] * q.shape[1]))
|
||||
for i in range(0, q.shape[1], slice_size):
|
||||
end = i + slice_size
|
||||
s1 = einsum('b i d, b j d -> b i j', q[:, i:end], k) * self.scale
|
||||
s2 = s1.softmax(dim=-1, dtype=r1.dtype)
|
||||
del s1
|
||||
r1[:, i:end] = einsum('b i j, b j d -> b i d', s2, v)
|
||||
del s2
|
||||
return r1
|
||||
|
||||
# mps 16-32 GB (can be optimized)
|
||||
def einsum_op_v2(self, q, k, v, r1):
|
||||
slice_size = math.floor(2**30 / (q.shape[0] * q.shape[1]))
|
||||
for i in range(0, q.shape[1], slice_size): # conservative/less mem: operation in steps
|
||||
end = i + slice_size
|
||||
s1 = einsum('b i d, b j d -> b i j', q[:, i:end], k) * self.scale
|
||||
s2 = s1.softmax(dim=-1, dtype=r1.dtype)
|
||||
del s1
|
||||
r1[:, i:end] = einsum('b i j, b j d -> b i d', s2, v)
|
||||
del s2
|
||||
return r1
|
||||
|
||||
# mps 8 GB
|
||||
def einsum_op_v3(self, q, k, v, r1):
|
||||
slice_size = 1
|
||||
for i in range(0, q.shape[0], slice_size): # iterate over q.shape[0]
|
||||
end = min(q.shape[0], i + slice_size)
|
||||
s1 = einsum('b i d, b j d -> b i j', q[i:end], k[i:end]) # adapted einsum for mem
|
||||
s1 *= self.scale
|
||||
s2 = s1.softmax(dim=-1, dtype=r1.dtype)
|
||||
del s1
|
||||
r1[i:end] = einsum('b i j, b j d -> b i d', s2, v[i:end]) # adapted einsum for mem
|
||||
del s2
|
||||
return r1
|
||||
|
||||
# cuda
|
||||
def einsum_op_v4(self, q, k, v, r1):
|
||||
stats = torch.cuda.memory_stats(q.device)
|
||||
mem_active = stats['active_bytes.all.current']
|
||||
mem_reserved = stats['reserved_bytes.all.current']
|
||||
mem_free_cuda, _ = torch.cuda.mem_get_info(torch.cuda.current_device())
|
||||
mem_free_torch = mem_reserved - mem_active
|
||||
mem_free_total = mem_free_cuda + mem_free_torch
|
||||
|
||||
gb = 1024 ** 3
|
||||
tensor_size = q.shape[0] * q.shape[1] * k.shape[1] * 4
|
||||
mem_required = tensor_size * 2.5
|
||||
steps = 1
|
||||
|
||||
if mem_required > mem_free_total:
|
||||
steps = 2**(math.ceil(math.log(mem_required / mem_free_total, 2)))
|
||||
|
||||
if steps > 64:
|
||||
max_res = math.floor(math.sqrt(math.sqrt(mem_free_total / 2.5)) / 8) * 64
|
||||
raise RuntimeError(f'Not enough memory, use lower resolution (max approx. {max_res}x{max_res}). '
|
||||
f'Need: {mem_required/64/gb:0.1f}GB free, Have:{mem_free_total/gb:0.1f}GB free')
|
||||
|
||||
slice_size = q.shape[1] // steps if (q.shape[1] % steps) == 0 else q.shape[1]
|
||||
for i in range(0, q.shape[1], slice_size):
|
||||
end = min(q.shape[1], i + slice_size)
|
||||
s1 = einsum('b i d, b j d -> b i j', q[:, i:end], k) * self.scale
|
||||
s2 = s1.softmax(dim=-1, dtype=r1.dtype)
|
||||
del s1
|
||||
r1[:, i:end] = einsum('b i j, b j d -> b i d', s2, v)
|
||||
del s2
|
||||
return r1
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, x, context=None, mask=None):
|
||||
h = self.heads
|
||||
|
||||
q = self.to_q(x)
|
||||
q_in = self.to_q(x)
|
||||
context = default(context, x)
|
||||
k = self.to_k(context)
|
||||
v = self.to_v(context)
|
||||
k_in = self.to_k(context)
|
||||
v_in = self.to_v(context)
|
||||
device_type = 'mps' if x.device.type == 'mps' else 'cuda'
|
||||
del context, x
|
||||
|
||||
q, k, v = map(
|
||||
lambda t: rearrange(t, 'b n (h d) -> (b h) n d', h=h), (q, k, v)
|
||||
)
|
||||
q, k, v = map(lambda t: rearrange(t, 'b n (h d) -> (b h) n d', h=h), (q_in, k_in, v_in))
|
||||
del q_in, k_in, v_in
|
||||
r1 = torch.zeros(q.shape[0], q.shape[1], v.shape[2], device=q.device, dtype=q.dtype)
|
||||
r1 = self.einsum_op(q, k, v, r1)
|
||||
del q, k, v
|
||||
|
||||
sim = einsum('b i d, b j d -> b i j', q, k) * self.scale
|
||||
r2 = rearrange(r1, '(b h) n d -> b n (h d)', h=h)
|
||||
del r1
|
||||
|
||||
if exists(mask):
|
||||
mask = rearrange(mask, 'b ... -> b (...)')
|
||||
max_neg_value = -torch.finfo(sim.dtype).max
|
||||
mask = repeat(mask, 'b j -> (b h) () j', h=h)
|
||||
sim.masked_fill_(~mask, max_neg_value)
|
||||
|
||||
# attention, what we cannot get enough of
|
||||
attn = sim.softmax(dim=-1)
|
||||
|
||||
out = einsum('b i j, b j d -> b i d', attn, v)
|
||||
out = rearrange(out, '(b h) n d -> b n (h d)', h=h)
|
||||
return self.to_out(out)
|
||||
return self.to_out(r2)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class BasicTransformerBlock(nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
dim,
|
||||
n_heads,
|
||||
d_head,
|
||||
dropout=0.0,
|
||||
context_dim=None,
|
||||
gated_ff=True,
|
||||
checkpoint=True,
|
||||
):
|
||||
def __init__(self, dim, n_heads, d_head, dropout=0., context_dim=None, gated_ff=True, checkpoint=True):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.attn1 = CrossAttention(
|
||||
query_dim=dim, heads=n_heads, dim_head=d_head, dropout=dropout
|
||||
) # is a self-attention
|
||||
self.attn1 = CrossAttention(query_dim=dim, heads=n_heads, dim_head=d_head, dropout=dropout) # is a self-attention
|
||||
self.ff = FeedForward(dim, dropout=dropout, glu=gated_ff)
|
||||
self.attn2 = CrossAttention(
|
||||
query_dim=dim,
|
||||
context_dim=context_dim,
|
||||
heads=n_heads,
|
||||
dim_head=d_head,
|
||||
dropout=dropout,
|
||||
) # is self-attn if context is none
|
||||
self.attn2 = CrossAttention(query_dim=dim, context_dim=context_dim,
|
||||
heads=n_heads, dim_head=d_head, dropout=dropout) # is self-attn if context is none
|
||||
self.norm1 = nn.LayerNorm(dim)
|
||||
self.norm2 = nn.LayerNorm(dim)
|
||||
self.norm3 = nn.LayerNorm(dim)
|
||||
self.checkpoint = checkpoint
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, x, context=None):
|
||||
return checkpoint(
|
||||
self._forward, (x, context), self.parameters(), self.checkpoint
|
||||
)
|
||||
return checkpoint(self._forward, (x, context), self.parameters(), self.checkpoint)
|
||||
|
||||
def _forward(self, x, context=None):
|
||||
x = x.contiguous() if x.device.type == 'mps' else x
|
||||
@ -249,43 +311,29 @@ class SpatialTransformer(nn.Module):
|
||||
Then apply standard transformer action.
|
||||
Finally, reshape to image
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
in_channels,
|
||||
n_heads,
|
||||
d_head,
|
||||
depth=1,
|
||||
dropout=0.0,
|
||||
context_dim=None,
|
||||
):
|
||||
def __init__(self, in_channels, n_heads, d_head,
|
||||
depth=1, dropout=0., context_dim=None):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.in_channels = in_channels
|
||||
inner_dim = n_heads * d_head
|
||||
self.norm = Normalize(in_channels)
|
||||
|
||||
self.proj_in = nn.Conv2d(
|
||||
in_channels, inner_dim, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.proj_in = nn.Conv2d(in_channels,
|
||||
inner_dim,
|
||||
kernel_size=1,
|
||||
stride=1,
|
||||
padding=0)
|
||||
|
||||
self.transformer_blocks = nn.ModuleList(
|
||||
[
|
||||
BasicTransformerBlock(
|
||||
inner_dim,
|
||||
n_heads,
|
||||
d_head,
|
||||
dropout=dropout,
|
||||
context_dim=context_dim,
|
||||
)
|
||||
for d in range(depth)
|
||||
]
|
||||
[BasicTransformerBlock(inner_dim, n_heads, d_head, dropout=dropout, context_dim=context_dim)
|
||||
for d in range(depth)]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
self.proj_out = zero_module(
|
||||
nn.Conv2d(
|
||||
inner_dim, in_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0
|
||||
)
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.proj_out = zero_module(nn.Conv2d(inner_dim,
|
||||
in_channels,
|
||||
kernel_size=1,
|
||||
stride=1,
|
||||
padding=0))
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, x, context=None):
|
||||
# note: if no context is given, cross-attention defaults to self-attention
|
||||
|
||||
@ -81,7 +81,9 @@ def make_ddim_timesteps(
|
||||
|
||||
# assert ddim_timesteps.shape[0] == num_ddim_timesteps
|
||||
# add one to get the final alpha values right (the ones from first scale to data during sampling)
|
||||
steps_out = ddim_timesteps + 1
|
||||
# steps_out = ddim_timesteps + 1
|
||||
steps_out = ddim_timesteps
|
||||
|
||||
if verbose:
|
||||
print(f'Selected timesteps for ddim sampler: {steps_out}')
|
||||
return steps_out
|
||||
|
||||
@ -24,9 +24,9 @@ def get_clip_token_for_string(tokenizer, string):
|
||||
return_tensors='pt',
|
||||
)
|
||||
tokens = batch_encoding['input_ids']
|
||||
assert (
|
||||
""" assert (
|
||||
torch.count_nonzero(tokens - 49407) == 2
|
||||
), f"String '{string}' maps to more than a single token. Please use another string"
|
||||
), f"String '{string}' maps to more than a single token. Please use another string" """
|
||||
|
||||
return tokens[0, 1]
|
||||
|
||||
@ -57,8 +57,9 @@ class EmbeddingManager(nn.Module):
|
||||
):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
|
||||
self.string_to_token_dict = {}
|
||||
self.embedder = embedder
|
||||
|
||||
self.string_to_token_dict = {}
|
||||
self.string_to_param_dict = nn.ParameterDict()
|
||||
|
||||
self.initial_embeddings = (
|
||||
@ -217,12 +218,28 @@ class EmbeddingManager(nn.Module):
|
||||
|
||||
def load(self, ckpt_path, full=True):
|
||||
ckpt = torch.load(ckpt_path, map_location='cpu')
|
||||
|
||||
# Handle .pt textual inversion files
|
||||
if 'string_to_token' in ckpt and 'string_to_param' in ckpt:
|
||||
self.string_to_token_dict = ckpt["string_to_token"]
|
||||
self.string_to_param_dict = ckpt["string_to_param"]
|
||||
|
||||
# Handle .bin textual inversion files from Huggingface Concepts
|
||||
# https://huggingface.co/sd-concepts-library
|
||||
else:
|
||||
for token_str in list(ckpt.keys()):
|
||||
token = get_clip_token_for_string(self.embedder.tokenizer, token_str)
|
||||
self.string_to_token_dict[token_str] = token
|
||||
ckpt[token_str] = torch.nn.Parameter(ckpt[token_str])
|
||||
|
||||
self.string_to_param_dict.update(ckpt)
|
||||
|
||||
if not full:
|
||||
for key, value in self.string_to_param_dict.items():
|
||||
self.string_to_param_dict[key] = torch.nn.Parameter(value.half())
|
||||
|
||||
print(f'Added terms: {", ".join(self.string_to_param_dict.keys())}')
|
||||
|
||||
def get_embedding_norms_squared(self):
|
||||
all_params = torch.cat(
|
||||
list(self.string_to_param_dict.values()), axis=0
|
||||
|
||||
849
ldm/simplet2i.py
@ -1,844 +1,13 @@
|
||||
# Copyright (c) 2022 Lincoln D. Stein (https://github.com/lstein)
|
||||
|
||||
# Derived from source code carrying the following copyrights
|
||||
# Copyright (c) 2022 Machine Vision and Learning Group, LMU Munich
|
||||
# Copyright (c) 2022 Robin Rombach and Patrick Esser and contributors
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import random
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import traceback
|
||||
from omegaconf import OmegaConf
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
from tqdm import tqdm, trange
|
||||
from itertools import islice
|
||||
from einops import rearrange, repeat
|
||||
from torchvision.utils import make_grid
|
||||
from pytorch_lightning import seed_everything
|
||||
from torch import autocast
|
||||
from contextlib import contextmanager, nullcontext
|
||||
import transformers
|
||||
import time
|
||||
import re
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
|
||||
from ldm.util import instantiate_from_config
|
||||
from ldm.models.diffusion.ddim import DDIMSampler
|
||||
from ldm.models.diffusion.plms import PLMSSampler
|
||||
from ldm.models.diffusion.ksampler import KSampler
|
||||
from ldm.dream.pngwriter import PngWriter
|
||||
from ldm.dream.image_util import InitImageResizer
|
||||
from ldm.dream.devices import choose_autocast_device, choose_torch_device
|
||||
|
||||
"""Simplified text to image API for stable diffusion/latent diffusion
|
||||
|
||||
Example Usage:
|
||||
|
||||
from ldm.simplet2i import T2I
|
||||
|
||||
# Create an object with default values
|
||||
t2i = T2I(model = <path> // models/ldm/stable-diffusion-v1/model.ckpt
|
||||
config = <path> // configs/stable-diffusion/v1-inference.yaml
|
||||
iterations = <integer> // how many times to run the sampling (1)
|
||||
steps = <integer> // 50
|
||||
seed = <integer> // current system time
|
||||
sampler_name= ['ddim', 'k_dpm_2_a', 'k_dpm_2', 'k_euler_a', 'k_euler', 'k_heun', 'k_lms', 'plms'] // k_lms
|
||||
grid = <boolean> // false
|
||||
width = <integer> // image width, multiple of 64 (512)
|
||||
height = <integer> // image height, multiple of 64 (512)
|
||||
cfg_scale = <float> // unconditional guidance scale (7.5)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# do the slow model initialization
|
||||
t2i.load_model()
|
||||
|
||||
# Do the fast inference & image generation. Any options passed here
|
||||
# override the default values assigned during class initialization
|
||||
# Will call load_model() if the model was not previously loaded and so
|
||||
# may be slow at first.
|
||||
# The method returns a list of images. Each row of the list is a sub-list of [filename,seed]
|
||||
results = t2i.prompt2png(prompt = "an astronaut riding a horse",
|
||||
outdir = "./outputs/samples",
|
||||
iterations = 3)
|
||||
|
||||
for row in results:
|
||||
print(f'filename={row[0]}')
|
||||
print(f'seed ={row[1]}')
|
||||
|
||||
# Same thing, but using an initial image.
|
||||
results = t2i.prompt2png(prompt = "an astronaut riding a horse",
|
||||
outdir = "./outputs/,
|
||||
iterations = 3,
|
||||
init_img = "./sketches/horse+rider.png")
|
||||
|
||||
for row in results:
|
||||
print(f'filename={row[0]}')
|
||||
print(f'seed ={row[1]}')
|
||||
|
||||
# Same thing, but we return a series of Image objects, which lets you manipulate them,
|
||||
# combine them, and save them under arbitrary names
|
||||
|
||||
results = t2i.prompt2image(prompt = "an astronaut riding a horse"
|
||||
outdir = "./outputs/")
|
||||
for row in results:
|
||||
im = row[0]
|
||||
seed = row[1]
|
||||
im.save(f'./outputs/samples/an_astronaut_riding_a_horse-{seed}.png')
|
||||
im.thumbnail(100,100).save('./outputs/samples/astronaut_thumb.jpg')
|
||||
|
||||
Note that the old txt2img() and img2img() calls are deprecated but will
|
||||
still work.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class T2I:
|
||||
"""T2I class
|
||||
Attributes
|
||||
----------
|
||||
model
|
||||
config
|
||||
iterations
|
||||
steps
|
||||
seed
|
||||
sampler_name
|
||||
width
|
||||
height
|
||||
cfg_scale
|
||||
latent_channels
|
||||
downsampling_factor
|
||||
precision
|
||||
strength
|
||||
embedding_path
|
||||
|
||||
The vast majority of these arguments default to reasonable values.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
iterations=1,
|
||||
steps=50,
|
||||
seed=None,
|
||||
cfg_scale=7.5,
|
||||
weights='models/ldm/stable-diffusion-v1/model.ckpt',
|
||||
config='configs/stable-diffusion/v1-inference.yaml',
|
||||
grid=False,
|
||||
width=512,
|
||||
height=512,
|
||||
sampler_name='k_lms',
|
||||
latent_channels=4,
|
||||
downsampling_factor=8,
|
||||
ddim_eta=0.0, # deterministic
|
||||
precision='autocast',
|
||||
full_precision=False,
|
||||
strength=0.75, # default in scripts/img2img.py
|
||||
embedding_path=None,
|
||||
device_type = 'cuda',
|
||||
# just to keep track of this parameter when regenerating prompt
|
||||
# needs to be replaced when new configuration system implemented.
|
||||
latent_diffusion_weights=False,
|
||||
):
|
||||
self.iterations = iterations
|
||||
self.width = width
|
||||
self.height = height
|
||||
self.steps = steps
|
||||
self.cfg_scale = cfg_scale
|
||||
self.weights = weights
|
||||
self.config = config
|
||||
self.sampler_name = sampler_name
|
||||
self.latent_channels = latent_channels
|
||||
self.downsampling_factor = downsampling_factor
|
||||
self.grid = grid
|
||||
self.ddim_eta = ddim_eta
|
||||
self.precision = precision
|
||||
self.full_precision = True if choose_torch_device() == 'mps' else full_precision
|
||||
self.strength = strength
|
||||
self.embedding_path = embedding_path
|
||||
self.device_type = device_type
|
||||
self.model = None # empty for now
|
||||
self.sampler = None
|
||||
self.device = None
|
||||
self.latent_diffusion_weights = latent_diffusion_weights
|
||||
|
||||
if device_type == 'cuda' and not torch.cuda.is_available():
|
||||
device_type = choose_torch_device()
|
||||
print(">> cuda not available, using device", device_type)
|
||||
self.device = torch.device(device_type)
|
||||
|
||||
# for VRAM usage statistics
|
||||
device_type = choose_torch_device()
|
||||
self.session_peakmem = torch.cuda.max_memory_allocated() if device_type == 'cuda' else None
|
||||
|
||||
if seed is None:
|
||||
self.seed = self._new_seed()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.seed = seed
|
||||
transformers.logging.set_verbosity_error()
|
||||
|
||||
def prompt2png(self, prompt, outdir, **kwargs):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Takes a prompt and an output directory, writes out the requested number
|
||||
of PNG files, and returns an array of [[filename,seed],[filename,seed]...]
|
||||
Optional named arguments are the same as those passed to T2I and prompt2image()
|
||||
"""
|
||||
results = self.prompt2image(prompt, **kwargs)
|
||||
pngwriter = PngWriter(outdir)
|
||||
prefix = pngwriter.unique_prefix()
|
||||
outputs = []
|
||||
for image, seed in results:
|
||||
name = f'{prefix}.{seed}.png'
|
||||
path = pngwriter.save_image_and_prompt_to_png(
|
||||
image, f'{prompt} -S{seed}', name)
|
||||
outputs.append([path, seed])
|
||||
return outputs
|
||||
|
||||
def txt2img(self, prompt, **kwargs):
|
||||
outdir = kwargs.pop('outdir', 'outputs/img-samples')
|
||||
return self.prompt2png(prompt, outdir, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
def img2img(self, prompt, **kwargs):
|
||||
outdir = kwargs.pop('outdir', 'outputs/img-samples')
|
||||
assert (
|
||||
'init_img' in kwargs
|
||||
), 'call to img2img() must include the init_img argument'
|
||||
return self.prompt2png(prompt, outdir, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
def prompt2image(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
# these are common
|
||||
prompt,
|
||||
iterations = None,
|
||||
steps = None,
|
||||
seed = None,
|
||||
cfg_scale = None,
|
||||
ddim_eta = None,
|
||||
skip_normalize = False,
|
||||
image_callback = None,
|
||||
step_callback = None,
|
||||
width = None,
|
||||
height = None,
|
||||
# these are specific to img2img
|
||||
init_img = None,
|
||||
fit = False,
|
||||
strength = None,
|
||||
gfpgan_strength= 0,
|
||||
save_original = False,
|
||||
upscale = None,
|
||||
sampler_name = None,
|
||||
log_tokenization= False,
|
||||
with_variations = None,
|
||||
variation_amount = 0.0,
|
||||
**args,
|
||||
): # eat up additional cruft
|
||||
"""
|
||||
ldm.prompt2image() is the common entry point for txt2img() and img2img()
|
||||
It takes the following arguments:
|
||||
prompt // prompt string (no default)
|
||||
iterations // iterations (1); image count=iterations
|
||||
steps // refinement steps per iteration
|
||||
seed // seed for random number generator
|
||||
width // width of image, in multiples of 64 (512)
|
||||
height // height of image, in multiples of 64 (512)
|
||||
cfg_scale // how strongly the prompt influences the image (7.5) (must be >1)
|
||||
init_img // path to an initial image - its dimensions override width and height
|
||||
strength // strength for noising/unnoising init_img. 0.0 preserves image exactly, 1.0 replaces it completely
|
||||
gfpgan_strength // strength for GFPGAN. 0.0 preserves image exactly, 1.0 replaces it completely
|
||||
ddim_eta // image randomness (eta=0.0 means the same seed always produces the same image)
|
||||
step_callback // a function or method that will be called each step
|
||||
image_callback // a function or method that will be called each time an image is generated
|
||||
with_variations // a weighted list [(seed_1, weight_1), (seed_2, weight_2), ...] of variations which should be applied before doing any generation
|
||||
variation_amount // optional 0-1 value to slerp from -S noise to random noise (allows variations on an image)
|
||||
|
||||
To use the step callback, define a function that receives two arguments:
|
||||
- Image GPU data
|
||||
- The step number
|
||||
|
||||
To use the image callback, define a function of method that receives two arguments, an Image object
|
||||
and the seed. You can then do whatever you like with the image, including converting it to
|
||||
different formats and manipulating it. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
def process_image(image,seed):
|
||||
image.save(f{'images/seed.png'})
|
||||
|
||||
The callback used by the prompt2png() can be found in ldm/dream_util.py. It contains code
|
||||
to create the requested output directory, select a unique informative name for each image, and
|
||||
write the prompt into the PNG metadata.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# TODO: convert this into a getattr() loop
|
||||
steps = steps or self.steps
|
||||
width = width or self.width
|
||||
height = height or self.height
|
||||
cfg_scale = cfg_scale or self.cfg_scale
|
||||
ddim_eta = ddim_eta or self.ddim_eta
|
||||
iterations = iterations or self.iterations
|
||||
strength = strength or self.strength
|
||||
self.log_tokenization = log_tokenization
|
||||
with_variations = [] if with_variations is None else with_variations
|
||||
|
||||
model = (
|
||||
self.load_model()
|
||||
) # will instantiate the model or return it from cache
|
||||
assert cfg_scale > 1.0, 'CFG_Scale (-C) must be >1.0'
|
||||
assert (
|
||||
0.0 <= strength <= 1.0
|
||||
), 'can only work with strength in [0.0, 1.0]'
|
||||
assert (
|
||||
0.0 <= variation_amount <= 1.0
|
||||
), '-v --variation_amount must be in [0.0, 1.0]'
|
||||
|
||||
if len(with_variations) > 0 or variation_amount > 0.0:
|
||||
assert seed is not None,\
|
||||
'seed must be specified when using with_variations'
|
||||
if variation_amount == 0.0:
|
||||
assert iterations == 1,\
|
||||
'when using --with_variations, multiple iterations are only possible when using --variation_amount'
|
||||
assert all(0 <= weight <= 1 for _, weight in with_variations),\
|
||||
f'variation weights must be in [0.0, 1.0]: got {[weight for _, weight in with_variations]}'
|
||||
|
||||
seed = seed or self.seed
|
||||
width, height, _ = self._resolution_check(width, height, log=True)
|
||||
|
||||
# TODO: - Check if this is still necessary to run on M1 devices.
|
||||
# - Move code into ldm.dream.devices to live alongside other
|
||||
# special-hardware casing code.
|
||||
if self.precision == 'autocast' and torch.cuda.is_available():
|
||||
scope = autocast
|
||||
else:
|
||||
scope = nullcontext
|
||||
|
||||
if sampler_name and (sampler_name != self.sampler_name):
|
||||
self.sampler_name = sampler_name
|
||||
self._set_sampler()
|
||||
|
||||
tic = time.time()
|
||||
if torch.cuda.is_available():
|
||||
torch.cuda.reset_peak_memory_stats()
|
||||
results = list()
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
if init_img:
|
||||
assert os.path.exists(init_img), f'{init_img}: File not found'
|
||||
init_image = self._load_img(init_img, width, height, fit).to(self.device)
|
||||
with scope(self.device.type):
|
||||
init_latent = self.model.get_first_stage_encoding(
|
||||
self.model.encode_first_stage(init_image)
|
||||
) # move to latent space
|
||||
|
||||
#print(f' DEBUG: seed at make_image time ={seed}')
|
||||
make_image = self._img2img(
|
||||
prompt,
|
||||
steps=steps,
|
||||
cfg_scale=cfg_scale,
|
||||
ddim_eta=ddim_eta,
|
||||
skip_normalize=skip_normalize,
|
||||
init_latent=init_latent,
|
||||
strength=strength,
|
||||
callback=step_callback,
|
||||
)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
init_latent = None
|
||||
make_image = self._txt2img(
|
||||
prompt,
|
||||
steps=steps,
|
||||
cfg_scale=cfg_scale,
|
||||
ddim_eta=ddim_eta,
|
||||
skip_normalize=skip_normalize,
|
||||
width=width,
|
||||
height=height,
|
||||
callback=step_callback,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
initial_noise = None
|
||||
if variation_amount > 0 or len(with_variations) > 0:
|
||||
# use fixed initial noise plus random noise per iteration
|
||||
seed_everything(seed)
|
||||
initial_noise = self._get_noise(init_latent,width,height)
|
||||
for v_seed, v_weight in with_variations:
|
||||
seed = v_seed
|
||||
seed_everything(seed)
|
||||
next_noise = self._get_noise(init_latent,width,height)
|
||||
initial_noise = self.slerp(v_weight, initial_noise, next_noise)
|
||||
if variation_amount > 0:
|
||||
random.seed() # reset RNG to an actually random state, so we can get a random seed for variations
|
||||
seed = random.randrange(0,np.iinfo(np.uint32).max)
|
||||
|
||||
device_type = choose_autocast_device(self.device)
|
||||
with scope(device_type), self.model.ema_scope():
|
||||
for n in trange(iterations, desc='Generating'):
|
||||
x_T = None
|
||||
if variation_amount > 0:
|
||||
seed_everything(seed)
|
||||
target_noise = self._get_noise(init_latent,width,height)
|
||||
x_T = self.slerp(variation_amount, initial_noise, target_noise)
|
||||
elif initial_noise is not None:
|
||||
# i.e. we specified particular variations
|
||||
x_T = initial_noise
|
||||
else:
|
||||
seed_everything(seed)
|
||||
if self.device.type == 'mps':
|
||||
x_T = self._get_noise(init_latent,width,height)
|
||||
# make_image will do the equivalent of get_noise itself
|
||||
#print(f' DEBUG: seed at make_image() invocation time ={seed}')
|
||||
image = make_image(x_T)
|
||||
results.append([image, seed])
|
||||
if image_callback is not None:
|
||||
image_callback(image, seed)
|
||||
seed = self._new_seed()
|
||||
|
||||
if upscale is not None or gfpgan_strength > 0:
|
||||
for result in results:
|
||||
image, seed = result
|
||||
try:
|
||||
if upscale is not None:
|
||||
from ldm.gfpgan.gfpgan_tools import (
|
||||
real_esrgan_upscale,
|
||||
)
|
||||
if len(upscale) < 2:
|
||||
upscale.append(0.75)
|
||||
image = real_esrgan_upscale(
|
||||
image,
|
||||
upscale[1],
|
||||
int(upscale[0]),
|
||||
prompt,
|
||||
seed,
|
||||
)
|
||||
if gfpgan_strength > 0:
|
||||
from ldm.gfpgan.gfpgan_tools import _run_gfpgan
|
||||
|
||||
image = _run_gfpgan(
|
||||
image, gfpgan_strength, prompt, seed, 1
|
||||
)
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
print(
|
||||
f'>> Error running RealESRGAN - Your image was not upscaled.\n{e}'
|
||||
)
|
||||
if image_callback is not None:
|
||||
if save_original:
|
||||
image_callback(image, seed)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
image_callback(image, seed, upscaled=True)
|
||||
else: # no callback passed, so we simply replace old image with rescaled one
|
||||
result[0] = image
|
||||
|
||||
except KeyboardInterrupt:
|
||||
print('*interrupted*')
|
||||
print(
|
||||
'>> Partial results will be returned; if --grid was requested, nothing will be returned.'
|
||||
)
|
||||
except RuntimeError as e:
|
||||
print(traceback.format_exc(), file=sys.stderr)
|
||||
print('>> Are you sure your system has an adequate NVIDIA GPU?')
|
||||
|
||||
toc = time.time()
|
||||
print('>> Usage stats:')
|
||||
print(
|
||||
f'>> {len(results)} image(s) generated in', '%4.2fs' % (toc - tic)
|
||||
)
|
||||
print(
|
||||
f'>> Max VRAM used for this generation:',
|
||||
'%4.2fG' % (torch.cuda.max_memory_allocated() / 1e9),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if self.session_peakmem:
|
||||
self.session_peakmem = max(
|
||||
self.session_peakmem, torch.cuda.max_memory_allocated()
|
||||
)
|
||||
print(
|
||||
f'>> Max VRAM used since script start: ',
|
||||
'%4.2fG' % (self.session_peakmem / 1e9),
|
||||
)
|
||||
return results
|
||||
|
||||
@torch.no_grad()
|
||||
def _txt2img(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
prompt,
|
||||
steps,
|
||||
cfg_scale,
|
||||
ddim_eta,
|
||||
skip_normalize,
|
||||
width,
|
||||
height,
|
||||
callback,
|
||||
):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns a function returning an image derived from the prompt and the initial image
|
||||
Return value depends on the seed at the time you call it
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
sampler = self.sampler
|
||||
|
||||
def make_image(x_T):
|
||||
uc, c = self._get_uc_and_c(prompt, skip_normalize)
|
||||
shape = [
|
||||
self.latent_channels,
|
||||
height // self.downsampling_factor,
|
||||
width // self.downsampling_factor,
|
||||
]
|
||||
samples, _ = sampler.sample(
|
||||
batch_size=1,
|
||||
S=steps,
|
||||
x_T=x_T,
|
||||
conditioning=c,
|
||||
shape=shape,
|
||||
verbose=False,
|
||||
unconditional_guidance_scale=cfg_scale,
|
||||
unconditional_conditioning=uc,
|
||||
eta=ddim_eta,
|
||||
img_callback=callback
|
||||
)
|
||||
return self._sample_to_image(samples)
|
||||
return make_image
|
||||
|
||||
@torch.no_grad()
|
||||
def _img2img(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
prompt,
|
||||
steps,
|
||||
cfg_scale,
|
||||
ddim_eta,
|
||||
skip_normalize,
|
||||
init_latent,
|
||||
strength,
|
||||
callback, # Currently not implemented for img2img
|
||||
):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns a function returning an image derived from the prompt and the initial image
|
||||
Return value depends on the seed at the time you call it
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
# PLMS sampler not supported yet, so ignore previous sampler
|
||||
if self.sampler_name != 'ddim':
|
||||
print(
|
||||
f">> sampler '{self.sampler_name}' is not yet supported. Using DDIM sampler"
|
||||
)
|
||||
sampler = DDIMSampler(self.model, device=self.device)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
sampler = self.sampler
|
||||
|
||||
sampler.make_schedule(
|
||||
ddim_num_steps=steps, ddim_eta=ddim_eta, verbose=False
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
t_enc = int(strength * steps)
|
||||
|
||||
def make_image(x_T):
|
||||
uc, c = self._get_uc_and_c(prompt, skip_normalize)
|
||||
|
||||
# encode (scaled latent)
|
||||
z_enc = sampler.stochastic_encode(
|
||||
init_latent,
|
||||
torch.tensor([t_enc]).to(self.device),
|
||||
noise=x_T
|
||||
)
|
||||
# decode it
|
||||
samples = sampler.decode(
|
||||
z_enc,
|
||||
c,
|
||||
t_enc,
|
||||
img_callback=callback,
|
||||
unconditional_guidance_scale=cfg_scale,
|
||||
unconditional_conditioning=uc,
|
||||
)
|
||||
return self._sample_to_image(samples)
|
||||
return make_image
|
||||
|
||||
# TODO: does this actually need to run every loop? does anything in it vary by random seed?
|
||||
def _get_uc_and_c(self, prompt, skip_normalize):
|
||||
|
||||
uc = self.model.get_learned_conditioning([''])
|
||||
|
||||
# get weighted sub-prompts
|
||||
weighted_subprompts = T2I._split_weighted_subprompts(
|
||||
prompt, skip_normalize)
|
||||
|
||||
if len(weighted_subprompts) > 1:
|
||||
# i dont know if this is correct.. but it works
|
||||
c = torch.zeros_like(uc)
|
||||
# normalize each "sub prompt" and add it
|
||||
for subprompt, weight in weighted_subprompts:
|
||||
self._log_tokenization(subprompt)
|
||||
c = torch.add(
|
||||
c,
|
||||
self.model.get_learned_conditioning([subprompt]),
|
||||
alpha=weight,
|
||||
)
|
||||
else: # just standard 1 prompt
|
||||
self._log_tokenization(prompt)
|
||||
c = self.model.get_learned_conditioning([prompt])
|
||||
return (uc, c)
|
||||
|
||||
def _sample_to_image(self, samples):
|
||||
x_samples = self.model.decode_first_stage(samples)
|
||||
x_samples = torch.clamp((x_samples + 1.0) / 2.0, min=0.0, max=1.0)
|
||||
if len(x_samples) != 1:
|
||||
raise Exception(
|
||||
f'>> expected to get a single image, but got {len(x_samples)}')
|
||||
x_sample = 255.0 * rearrange(
|
||||
x_samples[0].cpu().numpy(), 'c h w -> h w c'
|
||||
)
|
||||
return Image.fromarray(x_sample.astype(np.uint8))
|
||||
|
||||
def _new_seed(self):
|
||||
self.seed = random.randrange(0, np.iinfo(np.uint32).max)
|
||||
return self.seed
|
||||
|
||||
def load_model(self):
|
||||
"""Load and initialize the model from configuration variables passed at object creation time"""
|
||||
if self.model is None:
|
||||
seed_everything(self.seed)
|
||||
try:
|
||||
config = OmegaConf.load(self.config)
|
||||
model = self._load_model_from_config(config, self.weights)
|
||||
if self.embedding_path is not None:
|
||||
model.embedding_manager.load(
|
||||
self.embedding_path, self.full_precision
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.model = model.to(self.device)
|
||||
# model.to doesn't change the cond_stage_model.device used to move the tokenizer output, so set it here
|
||||
self.model.cond_stage_model.device = self.device
|
||||
except AttributeError as e:
|
||||
print(f'>> Error loading model. {str(e)}', file=sys.stderr)
|
||||
print(traceback.format_exc(), file=sys.stderr)
|
||||
raise SystemExit from e
|
||||
|
||||
self._set_sampler()
|
||||
|
||||
return self.model
|
||||
|
||||
# returns a tensor filled with random numbers from a normal distribution
|
||||
def _get_noise(self,init_latent,width,height):
|
||||
if init_latent is not None:
|
||||
if self.device.type == 'mps':
|
||||
return torch.randn_like(init_latent, device='cpu').to(self.device)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return torch.randn_like(init_latent, device=self.device)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if self.device.type == 'mps':
|
||||
return torch.randn([1,
|
||||
self.latent_channels,
|
||||
height // self.downsampling_factor,
|
||||
width // self.downsampling_factor],
|
||||
device='cpu').to(self.device)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return torch.randn([1,
|
||||
self.latent_channels,
|
||||
height // self.downsampling_factor,
|
||||
width // self.downsampling_factor],
|
||||
device=self.device)
|
||||
|
||||
def _set_sampler(self):
|
||||
msg = f'>> Setting Sampler to {self.sampler_name}'
|
||||
if self.sampler_name == 'plms':
|
||||
self.sampler = PLMSSampler(self.model, device=self.device)
|
||||
elif self.sampler_name == 'ddim':
|
||||
self.sampler = DDIMSampler(self.model, device=self.device)
|
||||
elif self.sampler_name == 'k_dpm_2_a':
|
||||
self.sampler = KSampler(
|
||||
self.model, 'dpm_2_ancestral', device=self.device
|
||||
)
|
||||
elif self.sampler_name == 'k_dpm_2':
|
||||
self.sampler = KSampler(self.model, 'dpm_2', device=self.device)
|
||||
elif self.sampler_name == 'k_euler_a':
|
||||
self.sampler = KSampler(
|
||||
self.model, 'euler_ancestral', device=self.device
|
||||
)
|
||||
elif self.sampler_name == 'k_euler':
|
||||
self.sampler = KSampler(self.model, 'euler', device=self.device)
|
||||
elif self.sampler_name == 'k_heun':
|
||||
self.sampler = KSampler(self.model, 'heun', device=self.device)
|
||||
elif self.sampler_name == 'k_lms':
|
||||
self.sampler = KSampler(self.model, 'lms', device=self.device)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
msg = f'>> Unsupported Sampler: {self.sampler_name}, Defaulting to plms'
|
||||
self.sampler = PLMSSampler(self.model, device=self.device)
|
||||
|
||||
print(msg)
|
||||
|
||||
def _load_model_from_config(self, config, ckpt):
|
||||
print(f'>> Loading model from {ckpt}')
|
||||
pl_sd = torch.load(ckpt, map_location='cpu')
|
||||
# if "global_step" in pl_sd:
|
||||
# print(f"Global Step: {pl_sd['global_step']}")
|
||||
sd = pl_sd['state_dict']
|
||||
model = instantiate_from_config(config.model)
|
||||
m, u = model.load_state_dict(sd, strict=False)
|
||||
model.to(self.device)
|
||||
model.eval()
|
||||
if self.full_precision:
|
||||
print(
|
||||
'Using slower but more accurate full-precision math (--full_precision)'
|
||||
)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print(
|
||||
'>> Using half precision math. Call with --full_precision to use more accurate but VRAM-intensive full precision.'
|
||||
)
|
||||
model.half()
|
||||
return model
|
||||
|
||||
def _load_img(self, path, width, height, fit=False):
|
||||
with Image.open(path) as img:
|
||||
image = img.convert('RGB')
|
||||
print(
|
||||
f'>> loaded input image of size {image.width}x{image.height} from {path}'
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# The logic here is:
|
||||
# 1. If "fit" is true, then the image will be fit into the bounding box defined
|
||||
# by width and height. It will do this in a way that preserves the init image's
|
||||
# aspect ratio while preventing letterboxing. This means that if there is
|
||||
# leftover horizontal space after rescaling the image to fit in the bounding box,
|
||||
# the generated image's width will be reduced to the rescaled init image's width.
|
||||
# Similarly for the vertical space.
|
||||
# 2. Otherwise, if "fit" is false, then the image will be scaled, preserving its
|
||||
# aspect ratio, to the nearest multiple of 64. Large images may generate an
|
||||
# unexpected OOM error.
|
||||
if fit:
|
||||
image = self._fit_image(image,(width,height))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
image = self._squeeze_image(image)
|
||||
image = np.array(image).astype(np.float32) / 255.0
|
||||
image = image[None].transpose(0, 3, 1, 2)
|
||||
image = torch.from_numpy(image)
|
||||
return 2.0 * image - 1.0
|
||||
|
||||
def _squeeze_image(self,image):
|
||||
x,y,resize_needed = self._resolution_check(image.width,image.height)
|
||||
if resize_needed:
|
||||
return InitImageResizer(image).resize(x,y)
|
||||
return image
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _fit_image(self,image,max_dimensions):
|
||||
w,h = max_dimensions
|
||||
print(
|
||||
f'>> image will be resized to fit inside a box {w}x{h} in size.'
|
||||
)
|
||||
if image.width > image.height:
|
||||
h = None # by setting h to none, we tell InitImageResizer to fit into the width and calculate height
|
||||
elif image.height > image.width:
|
||||
w = None # ditto for w
|
||||
else:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
image = InitImageResizer(image).resize(w,h) # note that InitImageResizer does the multiple of 64 truncation internally
|
||||
print(
|
||||
f'>> after adjusting image dimensions to be multiples of 64, init image is {image.width}x{image.height}'
|
||||
)
|
||||
return image
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# TO DO: Move this and related weighted subprompt code into its own module.
|
||||
def _split_weighted_subprompts(text, skip_normalize=False):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
grabs all text up to the first occurrence of ':'
|
||||
uses the grabbed text as a sub-prompt, and takes the value following ':' as weight
|
||||
if ':' has no value defined, defaults to 1.0
|
||||
repeats until no text remaining
|
||||
"""
|
||||
prompt_parser = re.compile("""
|
||||
(?P<prompt> # capture group for 'prompt'
|
||||
(?:\\\:|[^:])+ # match one or more non ':' characters or escaped colons '\:'
|
||||
) # end 'prompt'
|
||||
(?: # non-capture group
|
||||
:+ # match one or more ':' characters
|
||||
(?P<weight> # capture group for 'weight'
|
||||
-?\d+(?:\.\d+)? # match positive or negative integer or decimal number
|
||||
)? # end weight capture group, make optional
|
||||
\s* # strip spaces after weight
|
||||
| # OR
|
||||
$ # else, if no ':' then match end of line
|
||||
) # end non-capture group
|
||||
""", re.VERBOSE)
|
||||
parsed_prompts = [(match.group("prompt").replace("\\:", ":"), float(
|
||||
match.group("weight") or 1)) for match in re.finditer(prompt_parser, text)]
|
||||
if skip_normalize:
|
||||
return parsed_prompts
|
||||
weight_sum = sum(map(lambda x: x[1], parsed_prompts))
|
||||
if weight_sum == 0:
|
||||
print(
|
||||
"Warning: Subprompt weights add up to zero. Discarding and using even weights instead.")
|
||||
equal_weight = 1 / len(parsed_prompts)
|
||||
return [(x[0], equal_weight) for x in parsed_prompts]
|
||||
return [(x[0], x[1] / weight_sum) for x in parsed_prompts]
|
||||
|
||||
# shows how the prompt is tokenized
|
||||
# usually tokens have '</w>' to indicate end-of-word,
|
||||
# but for readability it has been replaced with ' '
|
||||
def _log_tokenization(self, text):
|
||||
if not self.log_tokenization:
|
||||
return
|
||||
tokens = self.model.cond_stage_model.tokenizer._tokenize(text)
|
||||
tokenized = ""
|
||||
discarded = ""
|
||||
usedTokens = 0
|
||||
totalTokens = len(tokens)
|
||||
for i in range(0, totalTokens):
|
||||
token = tokens[i].replace('</w>', ' ')
|
||||
# alternate color
|
||||
s = (usedTokens % 6) + 1
|
||||
if i < self.model.cond_stage_model.max_length:
|
||||
tokenized = tokenized + f"\x1b[0;3{s};40m{token}"
|
||||
usedTokens += 1
|
||||
else: # over max token length
|
||||
discarded = discarded + f"\x1b[0;3{s};40m{token}"
|
||||
print(f"\nTokens ({usedTokens}):\n{tokenized}\x1b[0m")
|
||||
if discarded != "":
|
||||
print(
|
||||
f"Tokens Discarded ({totalTokens-usedTokens}):\n{discarded}\x1b[0m")
|
||||
|
||||
def _resolution_check(self, width, height, log=False):
|
||||
resize_needed = False
|
||||
w, h = map(
|
||||
lambda x: x - x % 64, (width, height)
|
||||
) # resize to integer multiple of 64
|
||||
if h != height or w != width:
|
||||
if log:
|
||||
print(
|
||||
f'>> Provided width and height must be multiples of 64. Auto-resizing to {w}x{h}'
|
||||
)
|
||||
height = h
|
||||
width = w
|
||||
resize_needed = True
|
||||
|
||||
if (width * height) > (self.width * self.height):
|
||||
print(">> This input is larger than your defaults. If you run out of memory, please use a smaller image.")
|
||||
|
||||
return width, height, resize_needed
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def slerp(self, t, v0, v1, DOT_THRESHOLD=0.9995):
|
||||
'''
|
||||
Spherical linear interpolation
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
t (float/np.ndarray): Float value between 0.0 and 1.0
|
||||
v0 (np.ndarray): Starting vector
|
||||
v1 (np.ndarray): Final vector
|
||||
DOT_THRESHOLD (float): Threshold for considering the two vectors as
|
||||
colineal. Not recommended to alter this.
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
v2 (np.ndarray): Interpolation vector between v0 and v1
|
||||
This module is provided for backward compatibility with the
|
||||
original (hasty) API.
|
||||
|
||||
Please use ldm.generate instead.
|
||||
'''
|
||||
inputs_are_torch = False
|
||||
if not isinstance(v0, np.ndarray):
|
||||
inputs_are_torch = True
|
||||
v0 = v0.detach().cpu().numpy()
|
||||
if not isinstance(v1, np.ndarray):
|
||||
inputs_are_torch = True
|
||||
v1 = v1.detach().cpu().numpy()
|
||||
|
||||
dot = np.sum(v0 * v1 / (np.linalg.norm(v0) * np.linalg.norm(v1)))
|
||||
if np.abs(dot) > DOT_THRESHOLD:
|
||||
v2 = (1 - t) * v0 + t * v1
|
||||
else:
|
||||
theta_0 = np.arccos(dot)
|
||||
sin_theta_0 = np.sin(theta_0)
|
||||
theta_t = theta_0 * t
|
||||
sin_theta_t = np.sin(theta_t)
|
||||
s0 = np.sin(theta_0 - theta_t) / sin_theta_0
|
||||
s1 = sin_theta_t / sin_theta_0
|
||||
v2 = s0 * v0 + s1 * v1
|
||||
from ldm.generate import Generate
|
||||
|
||||
if inputs_are_torch:
|
||||
v2 = torch.from_numpy(v2).to(self.device)
|
||||
|
||||
return v2
|
||||
class T2I(Generate):
|
||||
def __init__(self,**kwargs):
|
||||
print(f'>> The ldm.simplet2i module is deprecated. Use ldm.generate instead. It is a drop-in replacement.')
|
||||
super().__init__(kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -65,25 +65,31 @@
|
||||
"imageio-ffmpeg==0.4.2\n",
|
||||
"imageio==2.9.0\n",
|
||||
"kornia==0.6.0\n",
|
||||
"# pip will resolve the version which matches torch\n",
|
||||
"numpy\n",
|
||||
"omegaconf==2.1.1\n",
|
||||
"opencv-python==4.6.0.66\n",
|
||||
"pillow==9.2.0\n",
|
||||
"pip>=22\n",
|
||||
"pudb==2019.2\n",
|
||||
"pytorch-lightning==1.4.2\n",
|
||||
"streamlit==1.12.0\n",
|
||||
"# Regular \"taming-transformers\" doesn't seem to work\n",
|
||||
"# \"CompVis/taming-transformers\" doesn't work\n",
|
||||
"# ldm\\models\\autoencoder.py\", line 6, in <module>\n",
|
||||
"# from taming.modules.vqvae.quantize import VectorQuantizer2 as VectorQuantizer\n",
|
||||
"# ModuleNotFoundError\n",
|
||||
"taming-transformers-rom1504==0.0.6\n",
|
||||
"test-tube>=0.7.5\n",
|
||||
"torch-fidelity==0.3.0\n",
|
||||
"torchmetrics==0.6.0\n",
|
||||
"torchvision==0.12.0\n",
|
||||
"transformers==4.19.2\n",
|
||||
"git+https://github.com/openai/CLIP.git@main#egg=clip\n",
|
||||
"git+https://github.com/lstein/k-diffusion.git@master#egg=k-diffusion\n",
|
||||
"# No CUDA in PyPi builds\n",
|
||||
"torch@https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu113/torch-1.11.0%2Bcu113-cp310-cp310-win_amd64.whl\n",
|
||||
"# No MKL in PyPi builds (faster, more robust than OpenBLAS)\n",
|
||||
"numpy@https://download.lfd.uci.edu/pythonlibs/archived/numpy-1.22.4+mkl-cp310-cp310-win_amd64.whl\n",
|
||||
"--extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu113 --trusted-host https://download.pytorch.org\n",
|
||||
"torch==1.11.0\n",
|
||||
"# Same as numpy - let pip do its thing\n",
|
||||
"torchvision\n",
|
||||
"-e .\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
@ -3,7 +3,6 @@
|
||||
"nbformat_minor": 0,
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"colab": {
|
||||
"name": "Stable_Diffusion_AI_Notebook.ipynb",
|
||||
"provenance": [],
|
||||
"collapsed_sections": [],
|
||||
"private_outputs": true
|
||||
@ -22,18 +21,18 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Stable Diffusion AI Notebook\n",
|
||||
"# Stable Diffusion AI Notebook (Release 1.13)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"<img src=\"https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/60411196/186547976-d9de378a-9de8-4201-9c25-c057a9c59bad.jpeg\" alt=\"stable-diffusion-ai\" width=\"170px\"/> <br>\n",
|
||||
"#### Instructions:\n",
|
||||
"1. Execute each cell in order to mount a Dream bot and create images from text. <br>\n",
|
||||
"2. Once cells 1-8 were run correctly you'll be executing a terminal in cell #9, you'll to enter `pipenv run scripts/dream.py` command to run Dream bot.<br> \n",
|
||||
"2. Once cells 1-8 were run correctly you'll be executing a terminal in cell #9, you'll need to enter `python scripts/dream.py` command to run Dream bot.<br> \n",
|
||||
"3. After launching dream bot, you'll see: <br> `Dream > ` in terminal. <br> Insert a command, eg. `Dream > Astronaut floating in a distant galaxy`, or type `-h` for help.\n",
|
||||
"3. After completion you'll see your generated images in path `stable-diffusion/outputs/img-samples/`, you can also display images in cell #10.\n",
|
||||
"3. After completion you'll see your generated images in path `stable-diffusion/outputs/img-samples/`, you can also show last generated images in cell #10.\n",
|
||||
"4. To quit Dream bot use `q` command. <br> \n",
|
||||
"---\n",
|
||||
"<font color=\"red\">Note:</font> It takes some time to load, but after installing all dependencies you can use the bot all time you want while colab instance is up. <br>\n",
|
||||
"<font color=\"red\">Requirements:</font> For this notebook to work you need to have [Stable-Diffusion-v-1-4](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion-v-1-4-original) stored in your Google Drive, it will be needed in cell #6\n",
|
||||
"<font color=\"red\">Requirements:</font> For this notebook to work you need to have [Stable-Diffusion-v-1-4](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion-v-1-4-original) stored in your Google Drive, it will be needed in cell #7\n",
|
||||
"##### For more details visit Github repository: [lstein/stable-diffusion](https://github.com/lstein/stable-diffusion)\n",
|
||||
"---\n"
|
||||
],
|
||||
@ -41,6 +40,15 @@
|
||||
"id": "ycYWcsEKc6w7"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## ◢ Installation"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"id": "dr32VLxlnouf"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
@ -68,43 +76,28 @@
|
||||
"from os.path import exists\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"if exists(\"/content/stable-diffusion/\")==True:\n",
|
||||
" %cd /content/stable-diffusion/\n",
|
||||
" print(\"Already downloaded repo\")\n",
|
||||
"else:\n",
|
||||
" !git clone --quiet https://github.com/lstein/stable-diffusion.git # Original repo\n",
|
||||
" %cd stable-diffusion/\n",
|
||||
" !git checkout --quiet tags/release-1.09\n",
|
||||
" "
|
||||
" %cd /content/stable-diffusion/\n",
|
||||
" !git checkout --quiet tags/release-1.13"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#@title 3. Install Python 3.8 \n",
|
||||
"%%capture --no-stderr\n",
|
||||
"#@title 3. Install dependencies\n",
|
||||
"import gc\n",
|
||||
"!apt-get -qq install python3.8\n",
|
||||
"gc.collect()"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"id": "daHlozvwKesj",
|
||||
"cellView": "form"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"outputs": []
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#@title 4. Install dependencies from file in a VirtualEnv\n",
|
||||
"#@markdown Be patient, it takes ~ 5 - 7min <br>\n",
|
||||
"%%capture --no-stderr\n",
|
||||
"#Virtual environment\n",
|
||||
"!pip install pipenv -q\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"if exists(\"/content/stable-diffusion/requirements-colab.txt\")==True:\n",
|
||||
" %cd /content/stable-diffusion/\n",
|
||||
" print(\"Already downloaded requirements file\")\n",
|
||||
"else:\n",
|
||||
" !wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lstein/stable-diffusion/development/requirements-colab.txt\n",
|
||||
"!pip install colab-xterm\n",
|
||||
"%load_ext colabxterm\n",
|
||||
"!pipenv --python 3.8\n",
|
||||
"!pipenv install -r requirements.txt --skip-lock\n",
|
||||
"gc.collect()\n"
|
||||
"!pip install -r requirements-colab.txt\n",
|
||||
"gc.collect()"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"cellView": "form",
|
||||
@ -116,7 +109,44 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#@title 5. Mount google Drive\n",
|
||||
"#@title 4. Load small ML models required\n",
|
||||
"%cd /content/stable-diffusion/\n",
|
||||
"!python scripts/preload_models.py\n",
|
||||
"gc.collect()"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"cellView": "form",
|
||||
"id": "ChIDWxLVHGGJ"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"outputs": []
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#@title 5. Restart Runtime\n",
|
||||
"exit()"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"cellView": "form",
|
||||
"id": "8rSMhgnAttQa"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"outputs": []
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## ◢ Configuration"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"id": "795x1tMoo8b1"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#@title 6. Mount google Drive\n",
|
||||
"from google.colab import drive\n",
|
||||
"drive.mount('/content/drive')"
|
||||
],
|
||||
@ -130,7 +160,7 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#@title 6. Drive Path to model\n",
|
||||
"#@title 7. Drive Path to model\n",
|
||||
"#@markdown Path should start with /content/drive/path-to-your-file <br>\n",
|
||||
"#@markdown <font color=\"red\">Note:</font> Model should be downloaded from https://huggingface.co <br>\n",
|
||||
"#@markdown Lastest release: [Stable-Diffusion-v-1-4](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion-v-1-4-original)\n",
|
||||
@ -152,7 +182,7 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#@title 7. Symlink to model\n",
|
||||
"#@title 8. Symlink to model\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"from os.path import exists\n",
|
||||
"import os \n",
|
||||
@ -181,32 +211,27 @@
|
||||
"outputs": []
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#@title 8. Load small ML models required\n",
|
||||
"%%capture --no-stderr\n",
|
||||
"!pipenv run scripts/preload_models.py\n",
|
||||
"gc.collect()"
|
||||
"## ◢ Execution"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"cellView": "form",
|
||||
"id": "ChIDWxLVHGGJ"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"outputs": []
|
||||
"id": "Mc28N0_NrCQH"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#@title 9. Run Terminal and Execute Dream bot\n",
|
||||
"#@markdown <font color=\"blue\">Steps:</font> <br>\n",
|
||||
"#@markdown 1. Execute command `pipenv run scripts/dream.py` to run dream bot.<br>\n",
|
||||
"#@markdown 1. Execute command `python scripts/dream.py` to run dream bot.<br>\n",
|
||||
"#@markdown 2. After initialized you'll see `Dream>` line.<br>\n",
|
||||
"#@markdown 3. Example text: `Astronaut floating in a distant galaxy` <br>\n",
|
||||
"#@markdown 4. To quit Dream bot use: `q` command.<br>\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"#Run from virtual env\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"import gc\n",
|
||||
"%cd /content/stable-diffusion/\n",
|
||||
"%load_ext colabxterm\n",
|
||||
"%xterm\n",
|
||||
"gc.collect()"
|
||||
],
|
||||
@ -220,18 +245,18 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#@title 10. Show generated images\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"#@title 10. Show the last 15 generated images\n",
|
||||
"import gc\n",
|
||||
"import glob\n",
|
||||
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n",
|
||||
"import matplotlib.image as mpimg\n",
|
||||
"%matplotlib inline\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"images = []\n",
|
||||
"for img_path in glob.glob('/content/stable-diffusion/outputs/img-samples/*.png'):\n",
|
||||
"for img_path in sorted(glob.glob('/content/stable-diffusion/outputs/img-samples/*.png'), reverse=True):\n",
|
||||
" images.append(mpimg.imread(img_path))\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Remove ticks and labels on x-axis and y-axis both\n",
|
||||
"images = images[:15] \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"plt.figure(figsize=(20,10))\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
26
requirements-colab.txt
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
|
||||
albumentations==0.4.3
|
||||
clean-fid==0.1.29
|
||||
einops==0.3.0
|
||||
huggingface-hub==0.8.1
|
||||
imageio-ffmpeg==0.4.2
|
||||
imageio==2.9.0
|
||||
kornia==0.6.0
|
||||
numpy==1.21.6
|
||||
omegaconf==2.1.1
|
||||
opencv-python==4.6.0.66
|
||||
pillow==9.2.0
|
||||
pip>=22
|
||||
pudb==2019.2
|
||||
pytorch-lightning==1.4.2
|
||||
streamlit==1.12.0
|
||||
taming-transformers-rom1504==0.0.6
|
||||
test-tube>=0.7.5
|
||||
torch-fidelity==0.3.0
|
||||
torchmetrics==0.6.0
|
||||
torchtext==0.6.0
|
||||
transformers==4.19.2
|
||||
torch==1.12.1+cu113
|
||||
torchvision==0.13.1+cu113
|
||||
git+https://github.com/openai/CLIP.git@main#egg=clip
|
||||
git+https://github.com/lstein/k-diffusion.git@master#egg=k-diffusion
|
||||
-e .
|
||||
33
requirements-lin.txt
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
||||
albumentations==0.4.3
|
||||
einops==0.3.0
|
||||
huggingface-hub==0.8.1
|
||||
imageio-ffmpeg==0.4.2
|
||||
imageio==2.9.0
|
||||
kornia==0.6.0
|
||||
# pip will resolve the version which matches torch
|
||||
numpy
|
||||
omegaconf==2.1.1
|
||||
opencv-python==4.6.0.66
|
||||
pillow==9.2.0
|
||||
pip>=22
|
||||
pudb==2019.2
|
||||
pytorch-lightning==1.4.2
|
||||
streamlit==1.12.0
|
||||
# "CompVis/taming-transformers" doesn't work
|
||||
# ldm\models\autoencoder.py", line 6, in <module>
|
||||
# from taming.modules.vqvae.quantize import VectorQuantizer2 as VectorQuantizer
|
||||
# ModuleNotFoundError
|
||||
taming-transformers-rom1504==0.0.6
|
||||
test-tube>=0.7.5
|
||||
torch-fidelity==0.3.0
|
||||
torchmetrics==0.6.0
|
||||
transformers==4.19.2
|
||||
git+https://github.com/openai/CLIP.git@main#egg=clip
|
||||
git+https://github.com/lstein/k-diffusion.git@master#egg=k-diffusion
|
||||
git+https://github.com/lstein/GFPGAN@fix-dark-cast-images#egg=gfpgan
|
||||
# No CUDA in PyPi builds
|
||||
--extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu113 --trusted-host https://download.pytorch.org
|
||||
torch==1.11.0
|
||||
# Same as numpy - let pip do its thing
|
||||
torchvision
|
||||
-e .
|
||||
@ -11,7 +11,7 @@ opencv-python==4.6.0.66
|
||||
pillow==9.2.0
|
||||
pudb==2019.2
|
||||
torch==1.12.1
|
||||
torchvision==0.12.0
|
||||
torchvision==0.13.0
|
||||
pytorch-lightning==1.4.2
|
||||
streamlit==1.12.0
|
||||
test-tube>=0.7.5
|
||||
@ -21,3 +21,4 @@ transformers==4.19.2
|
||||
-e git+https://github.com/openai/CLIP.git@main#egg=clip
|
||||
-e git+https://github.com/CompVis/taming-transformers.git@master#egg=taming-transformers
|
||||
-e git+https://github.com/Birch-san/k-diffusion.git@mps#egg=k-diffusion
|
||||
-e git+https://github.com/lstein/GFPGAN@fix-dark-cast-images#egg=gfpgan
|
||||
33
requirements-win.txt
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
||||
albumentations==0.4.3
|
||||
einops==0.3.0
|
||||
huggingface-hub==0.8.1
|
||||
imageio-ffmpeg==0.4.2
|
||||
imageio==2.9.0
|
||||
kornia==0.6.0
|
||||
# pip will resolve the version which matches torch
|
||||
numpy
|
||||
omegaconf==2.1.1
|
||||
opencv-python==4.6.0.66
|
||||
pillow==9.2.0
|
||||
pip>=22
|
||||
pudb==2019.2
|
||||
pytorch-lightning==1.4.2
|
||||
streamlit==1.12.0
|
||||
# "CompVis/taming-transformers" doesn't work
|
||||
# ldm\models\autoencoder.py", line 6, in <module>
|
||||
# from taming.modules.vqvae.quantize import VectorQuantizer2 as VectorQuantizer
|
||||
# ModuleNotFoundError
|
||||
taming-transformers-rom1504==0.0.6
|
||||
test-tube>=0.7.5
|
||||
torch-fidelity==0.3.0
|
||||
torchmetrics==0.6.0
|
||||
transformers==4.19.2
|
||||
git+https://github.com/openai/CLIP.git@main#egg=clip
|
||||
git+https://github.com/lstein/k-diffusion.git@master#egg=k-diffusion
|
||||
git+https://github.com/lstein/GFPGAN@fix-dark-cast-images#egg=gfpgan
|
||||
# No CUDA in PyPi builds
|
||||
--extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu113 --trusted-host https://download.pytorch.org
|
||||
torch==1.11.0
|
||||
# Same as numpy - let pip do its thing
|
||||
torchvision
|
||||
-e .
|
||||
116
scripts/dream.py
@ -15,6 +15,12 @@ from ldm.dream.server import DreamServer, ThreadingDreamServer
|
||||
from ldm.dream.image_util import make_grid
|
||||
from omegaconf import OmegaConf
|
||||
|
||||
# Placeholder to be replaced with proper class that tracks the
|
||||
# outputs and associates with the prompt that generated them.
|
||||
# Just want to get the formatting look right for now.
|
||||
output_cntr = 0
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def main():
|
||||
"""Initialize command-line parsers and the diffusion model"""
|
||||
arg_parser = create_argv_parser()
|
||||
@ -40,7 +46,7 @@ def main():
|
||||
print('* Initializing, be patient...\n')
|
||||
sys.path.append('.')
|
||||
from pytorch_lightning import logging
|
||||
from ldm.simplet2i import T2I
|
||||
from ldm.generate import Generate
|
||||
|
||||
# these two lines prevent a horrible warning message from appearing
|
||||
# when the frozen CLIP tokenizer is imported
|
||||
@ -52,7 +58,7 @@ def main():
|
||||
# defaults passed on the command line.
|
||||
# additional parameters will be added (or overriden) during
|
||||
# the user input loop
|
||||
t2i = T2I(
|
||||
t2i = Generate(
|
||||
width=width,
|
||||
height=height,
|
||||
sampler_name=opt.sampler_name,
|
||||
@ -61,9 +67,10 @@ def main():
|
||||
config=config,
|
||||
grid=opt.grid,
|
||||
# this is solely for recreating the prompt
|
||||
latent_diffusion_weights=opt.laion400m,
|
||||
seamless=opt.seamless,
|
||||
embedding_path=opt.embedding_path,
|
||||
device_type=opt.device
|
||||
device_type=opt.device,
|
||||
ignore_ctrl_c=opt.infile is None,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# make sure the output directory exists
|
||||
@ -87,12 +94,11 @@ def main():
|
||||
print(f'{e}. Aborting.')
|
||||
sys.exit(-1)
|
||||
|
||||
if opt.seamless:
|
||||
print(">> changed to seamless tiling mode")
|
||||
|
||||
# preload the model
|
||||
tic = time.time()
|
||||
t2i.load_model()
|
||||
print(
|
||||
f'>> model loaded in', '%4.2fs' % (time.time() - tic)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if not infile:
|
||||
print(
|
||||
@ -101,7 +107,7 @@ def main():
|
||||
|
||||
cmd_parser = create_cmd_parser()
|
||||
if opt.web:
|
||||
dream_server_loop(t2i, opt.host, opt.port)
|
||||
dream_server_loop(t2i, opt.host, opt.port, opt.outdir)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
main_loop(t2i, opt.outdir, opt.prompt_as_dir, cmd_parser, infile)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -109,8 +115,8 @@ def main():
|
||||
def main_loop(t2i, outdir, prompt_as_dir, parser, infile):
|
||||
"""prompt/read/execute loop"""
|
||||
done = False
|
||||
last_seeds = []
|
||||
path_filter = re.compile(r'[<>:"/\\|?*]')
|
||||
last_results = list()
|
||||
|
||||
# os.pathconf is not available on Windows
|
||||
if hasattr(os, 'pathconf'):
|
||||
@ -125,7 +131,10 @@ def main_loop(t2i, outdir, prompt_as_dir, parser, infile):
|
||||
command = get_next_command(infile)
|
||||
except EOFError:
|
||||
done = True
|
||||
break
|
||||
continue
|
||||
except KeyboardInterrupt:
|
||||
done = True
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
||||
# skip empty lines
|
||||
if not command.strip():
|
||||
@ -175,13 +184,25 @@ def main_loop(t2i, outdir, prompt_as_dir, parser, infile):
|
||||
if len(opt.prompt) == 0:
|
||||
print('Try again with a prompt!')
|
||||
continue
|
||||
# retrieve previous value!
|
||||
if opt.init_img is not None and re.match('^-\\d+$', opt.init_img):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
opt.init_img = last_results[int(opt.init_img)][0]
|
||||
print(f'>> Reusing previous image {opt.init_img}')
|
||||
except IndexError:
|
||||
print(
|
||||
f'>> No previous initial image at position {opt.init_img} found')
|
||||
opt.init_img = None
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
||||
if opt.seed is not None and opt.seed < 0: # retrieve previous value!
|
||||
try:
|
||||
opt.seed = last_seeds[opt.seed]
|
||||
print(f'reusing previous seed {opt.seed}')
|
||||
opt.seed = last_results[opt.seed][1]
|
||||
print(f'>> Reusing previous seed {opt.seed}')
|
||||
except IndexError:
|
||||
print(f'No previous seed at position {opt.seed} found')
|
||||
print(f'>> No previous seed at position {opt.seed} found')
|
||||
opt.seed = None
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
||||
do_grid = opt.grid or t2i.grid
|
||||
|
||||
@ -232,13 +253,15 @@ def main_loop(t2i, outdir, prompt_as_dir, parser, infile):
|
||||
current_outdir = outdir
|
||||
|
||||
# Here is where the images are actually generated!
|
||||
last_results = []
|
||||
try:
|
||||
file_writer = PngWriter(current_outdir)
|
||||
prefix = file_writer.unique_prefix()
|
||||
seeds = set()
|
||||
results = [] # list of filename, prompt pairs
|
||||
grid_images = dict() # seed -> Image, only used if `do_grid`
|
||||
|
||||
def image_writer(image, seed, upscaled=False):
|
||||
path = None
|
||||
if do_grid:
|
||||
grid_images[seed] = image
|
||||
else:
|
||||
@ -254,37 +277,41 @@ def main_loop(t2i, outdir, prompt_as_dir, parser, infile):
|
||||
else:
|
||||
iter_opt.with_variations = opt.with_variations + this_variation
|
||||
iter_opt.variation_amount = 0
|
||||
normalized_prompt = PromptFormatter(t2i, iter_opt).normalize_prompt()
|
||||
normalized_prompt = PromptFormatter(
|
||||
t2i, iter_opt).normalize_prompt()
|
||||
metadata_prompt = f'{normalized_prompt} -S{iter_opt.seed}'
|
||||
elif opt.with_variations is not None:
|
||||
normalized_prompt = PromptFormatter(t2i, opt).normalize_prompt()
|
||||
metadata_prompt = f'{normalized_prompt} -S{opt.seed}' # use the original seed - the per-iteration value is the last variation-seed
|
||||
normalized_prompt = PromptFormatter(
|
||||
t2i, opt).normalize_prompt()
|
||||
# use the original seed - the per-iteration value is the last variation-seed
|
||||
metadata_prompt = f'{normalized_prompt} -S{opt.seed}'
|
||||
else:
|
||||
normalized_prompt = PromptFormatter(t2i, opt).normalize_prompt()
|
||||
normalized_prompt = PromptFormatter(
|
||||
t2i, opt).normalize_prompt()
|
||||
metadata_prompt = f'{normalized_prompt} -S{seed}'
|
||||
path = file_writer.save_image_and_prompt_to_png(image, metadata_prompt, filename)
|
||||
path = file_writer.save_image_and_prompt_to_png(
|
||||
image, metadata_prompt, filename)
|
||||
if (not upscaled) or opt.save_original:
|
||||
# only append to results if we didn't overwrite an earlier output
|
||||
results.append([path, metadata_prompt])
|
||||
|
||||
seeds.add(seed)
|
||||
last_results.append([path, seed])
|
||||
|
||||
t2i.prompt2image(image_callback=image_writer, **vars(opt))
|
||||
|
||||
if do_grid and len(grid_images) > 0:
|
||||
grid_img = make_grid(list(grid_images.values()))
|
||||
first_seed = next(iter(seeds))
|
||||
grid_seeds = list(grid_images.keys())
|
||||
first_seed = last_results[0][1]
|
||||
filename = f'{prefix}.{first_seed}.png'
|
||||
# TODO better metadata for grid images
|
||||
normalized_prompt = PromptFormatter(t2i, opt).normalize_prompt()
|
||||
metadata_prompt = f'{normalized_prompt} -S{first_seed} --grid -N{len(grid_images)}'
|
||||
normalized_prompt = PromptFormatter(
|
||||
t2i, opt).normalize_prompt()
|
||||
metadata_prompt = f'{normalized_prompt} -S{first_seed} --grid -n{len(grid_images)} # {grid_seeds}'
|
||||
path = file_writer.save_image_and_prompt_to_png(
|
||||
grid_img, metadata_prompt, filename
|
||||
)
|
||||
results = [[path, metadata_prompt]]
|
||||
|
||||
last_seeds = list(seeds)
|
||||
|
||||
except AssertionError as e:
|
||||
print(e)
|
||||
continue
|
||||
@ -296,6 +323,7 @@ def main_loop(t2i, outdir, prompt_as_dir, parser, infile):
|
||||
print('Outputs:')
|
||||
log_path = os.path.join(current_outdir, 'dream_log.txt')
|
||||
write_log_message(results, log_path)
|
||||
print()
|
||||
|
||||
print('goodbye!')
|
||||
|
||||
@ -312,7 +340,8 @@ def get_next_command(infile=None) -> str: #command string
|
||||
print(f'#{command}')
|
||||
return command
|
||||
|
||||
def dream_server_loop(t2i, host, port):
|
||||
|
||||
def dream_server_loop(t2i, host, port, outdir):
|
||||
print('\n* --web was specified, starting web server...')
|
||||
# Change working directory to the stable-diffusion directory
|
||||
os.chdir(
|
||||
@ -321,10 +350,12 @@ def dream_server_loop(t2i, host, port):
|
||||
|
||||
# Start server
|
||||
DreamServer.model = t2i
|
||||
DreamServer.outdir = outdir
|
||||
dream_server = ThreadingDreamServer((host, port))
|
||||
print(">> Started Stable Diffusion dream server!")
|
||||
if host == '0.0.0.0':
|
||||
print(f"Point your browser at http://localhost:{port} or use the host's DNS name or IP address.")
|
||||
print(
|
||||
f"Point your browser at http://localhost:{port} or use the host's DNS name or IP address.")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print(">> Default host address now 127.0.0.1 (localhost). Use --host 0.0.0.0 to bind any address.")
|
||||
print(f">> Point your browser at http://{host}:{port}.")
|
||||
@ -339,8 +370,12 @@ def dream_server_loop(t2i, host, port):
|
||||
|
||||
def write_log_message(results, log_path):
|
||||
"""logs the name of the output image, prompt, and prompt args to the terminal and log file"""
|
||||
global output_cntr
|
||||
log_lines = [f'{path}: {prompt}\n' for path, prompt in results]
|
||||
print(*log_lines, sep='')
|
||||
for l in log_lines:
|
||||
output_cntr += 1
|
||||
print(f'[{output_cntr}] {l}',end='')
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
with open(log_path, 'a', encoding='utf-8') as file:
|
||||
file.writelines(log_lines)
|
||||
@ -357,6 +392,7 @@ SAMPLER_CHOICES=[
|
||||
'plms',
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def create_argv_parser():
|
||||
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
|
||||
description="""Generate images using Stable Diffusion.
|
||||
@ -418,6 +454,11 @@ def create_argv_parser():
|
||||
default='outputs/img-samples',
|
||||
help='Directory to save generated images and a log of prompts and seeds. Default: outputs/img-samples',
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
'--seamless',
|
||||
action='store_true',
|
||||
help='Change the model to seamless tiling (circular) mode',
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
'--embedding_path',
|
||||
type=str,
|
||||
@ -434,7 +475,7 @@ def create_argv_parser():
|
||||
'--gfpgan_bg_upsampler',
|
||||
type=str,
|
||||
default='realesrgan',
|
||||
help='Background upsampler. Default: realesrgan. Options: realesrgan, none. Only used if --gfpgan is specified',
|
||||
help='Background upsampler. Default: realesrgan. Options: realesrgan, none.',
|
||||
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
@ -452,7 +493,7 @@ def create_argv_parser():
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
'--gfpgan_dir',
|
||||
type=str,
|
||||
default='../GFPGAN',
|
||||
default='./src/gfpgan',
|
||||
help='Indicates the directory containing the GFPGAN code.',
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
@ -540,6 +581,11 @@ def create_cmd_parser():
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
help='Directory to save generated images and a log of prompts and seeds',
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
'--seamless',
|
||||
action='store_true',
|
||||
help='Change the model to seamless tiling (circular) mode',
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
'-i',
|
||||
'--individual',
|
||||
@ -552,6 +598,12 @@ def create_cmd_parser():
|
||||
type=str,
|
||||
help='Path to input image for img2img mode (supersedes width and height)',
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
'-M',
|
||||
'--init_mask',
|
||||
type=str,
|
||||
help='Path to input mask for inpainting mode (supersedes width and height)',
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
'-T',
|
||||
'-fit',
|
||||
|
||||
@ -232,7 +232,12 @@ def main():
|
||||
print(f"reading prompts from {opt.from_file}")
|
||||
with open(opt.from_file, "r") as f:
|
||||
data = f.read().splitlines()
|
||||
if (len(data) >= batch_size):
|
||||
data = list(chunk(data, batch_size))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
while (len(data) < batch_size):
|
||||
data.append(data[-1])
|
||||
data = [data]
|
||||
|
||||
sample_path = os.path.join(outpath, "samples")
|
||||
os.makedirs(sample_path, exist_ok=True)
|
||||
|
||||
BIN
static/dream_web/favicon.ico
Normal file
|
After Width: 16px | Height: 16px | Size: 1.1 KiB |
@ -1,11 +1,14 @@
|
||||
* {
|
||||
font-family: 'Arial';
|
||||
font-size: 100%;
|
||||
}
|
||||
#header {
|
||||
text-decoration: dotted underline;
|
||||
body {
|
||||
font-size: 1em;
|
||||
}
|
||||
#search {
|
||||
margin-top: 20vh;
|
||||
textarea {
|
||||
font-size: 0.95em;
|
||||
}
|
||||
header, form, #progress-section {
|
||||
margin-left: auto;
|
||||
margin-right: auto;
|
||||
max-width: 1024px;
|
||||
@ -13,11 +16,36 @@
|
||||
}
|
||||
fieldset {
|
||||
border: none;
|
||||
line-height: 2.2em;
|
||||
}
|
||||
select, input {
|
||||
margin-right: 10px;
|
||||
padding: 2px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
input[type=submit] {
|
||||
background-color: #666;
|
||||
color: white;
|
||||
}
|
||||
input[type=checkbox] {
|
||||
margin-right: 0px;
|
||||
width: 20px;
|
||||
height: 20px;
|
||||
vertical-align: middle;
|
||||
}
|
||||
input#seed {
|
||||
margin-right: 0px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
div {
|
||||
padding: 10px 10px 10px 10px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
#fieldset-search {
|
||||
header {
|
||||
margin-bottom: 16px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
header h1 {
|
||||
margin-bottom: 0;
|
||||
font-size: 2em;
|
||||
}
|
||||
#search-box {
|
||||
display: flex;
|
||||
}
|
||||
#scaling-inprocess-message {
|
||||
@ -27,33 +55,40 @@ div {
|
||||
}
|
||||
#prompt {
|
||||
flex-grow: 1;
|
||||
|
||||
border-radius: 20px 0px 0px 20px;
|
||||
padding: 5px 10px 5px 10px;
|
||||
border: 1px solid black;
|
||||
border-right: none;
|
||||
border: 1px solid #999;
|
||||
outline: none;
|
||||
}
|
||||
#submit {
|
||||
border-radius: 0px 20px 20px 0px;
|
||||
padding: 5px 10px 5px 10px;
|
||||
border: 1px solid black;
|
||||
border: 1px solid #999;
|
||||
}
|
||||
#reset-all {
|
||||
#reset-all, #remove-image {
|
||||
margin-top: 12px;
|
||||
font-size: 0.8em;
|
||||
background-color: pink;
|
||||
border: 1px solid #999;
|
||||
border-radius: 4px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
#results {
|
||||
text-align: center;
|
||||
// max-width: 1024px;
|
||||
margin: auto;
|
||||
padding-top: 10px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
#results img {
|
||||
cursor: pointer;
|
||||
height: 30vh;
|
||||
border-radius: 5px;
|
||||
#results figure {
|
||||
display: inline-block;
|
||||
margin: 10px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
#results figcaption {
|
||||
font-size: 0.8em;
|
||||
padding: 3px;
|
||||
color: #888;
|
||||
cursor: pointer;
|
||||
}
|
||||
#results img {
|
||||
border-radius: 5px;
|
||||
object-fit: cover;
|
||||
}
|
||||
#fieldset-config {
|
||||
line-height:2em;
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -63,8 +98,15 @@ input[type="number"] {
|
||||
#seed {
|
||||
width: 150px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
hr {
|
||||
// width: 200px;
|
||||
button#reset-seed {
|
||||
font-size: 1.7em;
|
||||
background: #efefef;
|
||||
border: 1px solid #999;
|
||||
border-radius: 4px;
|
||||
line-height: 0.8;
|
||||
margin: 0 10px 0 0;
|
||||
padding: 0 5px 3px;
|
||||
vertical-align: middle;
|
||||
}
|
||||
label {
|
||||
white-space: nowrap;
|
||||
@ -83,6 +125,9 @@ label {
|
||||
#txt2img {
|
||||
background-color: #DCDCDC;
|
||||
}
|
||||
#variations {
|
||||
background-color: #EEEEEE;
|
||||
}
|
||||
#img2img {
|
||||
background-color: #F5F5F5;
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -92,6 +137,8 @@ label {
|
||||
#progress-section {
|
||||
background-color: #F5F5F5;
|
||||
}
|
||||
#about {
|
||||
background-color: #DCDCDC;
|
||||
|
||||
#no-results-message:not(:only-child) {
|
||||
display: none;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2,32 +2,37 @@
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<title>Stable Diffusion Dream Server</title>
|
||||
<meta charset="utf-8">
|
||||
<link rel="icon" href="data:,">
|
||||
<link rel="icon" type="image/x-icon" href="static/dream_web/favicon.ico" />
|
||||
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
|
||||
|
||||
<link rel="stylesheet" href="static/dream_web/index.css">
|
||||
<script src="config.js"></script>
|
||||
<script src="static/dream_web/index.js"></script>
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
<body>
|
||||
<div id="search">
|
||||
<h2 id="header">Stable Diffusion Dream Server</h2>
|
||||
<header>
|
||||
<h1>Stable Diffusion Dream Server</h1>
|
||||
<div id="about">
|
||||
For news and support for this web service, visit our <a href="http://github.com/lstein/stable-diffusion">GitHub site</a>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</header>
|
||||
|
||||
<main>
|
||||
<form id="generate-form" method="post" action="#">
|
||||
<div id="txt2img">
|
||||
<fieldset id="fieldset-search">
|
||||
<input type="text" id="prompt" name="prompt">
|
||||
<fieldset id="txt2img">
|
||||
<div id="search-box">
|
||||
<textarea rows="3" id="prompt" name="prompt"></textarea>
|
||||
<input type="submit" id="submit" value="Generate">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</fieldset>
|
||||
<fieldset id="fieldset-config">
|
||||
<label for="iterations">Images to generate:</label>
|
||||
<input value="1" type="number" id="iterations" name="iterations" size="4">
|
||||
<label for="steps">Steps:</label>
|
||||
<input value="50" type="number" id="steps" name="steps">
|
||||
<label for="cfgscale">Cfg Scale:</label>
|
||||
<input value="7.5" type="number" id="cfgscale" name="cfgscale" step="any">
|
||||
<label for="sampler">Sampler:</label>
|
||||
<select id="sampler" name="sampler" value="k_lms">
|
||||
<label for="cfg_scale">Cfg Scale:</label>
|
||||
<input value="7.5" type="number" id="cfg_scale" name="cfg_scale" step="any">
|
||||
<label for="sampler_name">Sampler:</label>
|
||||
<select id="sampler_name" name="sampler_name" value="k_lms">
|
||||
<option value="ddim">DDIM</option>
|
||||
<option value="plms">PLMS</option>
|
||||
<option value="k_lms" selected>KLMS</option>
|
||||
@ -37,6 +42,8 @@
|
||||
<option value="k_euler_a">KEULER_A</option>
|
||||
<option value="k_heun">KHEUN</option>
|
||||
</select>
|
||||
<input type="checkbox" name="seamless" id="seamless">
|
||||
<label for="seamless">Seamless circular tiling</label>
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
<label title="Set to multiple of 64" for="width">Width:</label>
|
||||
<select id="width" name="width" value="512">
|
||||
@ -64,19 +71,26 @@
|
||||
<input value="-1" type="number" id="seed" name="seed">
|
||||
<button type="button" id="reset-seed">↺</button>
|
||||
<input type="checkbox" name="progress_images" id="progress_images">
|
||||
<label for="progress_images">Display in-progress images (slows down generation):</label>
|
||||
<label for="progress_images">Display in-progress images (slower)</label>
|
||||
<button type="button" id="reset-all">Reset to Defaults</button>
|
||||
<div id="variations">
|
||||
<label title="If > 0, generates variations on the initial seed instead of random seeds per iteration. Must be between 0 and 1. Higher values will be more different." for="variation_amount">Variation amount (0 to disable):</label>
|
||||
<input value="0" type="number" id="variation_amount" name="variation_amount" step="0.01" min="0" max="1">
|
||||
<label title="list of variations to apply, in the format `seed:weight,seed:weight,..." for="with_variations">With variations (seed:weight,seed:weight,...):</label>
|
||||
<input value="" type="text" id="with_variations" name="with_variations">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div id="img2img">
|
||||
<label title="Upload an image to use img2img" for="initimg">Initial image:</label>
|
||||
<input type="file" id="initimg" name="initimg" accept=".jpg, .jpeg, .png">
|
||||
<button type="button" id="remove-image">Remove Image</button>
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
<label for="strength">Img2Img Strength:</label>
|
||||
<input value="0.75" type="number" id="strength" name="strength" step="0.01" min="0" max="1">
|
||||
<input type="checkbox" id="fit" name="fit" checked>
|
||||
<label title="Rescale image to fit within requested width and height" for="fit">Fit to width/height:</label>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div id="gfpgan">
|
||||
</fieldset>
|
||||
<fieldset id="gfpgan">
|
||||
<label title="Strength of the gfpgan (face fixing) algorithm." for="gfpgan_strength">GPFGAN Strength (0 to disable):</label>
|
||||
<input value="0.8" min="0" max="1" type="number" id="gfpgan_strength" name="gfpgan_strength" step="0.05">
|
||||
<label title="Upscaling to perform using ESRGAN." for="upscale_level">Upscaling Level</label>
|
||||
@ -87,25 +101,26 @@
|
||||
</select>
|
||||
<label title="Strength of the esrgan (upscaling) algorithm." for="upscale_strength">Upscale Strength:</label>
|
||||
<input value="0.75" min="0" max="1" type="number" id="upscale_strength" name="upscale_strength" step="0.05">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</fieldset>
|
||||
</form>
|
||||
<div id="about">For news and support for this web service, visit our <a href="http://github.com/lstein/stable-diffusion">GitHub site</a></div>
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
<div id="progress-section">
|
||||
<section id="progress-section">
|
||||
<div id="progress-container">
|
||||
<progress id="progress-bar" value="0" max="1"></progress>
|
||||
<span id="cancel-button" title="Cancel">✖</span>
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
<img id="progress-image" src='data:image/svg+xml,<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"/>'></img>
|
||||
<img id="progress-image" src='data:image/svg+xml,<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"/>'>
|
||||
<div id="scaling-inprocess-message">
|
||||
<i><span>Postprocessing...</span><span id="processing_cnt">1/3</span></i>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</section>
|
||||
|
||||
<div id="results">
|
||||
<div id="no-results-message">
|
||||
<i><p>No results...</p></i>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</main>
|
||||
</body>
|
||||
</html>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -8,20 +8,44 @@ function toBase64(file) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function appendOutput(src, seed, config) {
|
||||
let outputNode = document.createElement("img");
|
||||
outputNode.src = src;
|
||||
let outputNode = document.createElement("figure");
|
||||
|
||||
let altText = seed.toString() + " | " + config.prompt;
|
||||
outputNode.alt = altText;
|
||||
outputNode.title = altText;
|
||||
let variations = config.with_variations;
|
||||
if (config.variation_amount > 0) {
|
||||
variations = (variations ? variations + ',' : '') + seed + ':' + config.variation_amount;
|
||||
}
|
||||
let baseseed = (config.with_variations || config.variation_amount > 0) ? config.seed : seed;
|
||||
let altText = baseseed + ' | ' + (variations ? variations + ' | ' : '') + config.prompt;
|
||||
|
||||
// img needs width and height for lazy loading to work
|
||||
const figureContents = `
|
||||
<a href="${src}" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="${src}"
|
||||
alt="${altText}"
|
||||
title="${altText}"
|
||||
loading="lazy"
|
||||
width="256"
|
||||
height="256">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<figcaption>${seed}</figcaption>
|
||||
`;
|
||||
|
||||
outputNode.innerHTML = figureContents;
|
||||
let figcaption = outputNode.querySelector('figcaption');
|
||||
|
||||
// Reload image config
|
||||
outputNode.addEventListener('click', () => {
|
||||
figcaption.addEventListener('click', () => {
|
||||
let form = document.querySelector("#generate-form");
|
||||
for (const [k, v] of new FormData(form)) {
|
||||
if (k == 'initimg') { continue; }
|
||||
form.querySelector(`*[name=${k}]`).value = config[k];
|
||||
}
|
||||
document.querySelector("#seed").value = seed;
|
||||
|
||||
document.querySelector("#seed").value = baseseed;
|
||||
document.querySelector("#with_variations").value = variations || '';
|
||||
if (document.querySelector("#variation_amount").value <= 0) {
|
||||
document.querySelector("#variation_amount").value = 0.2;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
saveFields(document.querySelector("#generate-form"));
|
||||
});
|
||||
@ -59,6 +83,7 @@ async function generateSubmit(form) {
|
||||
|
||||
// Convert file data to base64
|
||||
let formData = Object.fromEntries(new FormData(form));
|
||||
formData.initimg_name = formData.initimg.name
|
||||
formData.initimg = formData.initimg.name !== '' ? await toBase64(formData.initimg) : null;
|
||||
|
||||
let strength = formData.strength;
|
||||
@ -94,7 +119,6 @@ async function generateSubmit(form) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (data.event === 'result') {
|
||||
noOutputs = false;
|
||||
document.querySelector("#no-results-message")?.remove();
|
||||
appendOutput(data.url, data.seed, data.config);
|
||||
progressEle.setAttribute('value', 0);
|
||||
progressEle.setAttribute('max', totalSteps);
|
||||
@ -130,7 +154,25 @@ async function generateSubmit(form) {
|
||||
document.querySelector("#prompt").value = `Generating: "${prompt}"`;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
window.onload = () => {
|
||||
async function fetchRunLog() {
|
||||
try {
|
||||
let response = await fetch('/run_log.json')
|
||||
const data = await response.json();
|
||||
for(let item of data.run_log) {
|
||||
appendOutput(item.url, item.seed, item);
|
||||
}
|
||||
} catch (e) {
|
||||
console.error(e);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
window.onload = async () => {
|
||||
document.querySelector("#prompt").addEventListener("keydown", (e) => {
|
||||
if (e.key === "Enter" && !e.shiftKey) {
|
||||
const form = e.target.form;
|
||||
generateSubmit(form);
|
||||
}
|
||||
});
|
||||
document.querySelector("#generate-form").addEventListener('submit', (e) => {
|
||||
e.preventDefault();
|
||||
const form = e.target;
|
||||
@ -147,6 +189,9 @@ window.onload = () => {
|
||||
document.querySelector("#reset-all").addEventListener('click', (e) => {
|
||||
clearFields(e.target.form);
|
||||
});
|
||||
document.querySelector("#remove-image").addEventListener('click', (e) => {
|
||||
initimg.value=null;
|
||||
});
|
||||
loadFields(document.querySelector("#generate-form"));
|
||||
|
||||
document.querySelector('#cancel-button').addEventListener('click', () => {
|
||||
@ -154,8 +199,15 @@ window.onload = () => {
|
||||
console.error(e);
|
||||
});
|
||||
});
|
||||
document.documentElement.addEventListener('keydown', (e) => {
|
||||
if (e.key === "Escape")
|
||||
fetch('/cancel').catch(err => {
|
||||
console.error(err);
|
||||
});
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
if (!config.gfpgan_model_exists) {
|
||||
document.querySelector("#gfpgan").style.display = 'none';
|
||||
}
|
||||
await fetchRunLog()
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
|
Before 
(image error) Size: 34 KiB |
1
tests/prompts.txt
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1 @@
|
||||
test trending on artstation -s 1 -S 1
|
||||